Abstract
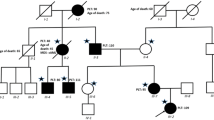
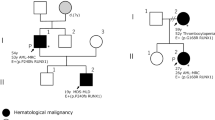
Familial platelet disorder (FPD) is a rare autosomal dominant disorder which causes moderate thrombocytopenia with or without impaired platelet function. Patients have a propensity to develop acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and various types of second hits have been postulated in the evolution to AML. However, only a few cases of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) have been reported thus far. Here, we report a family of FPD with a germ-line hemi-allelic mutation R174X in the RUNX1 gene. The proband of the family developed AML and her son had ALL of the T cell lineage. The balanced translocation t(1;7)(p34.1;q22) was detected in the lymphoblasts from the patient with ALL. This translocation was not seen in any other affected members of the family or in the bone marrow sample of this patient in complete remission. Taken together, t(1;7)(p34.1;q22) is thought to be one of the somatic second hits that predisposes FPD to acute leukemia with T cell phenotype.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dowton SB, Beardsley D, Jamison D, Blattner S, Li FP. Studies of a familial platelet disorder. Blood. 1985;65:557–63.
Ho CY, Otterud B, Legare RD, Varvil T, Saxena R, DeHart DB, et al. Linkage of a familial platelet disorder with a propensity to develop myeloid malignancies to human chromosome 21q22.1–22.2. Blood. 1996;87:5218–24.
Song WJ, Sullivan MG, Legare RD, Hutchings S, Tan X, Kufrin D, et al. Haploinsufficiency of CBFA2 causes familial thrombocytopenia with propensity to develop acute myelogenous leukaemia. Nat Genet. 1999;23:166–75.
Preudhomme C, Renneville A, Bourdon V, Philippe N, Roche-Lestienne C, Boissel N, et al. High frequency of RUNX1 biallelic alteration in acute myeloid leukemia secondary to familial platelet disorder. Blood. 2009;113:5583–7.
Sun W, Downing JR. Haploinsufficiency of AML1 results in a decrease in the number of LTR-HSCs while simultaneously inducing an increase in more mature progenitors. Blood. 2004;104:3565–72.
Ichikawa M, Asai T, Saito T, Seo S, Yamazaki I, Yamagata T, et al. AML-1 is required for megakaryocytic maturation and lymphocytic differentiation, but not for maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells in adult hematopoiesis. Nat Med. 2004;10:299–304.
Higuchi M, O’Brien D, Kumaravelu P, Lenny N, Yeoh EJ, Downing JR. Expression of a conditional AML1-ETO oncogene bypasses embryonic lethality and establishes a murine model of human t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:63–74.
Minelli A, Maserati E, Rossi G, Bernardo ME, De Stefano P, Cecchini MP, et al. Familial platelet disorder with propensity to acute myelogenous leukemia: genetic heterogeneity and progression to leukemia via acquisition of clonal chromosome anomalies. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2004;40:165–71.
Owen CJ, Toze CL, Koochin A, Forrest DL, Smith CA, Stevens JM, et al. Five new pedigrees with inherited RUNX1 mutations causing familial platelet disorder with propensity to myeloid malignancy. Blood. 2008;112:4639–45.
Kundu M, Compton S, Garrett-Beal L, Stacy T, Starost MF, Eckhaus M, et al. Runx1 deficiency predisposes mice to T-lymphoblastic lymphoma. Blood. 2005;106:3621–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
N. Nishimoto and Y. Imai contributed equally to the work.
About this article
Cite this article
Nishimoto, N., Imai, Y., Ueda, K. et al. T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia arising from familial platelet disorder. Int J Hematol 92, 194–197 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-010-0612-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-010-0612-y