Abstract
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) is a malignancy of mature CD4 + T cells induced by human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-1). HTLV-1 maintains life-long infection in the human host by clonal proliferation of infected cells and cell-to-cell spread of the virus. Two viral genes, tax and HTLV-1 bZIP factor (HBZ), promote expansion of infected cells through the important roles they play in acceleration of cell proliferation and protection from cell death. Long-term survival of infected clones in vivo causes genetic mutations and aberrant epigenetic changes to accumulate in host genes, resulting in the emergence of an ATL clone. Recent advances in sequencing technology have revealed the broad picture of genetic and transcriptional abnormalities in ATL cells. ATL cells have hyper-proliferative and anti-apoptotic signatures like those observed in other malignancies, but also notably have traits related to immune evasion. ATL cells exhibit a regulatory T-cell-like immuno-phenotype due to both the function of HBZ and mutation of several host genes, such as CCR4 and CIC. These findings suggest that immune evasion is a critical step in the oncogenesis of ATL, and thus novel therapies that activate anti-ATL/HTLV-1 immunity may be effective in the treatment and prevention of ATL.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Gallo RC. The discovery of the first human retrovirus: HTLV-1 and HTLV-2. Retrovirology. 2005;2:17.
Takatsuki K. Discovery of adult T-cell leukemia. Retrovirology. 2005;2:16.
Matsuoka M, Yasunaga JI. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1: replication, proliferation and propagation by Tax and HTLV-1 bZIP factor. Curr Opin Virol. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2013.08.010.
Yasunaga JI. Strategies of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 for persistent infection: implications for leukemogenesis of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:979.
Bangham CRM, Matsuoka M. Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1: parasitism and pathogenesis. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2017;372:20160272.
Laydon DJ, Sunkara V, Boelen L, Bangham CRM, Asquith B. The relative contributions of infectious and mitotic spread to HTLV-1 persistence. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020;16: e1007470.
Yoshie O, Fujisawa R, Nakayama T, Harasawa H, Tago H, Izawa D, et al. Frequent expression of CCR4 in adult T-cell leukemia and human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-transformed T cells. Blood. 2002;99:1505–11.
Sasaki H, Nishikata I, Shiraga T, Akamatsu E, Fukami T, Hidaka T, et al. Overexpression of a cell adhesion molecule, TSLC1, as a possible molecular marker for acute-type adult T-cell leukemia. Blood. 2005;105:1204–13.
Sugata K, Yasunaga J, Kinosada H, Mitobe Y, Furuta R, Mahgoub M, et al. HTLV-1 viral factor HBZ induces CCR4 to promote T-cell migration and proliferation. Cancer Res. 2016;76:5068–79.
Yoshie O, Matsushima K. CCR4 and its ligands: from bench to bedside. Int Immunol. 2015;27:11–20.
Matsuoka M, Jeang KT. Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infectivity and cellular transformation. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:270–80.
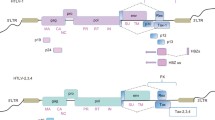
Tamiya S, Matsuoka M, Etoh K, Watanabe T, Kamihira S, Yamaguchi K, et al. Two types of defective human T-lymphotropic virus type I provirus in adult T-cell leukemia. Blood. 1996;88:3065–73.
Miyazaki M, Yasunaga J, Taniguchi Y, Tamiya S, Nakahata T, Matsuoka M. Preferential selection of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 provirus lacking the 5’ long terminal repeat during oncogenesis. J Virol. 2007;81:5714–23.
Etoh K, Tamiya S, Yamaguchi K, Okayama A, Tsubouchi H, Ideta T, et al. Persistent clonal proliferation of human T-lymphotropic virus type I-infected cells in vivo. Can Res. 1997;57:4862–7.
Gillet NA, Malani N, Melamed A, Gormley N, Carter R, Bentley D, et al. The host genomic environment of the provirus determines the abundance of HTLV-1-infected T-cell clones. Blood. 2011;117:3113–22.
Bushman FD. Retroviral insertional mutagenesis in humans: evidence for four genetic mechanisms promoting expansion of cell clones. Mol Ther. 2020;28:352–6.
Doi K, Wu X, Taniguchi Y, Yasunaga J, Satou Y, Okayama A, et al. Preferential selection of human T-cell leukemia virus type I provirus integration sites in leukemic versus carrier states. Blood. 2005;106:1048–53.
Rosewick N, Durkin K, Artesi M, Marcais A, Hahaut V, Griebel P, et al. Cis-perturbation of cancer drivers by the HTLV-1/BLV proviruses is an early determinant of leukemogenesis. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15264.
Matsuo M, Ueno T, Monde K, Sugata K, Tan BJY, Rahman A, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel enhancer in the HTLV-1 proviral genome. Nat Commun. 2022;13:2405.
Fan J, Ma G, Nosaka K, Tanabe J, Satou Y, Koito A, et al. APOBEC3G generates nonsense mutations in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 proviral genomes in vivo. J Virol. 2010;84:7278–87.
Katsuya H, Islam S, Tan BJY, Ito J, Miyazato P, Matsuo M, et al. The Nature of the HTLV-1 Provirus in Naturally Infected Individuals Analyzed by the Viral DNA-Capture-Seq Approach. Cell Rep. 2019;29(724–35): e4.
Boxus M, Twizere JC, Legros S, Dewulf JF, Kettmann R, Willems L. The HTLV-1 Tax interactome. Retrovirology. 2008;5:76.
Yasunaga J, Matsuoka M. Molecular mechanisms of HTLV-1 infection and pathogenesis. Int J Hematol. 2011;94:435–42.
Harhaj EW, Giam CZ. NF-kappaB signaling mechanisms in HTLV-1-induced adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. FEBS J. 2018;285:3324–36.
Robek MD, Ratner L. Immortalization of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T lymphocytes by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax mutants expressed in a functional molecular clone. J Virol. 1999;73:4856–65.
Kwon H, Ogle L, Benitez B, Bohuslav J, Montano M, Felsher DW, et al. Lethal cutaneous disease in transgenic mice conditionally expressing type I human T cell leukemia virus Tax. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:35713–22.
Sun SC, Yamaoka S. Activation of NF-kappaB by HTLV-I and implications for cell transformation. Oncogene. 2005;24:5952–64.
Currer R, Van Duyne R, Jaworski E, Guendel I, Sampey G, Das R, et al. HTLV tax: a fascinating multifunctional co-regulator of viral and cellular pathways. Front Microbiol. 2012;3:406.
Ho YK, Zhi H, Bowlin T, Dorjbal B, Philip S, Zahoor MA, et al. HTLV-1 tax stimulates ubiquitin E3 ligase, ring finger protein 8, to assemble lysine 63-linked polyubiquitin chains for TAK1 and IKK activation. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11: e1005102.
Shibata Y, Tokunaga F, Goto E, Komatsu G, Gohda J, Saeki Y, et al. HTLV-1 tax induces formation of the active macromolecular IKK complex by generating Lys63- and Met1-linked hybrid polyubiquitin chains. PLoS Pathog. 2017;13: e1006162.
Kinjo T, Ham-Terhune J, Peloponese JM Jr, Jeang KT. Induction of reactive oxygen species by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax correlates with DNA damage and expression of cellular senescence marker. J Virol. 2010;84:5431–7.
Zhi H, Yang L, Kuo YL, Ho YK, Shih HM, Giam CZ. NF-kappaB hyper-activation by HTLV-1 tax induces cellular senescence, but can be alleviated by the viral anti-sense protein HBZ. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7: e1002025.
Usui T, Yanagihara K, Tsukasaki K, Murata K, Hasegawa H, Yamada Y, et al. Characteristic expression of HTLV-1 basic zipper factor (HBZ) transcripts in HTLV-1 provirus-positive cells. Retrovirology. 2008;5:34.
Mahgoub M, Yasunaga JI, Iwami S, Nakaoka S, Koizumi Y, Shimura K, et al. Sporadic on/off switching of HTLV-1 Tax expression is crucial to maintain the whole population of virus-induced leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E1269–78.
Nosaka K, Matsuoka M. Adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma as a viral disease: subtypes based on viral aspects. Cancer Sci. 2021;112:1688–94.
Satou Y, Yasunaga J, Yoshida M, Matsuoka M. HTLV-I basic leucine zipper factor gene mRNA supports proliferation of adult T cell leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:720–5.
Tanaka-Nakanishi A, Yasunaga J, Takai K, Matsuoka M. HTLV-1 bZIP factor suppresses apoptosis by attenuating the function of FoxO3a and altering its localization. Cancer Res. 2014;74:188–200.
Vernin C, Thenoz M, Pinatel C, Gessain A, Gout O, Delfau-Larue MH, et al. HTLV-1 bZIP factor HBZ promotes cell proliferation and genetic instability by activating OncomiRs. Cancer Res. 2014;74:6082–93.
Takiuchi Y, Kobayashi M, Tada K, Iwai F, Sakurada M, Hirabayashi S, et al. HTLV-1 bZIP factor suppresses TDP1 expression through inhibition of NRF-1 in adult T-cell leukemia. Sci Rep. 2017;7:12849.
Rushing AW, Hoang K, Polakowski N, Lemasson I. The Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 Basic Leucine Zipper Factor Attenuates Repair of Double-Stranded DNA Breaks via Nonhomologous End Joining. J Virol. 2018; 92.
Kasugai Y, Yoshida N, Ohshima K, Matsuo K, Seto M, Tsuzuki S. New mouse model of acute adult T-cell leukemia generated by transplantation of AKT, BCLxL, and HBZ-transduced T cells. Cancer Sci. 2016;107:1072–8.
Nakagawa M, Shaffer AL 3rd, Ceribelli M, Zhang M, Wright G, Huang DW, et al. Targeting the HTLV-I-Regulated BATF3/IRF4 Transcriptional Network in Adult T Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2018;34(286–97): e10.
Ma G, Yasunaga J, Matsuoka M. Multifaceted functions and roles of HBZ in HTLV-1 pathogenesis. Retrovirology. 2016;13:16.
Yasunaga JI, Matsuoka M. Oncogenic spiral by infectious pathogens: Cooperation of multiple factors in cancer development. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:24–32.
Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T, Ono M. Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 2008;133:775–87.
Satou Y, Yasunaga J, Zhao T, Yoshida M, Miyazato P, Takai K, et al. HTLV-1 bZIP factor induces T-cell lymphoma and systemic inflammation in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2011;7: e1001274.
Zhao T, Satou Y, Sugata K, Miyazato P, Green PL, Imamura T, et al. HTLV-1 bZIP factor enhances TGF-beta signaling through p300 coactivator. Blood. 2011;118:1865–76.
Tsukasaki K. Genetic instability of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma by comparative genomic hybridization analysis. J Clin Immunol. 2002;22:57–63.
Kataoka K, Nagata Y, Kitanaka A, Shiraishi Y, Shimamura T, Yasunaga J, et al. Integrated molecular analysis of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. Nat Genet. 2015;47:1304–15.
Kogure Y, Kameda T, Koya J, Yoshimitsu M, Nosaka K, Yasunaga JI, et al. Whole-genome landscape of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood. 2022;139:967–82.
Yamagishi M, Kubokawa M, Kuze Y, Suzuki A, Yokomizo A, Kobayashi S, et al. Chronological genome and single-cell transcriptome integration characterizes the evolutionary process of adult T cell leukemia-lymphoma. Nat Commun. 2021;12:4821.
Koya J, Saito Y, Kameda T, Kogure Y, Yuasa M, Nagasaki J, et al. Single-Cell Analysis of the Multicellular Ecosystem in Viral Carcinogenesis by HTLV-1. Blood Cancer Discov. 2021;2:450–67.
Tan BJ, Sugata K, Reda O, Matsuo M, Uchiyama K, Miyazato P, et al. HTLV-1 infection promotes excessive T cell activation and transformation into adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI150472.
Nosaka K, Maeda M, Tamiya S, Sakai T, Mitsuya H, Matsuoka M. Increasing methylation of the CDKN2A gene is associated with the progression of adult T-cell leukemia. Cancer Res. 2000;60:1043–8.
Yamagishi M, Nakano K, Miyake A, Yamochi T, Kagami Y, Tsutsumi A, et al. Polycomb-mediated loss of miR-31 activates NIK-dependent NF-kappaB pathway in adult T cell leukemia and other cancers. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:121–35.
Nakahata S, Ichikawa T, Maneesaay P, Saito Y, Nagai K, Tamura T, et al. Loss of NDRG2 expression activates PI3K-AKT signalling via PTEN phosphorylation in ATLL and other cancers. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3393.
Fujikawa D, Nakagawa S, Hori M, Kurokawa N, Soejima A, Nakano K, et al. Polycomb-dependent epigenetic landscape in adult T-cell leukemia. Blood. 2016;127:1790–802.
Nishikawa H, Maeda Y, Ishida T, Gnjatic S, Sato E, Mori F, et al. Cancer/testis antigens are novel targets of immunotherapy for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood. 2012;119:3097–104.
Harashima N, Kurihara K, Utsunomiya A, Tanosaki R, Hanabuchi S, Masuda M, et al. Graft-versus-Tax response in adult T-cell leukemia patients after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cancer Res. 2004;64:391–9.
Sugiyama D, Nishikawa H, Maeda Y, Nishioka M, Tanemura A, Katayama I, et al. Anti-CCR4 mAb selectively depletes effector-type FoxP3+CD4+ regulatory T cells, evoking antitumor immune responses in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(44):17945–50.
Kannagi M, Hasegawa A, Kinpara S, Shimizu Y, Takamori A, Utsunomiya A. Double control systems for human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 by innate and acquired immunity. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:670–6.
Suehiro Y, Hasegawa A, Iino T, Sasada A, Watanabe N, Matsuoka M, et al. Clinical outcomes of a novel therapeutic vaccine with Tax peptide-pulsed dendritic cells for adult T cell leukaemia/lymphoma in a pilot study. Br J Haematol. 2015;169:356–67.
Furukawa Y, Kubota R, Tara M, Izumo S, Osame M. Existence of escape mutant in HTLV-I tax during the development of adult T-cell leukemia. Blood. 2001;97:987–93.
Chiba M, Shimono J, Ishio T, Takei N, Kasahara K, Ogasawara R, et al. Genome-wide CRISPR screens identify CD48 defining susceptibility to NK cytotoxicity in peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Blood. 2022;140:1951–63.
Yasuma K, Yasunaga J, Takemoto K, Sugata K, Mitobe Y, Takenouchi N, et al. HTLV-1 bZIP factor impairs anti-viral Immunity by Inducing Co-inhibitory Molecule, T cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT). PLoS Pathog. 2016;12: e1005372.
Sharma S, Grandvaux N, Mamane Y, Genin P, Azimi N, Waldmann T, et al. Regulation of IFN regulatory factor 4 expression in human T cell leukemia virus-I-transformed T cells. J Immunol. 2002;169:3120–30.
Mitagami Y, Yasunaga J, Kinosada H, Ohshima K, Matsuoka M. Interferon-gamma promotes inflammation and development of T-cell lymphoma in HTLV-1 bZIP factor transgenic mice. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11: e1005120.
Higuchi Y, Yasunaga JI, Mitagami Y, Tsukamoto H, Nakashima K, Ohshima K, et al. HTLV-1 induces T cell malignancy and inflammation by viral antisense factor-mediated modulation of the cytokine signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2020;117:13740–9.
Wright DG, Marchal C, Hoang K, Ankney JA, Nguyen ST, Rushing AW, et al. Human T-cell leukemia virus type-1-encoded protein HBZ represses p53 function by inhibiting the acetyltransferase activity of p300/CBP and HBO1. Oncotarget. 2016;7:1687–706.
Kawatsuki A, Yasunaga JI, Mitobe Y, Green PL, Matsuoka M. HTLV-1 bZIP factor protein targets the Rb/E2F-1 pathway to promote proliferation and apoptosis of primary CD4 T cells. Oncogene. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.510.
Clerc I, Polakowski N, Andre-Arpin C, Cook P, Barbeau B, Mesnard JM, et al. An interaction between the human T cell leukemia virus type 1 basic leucine zipper factor (HBZ) and the KIX domain of p300/CBP contributes to the down-regulation of tax-dependent viral transcription by HBZ. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:23903–13.
Acknowledgements
I thank Dr. Linda Kingsbury for proofreading. This study was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number 20H03514), and Core-to-Core Program A, Advanced Research Networks. I apologize, in view of space and format limitations, for my failure to cover other examples and issues.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest to be disclosed.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Yasunaga, Ji. Viral, genetic, and immune factors in the oncogenesis of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Int J Hematol 117, 504–511 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-023-03547-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-023-03547-5