Abstract
Introduction
Atherosclerosis (ATH), the build up of fat in the arteries, is a principal cause of heart attack and stroke. Drug instability and lack of target specificity are major drawbacks of current clinical therapeutics. These undesirable effects can be eliminated by site-specific drug delivery. The endothelial surface over ATH lesions has been shown to overexpress vascular cell adhesion molecule1 (VCAM1), which can be used for targeted therapy.
Methods
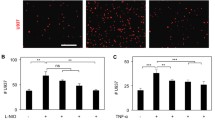
Here, we report the synthesis, characterization, and development of anti VCAM1-functionalized liposomes to target cells overexpressing VCAM1 under static and flow conditions. Liposomes were composed of dioleoyl-phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin, cholesterol, and distearoyl-phosphatidylethanolamine-polyethylene glycol-cyanur (31.67:31.67:31.67:5 mol%). VCAM1 expression in endothelial cells was induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment.
Results
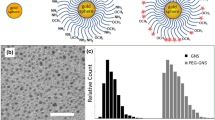
Characterization study revealed that liposomes were negatively charged (− 7.7 ± 2.6 mV) with an average diameter of 201.3 ± 3.3 nm. Liposomes showed no toxicity toward THP-1 derived macrophages and endothelial cells. Liposomes were able to target both fixed and non-fixed endothelial cells, in vitro, with significantly higher localization observed in non-fixed conditions. To mimic biological and physiologically-relevant conditions, liposome targeting was also examined under flow (4 dyn/cm2) with or without erythrocytes (40% v/v hematocrit). Liposomes were able to target LPS-treated endothelial cells under dynamic culture, in the presence or absence of erythrocytes, although targeting efficiency was five-fold lower in flow compared to static conditions.
Conclusions
This liposomal delivery system showed a significant improvement in localization on dysfunctional endothelium after surface functionalization. We conclude that VCAM1-functionalized liposomes can target and potentially deliver therapeutic compounds to ATH regions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramoff, M. D., P. J. Magalhaes, and S. J. Ram. Image processing with ImageJ. Biophoton. Int. 11:36–42, 2004.
Ackers, I., and R. Malgor. Interrelationship of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways in chronic metabolic diseases. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 15:3–13, 2018.
Adib, A. A., S. Nazemidashtarjandi, A. Kelly, A. Kruse, K. Cimatu, A. E. David, and A. M. Farnoud. Engineered silica nanoparticles interact differently with lipid monolayers compared to lipid bilayers. Environ. Sci. Nano. 5:289–303, 2018.
Bakker-Arkema, R. G., J. Best, R. Fayyad, T. M. Heinonen, A. D. Marais, J. W. Nawrocki, and D. M. Black. A brief review paper of the efficacy and safety of atorvastatin in early clinical trials. Atherosclerosis 131:17–23, 1997.
Bendas, G., A. Krause, U. Bakowsky, J. Vogel, and U. Rothe. Targetability of novel immunoliposomes prepared by a new antibody conjugation technique. Int. J. Pharm. 181:79–93, 1999.
Benjamin, E. J., P. Muntner, and M. S. Bittencourt. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 139:e56–e528, 2019.
Bhowmick, T., E. Berk, X. Cui, V. R. Muzykantov, and S. Muro. Effect of flow on endothelial endocytosis of nanocarriers targeted to ICAM-1. J Control Release 157:485–492, 2012.
Bobryshev, Y. V. Monocyte recruitment and foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. Micron 37:208–222, 2006.
Cao, Z., R. Tong, A. Mishra, W. Xu, G. C. Wong, J. Cheng, and Y. Lu. Reversible cell-specific drug delivery with aptamer-functionalized liposomes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 48:6494–6498, 2009.
Chen, W., E. Vucic, E. Leupold, W. J. Mulder, D. P. Cormode, K. C. Briley-Saebo, A. Barazza, E. A. Fisher, M. Dathe, and Z. A. Fayad. Incorporation of an apoE-derived lipopeptide in high-density lipoprotein MRI contrast agents for enhanced imaging of macrophages in atherosclerosis. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 3:233–242, 2008.
Cheung, L. S. L., and K. Konstantopoulos. An analytical model for determining two-dimensional receptor-ligand kinetics. Biophys. J. 100:2338–2346, 2011.
Cybulsky, M. I., K. Iiyama, H. Li, S. Zhu, M. Chen, M. Iiyama, V. Davis, J. C. Gutierrez-Ramos, P. W. Connelly, and D. S. Milstone. A major role for VCAM-1, but not ICAM-1, in early atherosclerosis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 107:1255–1262, 2001.
Da Silva-Candal, A., T. Brown, V. Krishnan, I. Lopez-Loureiro, P. Ávila-Gómez, A. Pusuluri, A. Pérez-Díaz, C. Correa-Paz, P. Hervella, J. Castillo, and S. Mitragotri. Shape effect in active targeting of nanoparticles to inflamed cerebral endothelium under static and flow conditions. J Control Release 309:94–105, 2019.
Date, A. A., M. D. Joshi, and V. B. Patravale. Parasitic diseases: liposomes and polymeric nanoparticles versus lipid nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 59:505–521, 2007.
Davies, M. J., J. L. Gordon, A. J. H. Gearing, R. Pigott, N. Woolf, D. Katz, and A. Kyriakopoulos. The expression of the adhesion molecules ICAM-1, VCAM-1, PECAM, and E-selectin in human atherosclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 171:223–229, 1993.
Deosarkar, S. P., R. Malgor, J. Fu, L. D. Kohn, J. Hanes, and D. J. Goetz. Polymeric particles conjugated with a ligand to VCAM-1 exhibit selective, avid, and focal adhesion to sites of atherosclerosis. Biotechnol. Biomed. Eng. 101:400–407, 2008.
Doll, R. Efficacy of cholesterol-lowering therapy in 18 686 people with diabetes in 14 randomised trials of statins: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 371:117–125, 2008.
Elbahnasawy, M. A., L. R. Donius, E. L. Reinherz, and M. Kim. Co-delivery of a CD4 T cell helper epitope via covalent liposome attachment with a surface-arrayed B cell target antigen fosters higher affinity antibody responses. Vaccine. 36:6191–6201, 2018.
Evans, E., and K. Kinoshita. Using force to probe single-molecule receptor–cytoskeletal anchoring beneath the surface of a living cell. Methods Cell Biol. 83:373–396, 2007.
Farhood, H., N. Serbina, and L. Huang. The role of dioleoyl phosphatidylethanolamine in cationic liposome mediated gene transfer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1235:289–295, 1995.
Finger, E. B., K. D. Purl, R. Alon, M. B. Lawrence, U. H. von Andrian, and T. A. Springer. Adhesion through L-selectin requires a threshold hydrodynamic shear. Nature 379:266, 1996.
Galkina, E., and K. Ley. Immune and inflammatory mechanisms of atherosclerosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 27:165–197, 2009.
Gosk, S., T. Moos, C. Gottstein, and G. Bendas. VCAM-1 directed immunoliposomes selectively target tumor vasculature in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1778:854–863, 2008.
Gu, W., L. Yao, L. Li, J. Zhang, A. T. Place, R. D. Minshall, and G. Liu. ICAM-1 regulates macrophage polarization by suppressing MCP-1 expression via miR-124 upregulation. Oncotarget. 8:111882, 2017.
Herd, J. A., M. S. West, C. Ballantyne, J. Farmer, and A. M. Gotto. Baseline characteristics of subjects in the lipoprotein and coronary atherosclerosis study (LCAS) with fluvastatin. Am. J. Cardiol. 73:D42–D49, 1994.
Jung, J. J., K. A. Grayson, M. R. King, and K. A. Lamkin-Kennard. Isolating the influences of fluid dynamics on selectin-mediated particle rolling at venular junctional regions. Microvasc. Res. 118:144–154, 2018.
Khodabandehlou, K., J. J. Masehi-Lano, C. Poon, J. Wang, and E. J. Chung. Targeting cell adhesion molecules with nanoparticles using in vivo and flow-based in vitro models of atherosclerosis. Exp Biol Med. 242:799–812, 2017.
Konstantopoulos, K., and L. V. McIntire. Effects of fluid dynamic forces on vascular cell adhesion. J. Clin. Investig. 98:2661–2665, 1996.
Lee, W., E. J. Yang, S. K. Ku, K. S. Song, and J. S. Bae. Anti-inflammatory effects of oleanolic acid on LPS-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo. Inflammation 36:94–102, 2013.
Malek, A. M., S. L. Alper, and S. Izumo. Hemodynamic shear stress and its role in atherosclerosis. Jama. 282:2035–2042, 1999.
Mamot, C., D. C. Drummond, C. O. Noble, V. Kallab, Z. Guo, K. Hong, D. B. Kirpotin, and J. W. Park. Epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted immunoliposomes significantly enhance the efficacy of multiple anticancer drugs in vivo. J. Cancer Res. 65:11631–11638, 2005.
McCarty, O. J., S. A. Mousa, P. F. Bray, and K. Konstantopoulos. Immobilized platelets support human colon carcinoma cell tethering, rolling, and firm adhesion under dynamic flow conditions. Blood. 96:1789–1797, 2000.
Mlinar, L. B., E. J. Chung, E. A. Wonder, and M. Tirrell. Active targeting of early and mid-stage atherosclerotic plaques using self-assembled peptide amphiphile micelles. Biomaterials 35:8678–8686, 2014.
Moore, K. J., F. J. Sheedy, and E. A. Fisher. Macrophages in atherosclerosis: a dynamic balance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 13:709, 2013.
Namiki, M., S. Kawashima, T. Yamashita, M. Ozaki, T. Hirase, T. Ishida, N. Inoue, K. I. Hirata, A. Matsukawa, R. Morishita, and Y. Kaneda. Local overexpression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 at vessel wall induces infiltration of macrophages and formation of atherosclerotic lesion: synergism with hypercholesterolemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 22:115–120, 2002.
Ohsawa, T., H. Miura, and K. Harada. Improvement of encapsulation efficiency of water-soluble drugs in liposomes formed by the freeze-thawing method. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 33:3945–3952, 1985.
Pagano, R. E., and J. N. Weinstein. Interactions of liposomes with mammalian cells. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng. 7:435–468, 1978.
Pan, H., J. W. Myerson, L. Hu, J. N. Marsh, K. Hou, M. J. Scott, J. S. Allen, G. Hu, S. San Roman, G. M. Lanza, and R. D. Schreiber. Programmable nanoparticle functionalization for in vivo targeting. FASEB J. 27:255–264, 2013.
Rubio-Guerra, A. F., H. Vargas-Robles, A. M. Serrano, G. Vargas-Ayala, L. Rodriguez-Lopez, and B. A. Escalante-Acosta. Correlation between the levels of circulating adhesion molecules and atherosclerosis in hypertensive type-2 diabetic patients. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 32:308–310, 2010.
Shirure, V. S., N. M. Reynolds, and M. M. Burdick. Mac-2 binding protein is a novel E-selectin ligand expressed by breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 7:e44529, 2012.
Suk, J. S., Q. Xu, N. Kim, J. Hanes, and L. M. Ensign. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 99:28–51, 2016.
Sun, T., R. Simmons, D. Huo, B. Pang, X. Zhao, C. W. Kim, H. Jo, and Y. Xia. Targeted delivery of Anti-miR-712 by VCAM1-Binding Au Nanospheres for Atherosclerosis Therapy. ChemNanoMat. 2:400–406, 2016.
Tan, J., A. Thomas, and Y. Liu. Influence of red blood cells on nanoparticle targeted delivery in microcirculation. Soft Matter 8:1934–1946, 2012.
Winter, P. M., A. M. Neubauer, S. D. Caruthers, T. D. Harris, J. D. Robertson, T. A. Williams, A. H. Schmieder, G. Hu, J. S. Allen, E. K. Lacy, and H. Zhang. Endothelial ανβ3 integrin-targeted fumagillin nanoparticles inhibit angiogenesis in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 26:2103–2109, 2006.
Yoo, S. P., F. Pineda, J. C. Barrett, C. Poon, M. Tirrell, and E. J. Chung. Gadolinium-functionalized peptide amphiphile micelles for multimodal imaging of atherosclerotic lesions. ACS Omega 1:996–1003, 2016.
Yoon, H. J., M. E. Moon, H. S. Park, S. Y. Im, and Y. H. Kim. Chitosan oligosaccharide (COS) inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory effects in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 358:954–959, 2007.
Zhu, L., M. Li, L. Wei, X. Liu, J. Yin, and Y. Gao. Fast fixing and comprehensive identification to help improve real-time ligands discovery based on formaldehyde crosslinking, immunoprecipitation and SDS-PAGE separation. Proteome Sci. 12:6, 2014.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Institutes of Health and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI-R15HL133885) awarded to R.M. and A.F. We acknowledge the use of the Ohio University Heritage College Microscopy Core. The authors would like to thank Nicholas Cellars (Ohio University, Biomedical Engineering Program) and Nathan Reynolds (Ohio University, Translational Biomedical Science Program) for technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
Authors Mahsa Kheradmandi, Ian Ackers, Monica M. Burdick, Ramiro Malgor, and Amir M. Farnoud declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Standards
No human and animal studies were carried out by the authors for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Michael R. King oversaw the review of this article.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kheradmandi, M., Ackers, I., Burdick, M.M. et al. Targeting Dysfunctional Vascular Endothelial Cells Using Immunoliposomes Under Flow Conditions. Cel. Mol. Bioeng. 13, 189–199 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-020-00616-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-020-00616-1