Abstract
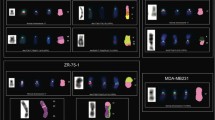
Complex chromosomal aberrations (CCAs) can be detected in a substantial proportion of myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Comprehensive analysis of the chromosomal rearrangements in these CCAs has been hampered by the limitations of conventional cytogenetics (CC). Multiplex fluorescence in situ hybridization (M-FISH) is a new generation FISH technique which allows simultaneous identification of all the 24 human chromosomes. So it is very useful in clarifing CCAs, identifing cryptic interchromosomal rearrangements and characterizing marker chromosomes. But it also has some limitations. We used M-FISH and whole chromosome painting (WCP) to accurately refine the CCAs revealed by R-banding CC in seven cases with MDS. The composition and origin of 6 kinds of marker chromosomes, nine kinds of chromosomes with additional material undetermined and five kinds of derivative chromosomes undefined by CC were defined after M-FISH analysis. Four kinds of cryptic translocations overlooked by CC were found on derivative chromosomes and previously normal appearing chromosomes. In addition, M-FISH revealed some nonrandom aberrations which most frequently involved chromosome 17 (5/7) and -5/5q-(4/7). Fluorescence flaring is a main factor leading to misinterpretations. Some misclassified and missed chromosomal aberrations by M-FISH were corrected by WCP. M-FISH is a powerful molecular cytogenetic tool in clarification of CCAs. Complementary WCP can further identify misclassified and missed chromosomal aberrations by M-FISH. CC in combination with molecular cytogenetic techniques including M-FISH and WCP can more precisely unravel CCAs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee C, Gisselsson D, Jin C, Nordgren A, Ferguson DO, Blennow E, et al. Limitations of chromosome classification by multicolor karyotyping. Am J Hum Genet. 2001;68:1043–7.
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT, Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR, et al. Proposals for the classification of the myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Hematol. 1982;51:189–99.
Mitelman F (ed) ISCN: an international system for human cytogenetic nomenclature. Basel: S. Karger;1995.
X Yongquan (2003) Bai xue bing xi hao yi chuan xue ji tu pu. Tian jin ke xue ji shu chu ban she, 101.
Schoch C, Haferlach T, Haasse D, Fonatsch C, Loffler H, Schlegelberger B, et al. Patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia and complex karyotype aberrations show a poor prognosis despite intensive treatment: a study of 90 patients. Br J Hematol. 2001;112:118–26.
Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, Wheatley K, Harrison C, Harrison G, et al. The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial. The medical research council adult and children’s leukemia working parties. Blood. 1998;92:2322–33.
Fenaux P, Morel P, Lai JL. Cytogenetics of myelodysplastic syndromes. Semin Hematol. 1996;33:127–38.
Barcuk-Simonet E, Soenen-Cornu V, Roumier C, Cosson A, Lai J-L, Fenaux P, et al. Role of multiplex FISH in identifying chromosome involvement in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemias with complex karyotypes: a report on 28 cases. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2005;157:118–26.
Limbergen HV, Poppe B, Michaux L, Herens C, Brown J, Noens L, et al. Identification of cytogenetic subclasses and recurring chromosomal aberrations in AML and MDS with complex karyotypes using M-FISH. Gene Chromosome Cancer. 2002;33:60–72.
Lee C, Wevrick R, Fisher RB, Ferguson-Smith MA, Lin CC. Human centromeric DNAs. Hum Genet. 1997;100:291–304.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Science and Research Foundation of the Ministry of Health of China (Proj. No. WKJ2005-2-025), the 135 Foundation of Jiangsu Provine (Proj. No. RC2002044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Li, JY., Xiao, B., Chen, LJ. et al. An analysis of complex chromosomal aberrations in seven cases of myelodysplastic syndromes by M-FISH and whole chromosome painting. Int J Hematol 88, 369–373 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-008-0195-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-008-0195-z