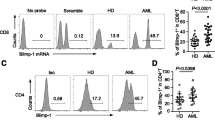
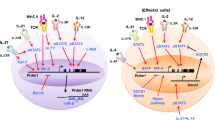
Abstract
B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein (Blimp-1) is a transcriptional factor, which controls the terminal differentiation of mature B cells to plasma cells. Blimp-1 is also called positive regulatory domain I-binding factor-1 (PRDI-BF1) or PR (PRDI-BF1-RIZ) domain zinc finger protein 1 (PRDM1). Furthermore, Blimp-1 is located in chromosome 6q21-22.1, a region frequently deleted in several tumors including lymphoid malignancies and has been supposed to be a candidate of tumor suppressor gene. Recently, mutational inactivation of Blimp-1 has been identified in a subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of the activated B-cell type. In addition, an important role for Blimp-1 in maintaining the homeostasis of effector T cells is emerging and high expression of Blimp-1β, a splicing variant of Blimp-1, have been presumed to be associated with poor prognosis in T cell lymphoma although this aspect of the gene needs further investigation. For this reason, we focused on the tumor suppressor function of Blimp-1 on not only B but also T cell malignancies in this review.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keller AD, Maniatis T. Identification and characterization of a novel repressor of beta-interferon gene expression. Genes Dev. 1991;5:868–79.
Turner CA Jr, Mack DH, Davis MM. Blimp-1, a novel zinc finger-containing protein that can drive the maturation of B lymphocytes into immunoglobulin-secreting cells. Cell. 1994;77:297–306.
Huang S. Blimp-1 is the murine homolog of the human transcriptional repressor PRDI-BF1. Cell. 1994;78:9.
Buyse I M, Shao G, Huang S. The retinoblastoma protein binds to RIZ, a zinc-finger protein that shares an epitope with the adenovirus E1A protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:4467–71.
Staudt LM, Dave S. The biology of human lymphoid malignancies revealed by gene expression profiling. Adv Immunol. 2005;87:163–208.
Klein B, Tarte K, Jourdan M, et al. Survival and proliferation factors of normal and malignant plasma cells. Int J Hematol. 2003;78:106–13.
Angelin-Duclos C, Cattoretti G, Lin KI, Calame K. Commitment of B lymphocytes to a plasma cell fate is associated with Blimp-1 expression in vivo. J Immunol. 2000;165:5462–71.
Kallies A, Hasbold J, Tarlinton DM, et al. Plasma cell ontogeny defined by quantitative changes in blimp-1 expression. J Exp Med. 2004;200:967–77.
Shaffer AL, Yu X, He Y, Boldrick J, Chan EP, Staudt LM. BCL-6 represses genes that function in lymphocyte differentiation, inflammation, and cell cycle control. Immunity. 2000;13:199–212.
Shaffer AL, Lin KI, Kuo TC, et al. Blimp-1 orchestrates plasma cell differentiation by extinguishing the mature B cell gene expression program. Immunity. 2002;17:51–62.
Lin KI, Angelin-Duclos C, Kuo TC, Calame K. Blimp-1-dependent repression of Pax-5 is required for differentiation of B cells to immunoglobulin M-secreting plasma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:4771–80.
Shapiro-Shelef M, Lin KI, McHeyzer-Williams LJ, Liao J, McHeyzer-Williams MG, Calame K. Blimp-1 is required for the formation of immunoglobulin secreting plasma cells and pre-plasma memory B cells. Immunity. 2003;19:607–20.
John SA, Garrett-Sinha LA. Blimp1: a conserved transcriptional repressor critical for differentiation of many tissues. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315:1077–84.
Kallies A, Hawkins ED, Belz GT, et al. Transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 is essential for T cell homeostasis and self-tolerance. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:466–74.
Martins GA, Cimmino L, Shapiro-Shelef M, et al. Transcriptional repressor Blimp-1 regulates T cell homeostasis and function. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:457–65.
Awasthi A, Kuchroo VK. The yin and yang of follicular helper T cells. Science. 2009;325:953–5.
Johnston RJ, Poholek AC, DiToro D, et al. Bcl6 and Blimp-1 are reciprocal and antagonistic regulators of T follicular helper cell differentiation. Science. 2009;325:1006–10.
Ohinata Y, Payer B, O’Carroll D, et al. Blimp1 is a critical determinant of the germ cell lineage in mice. Nature. 2005;436:207–13.
Xie M, Shao G, Buyse IM, Huang S. Transcriptional repression mediated by the PR domain zinc finger gene RIZ. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:26360–6.
Jiang G, Liu L, Buyse IM, Simon D, Huang S. Decreased RIZ1 expression but not RIZ2 in hepatoma and suppression of hepatoma tumorigenicity by RIZ1. Int J Cancer. 1999;83:541–6.
Sasaki O, Meguro K, Tohmiya Y, Funato T, Shibahara S, Sasaki T. Altered expression of retinoblastoma protein-interacting zinc finger gene, RIZ, in human leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2002;119:940–8.
Fears S, Mathieu C, Zeleznik-Le N, Huang S, Rowley J D, Nucifora G. Intergenic splicing of MDS1 and EVI1 occurs in normal tissues as well as in myeloid leukemia and produces a new member of the PR domain family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:1642–7.
Nucifora G. The EVI1 gene in myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 1997;11:2022–31.
Cattoretti G, Angelin-Duclos C, Shaknovich R, Zhou H, Wang D, Alobeid B. PRDM1/Blimp-1 is expressed in human B-lymphocytes committed to the plasma cell lineage. J Pathol. 2005;206:76–86.
Gyory I, Fejer G, Ghosh N, Seto E, Wright KL. Identification of a functionally impaired positive regulatory domain I binding factor 1 transcription repressor in myeloma cell lines. J Immunol. 2003;170:3125–33.
Tam W, Gomez M, Chadburn A, Lee JW, Chan WC, Knowles DM. Mutational analysis of PRDM1 indicates a tumor-suppressor role in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood. 2006;107:4090–100.
Pasqualucci L, Compagno M, Houldsworth J, et al. Inactivation of the PRDM1/BLIMP1 gene in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J Exp Med. 2006;203:311–7.
Liu YY, Leboeuf C, Shi JY, et al. Rituximab plus CHOP (R-CHOP) overcomes PRDM1-associated resistance to chemotherapy in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2007;110:339–44.
Tate G, Hirayama-Ohashi Y, Kishimoto K, Mitsuya T. Novel BLIMP1/PRDM1 gene mutations in B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2007;172:151–3.
Courts C, Montesinos-Rongen M, Brunn A, et al. Recurrent inactivation of the PRDM1 gene in primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008;67:720–7.
Garcia JF, Roncador G, Garcia JF, et al. PRDM1/BLIMP-1 expression in multiple B and T-cell lymphoma. Haematologica. 2006;91:467–74.
Yoo NJ, Jeong EG, Lee SH, Lee SH. Absence of PRDM1 exon 2 mutation in acute leukemia. Eur J Haematol. 2007;78:171–2.
Zhao WL, Liu YY, Zhang QL, et al. PRDM1 is involved in chemoresistance of T-cell lymphoma and down-regulated by the proteasome inhibitor. Blood. 2008;111:3867–71.
Nie K, Gomez M, Landgraf P, et al. MicroRNA-mediated down-regulation of PRDM1/Blimp-1 in Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells: a potential pathogenetic lesion in Hodgkin lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 2008;173:242–52.
Chang DH, Angelin-Duclos C, Calame K. BLIMP-1: trigger for differentiation of myeloid lineage. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:169–76.
Kato M, Sanada M, Kato I, et al. Frequent inactivation of A20 in B-cell lymphomas. Nature. 2009;459:712–6.
Honma K, Tsuzuki S, Nakagawa M, et al. TNFAIP3/A20 functions as a novel tumor suppressor gene in several subtypes of non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Blood. 2009;114:2467–75.
Thelander EF, Ichimura K, Corcoran M, et al. Characterization of 6q deletions in mature B cell lymphomas and childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49:477–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hangaishi, A., Kurokawa, M. Blimp-1 is a tumor suppressor gene in lymphoid malignancies. Int J Hematol 91, 46–53 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-009-0472-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-009-0472-5