Abstract
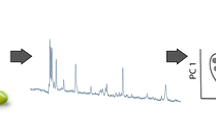
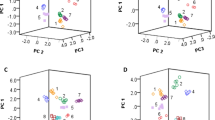
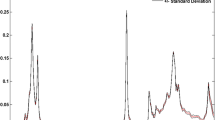
One of the main concerns about the use of edible vegetable oils in food industry frying processes is the oxidative degradation due to the high temperatures, presence of oxygen, ultraviolet radiation, and the presence of metal ions. The main compounds formed during oxidative reactions include aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, and carboxylic acids, being some of these electroactive compounds, which can be used with quantification purposes. In this work, cyclic voltammetry and a flow method based on headspace sampling with amperometric detection were performed, followed by principal component and cluster analysis to classify palm olein, soya bean, and sunflower oil samples according to their degradation state. The electrochemical techniques were based on the use of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate as conductive media. The amperometric profile information provided a clearer classification than the voltammetric profile. Additionally, the amperometric results were applied to determine iodine value and aldehyde content by means of a partial least square regression. The values obtained were statistically similar than the estimated using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and HPLC. The combination of electrochemical techniques and chemometric analysis offers valuable information for classification and quantification purposes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Samples are not available from the authors.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdi H, Williams LJ (2010) Principal component analysis. WIREs Comp Stat 2:433–459. https://doi.org/10.1002/wics.101
Adhoum N, Monser L (2008) Electrochemical sensor for hydroperoxides determination based on Prussian blue film modified electrode. Sens Actuator B-Chem 133:588–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2008.03.039
Alves JO, Sena MM, Augusti R (2014) Multivariate calibration applied to ESI mass spectrometry data: a tool to quantify adulteration in extra virgin olive oil with inexpensive edible oils. Anal Methods 6:7502–7509. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ay00967c
Andersen CM, Bro R (2010) Variable selection in regression-a tutorial. J Chemometr 24:728–737. https://doi.org/10.1002/cem.1360
Aparicio R, Rocha SM, Delgadillo I, Morales MT (2000) Detection of rancid defect in virgin olive oil by the electronic nose. J Agric Food Chem 48:853–860. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9814087
Apetrei C, Rodriguez-Mendez ML, de Saja JA (2005) Modified carbon paste electrodes for discrimination of vegetable oils. Sens Actuator B-Chem 111:403–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2005.03.041
Armstrong DW, He L, Liu YS (1999) Examination of ionic liquids and their interaction with molecules, when used as stationary phases in gas chromatography. Anal Chem 71:3873–3876. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac990443p
Baldo MA, Oliveri P, Simonetti R, Daniele S (2016) A novel electroanalytical approach based on the use of a room temperature ionic liquid for the determination of olive oil acidity. Talanta 161:881–887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.09.045
Bastos LSC, de Almeida Costa EA, Pereira PAP (2017) Development, validation and application of an UFLC-DAD-ESI-MS method for determination of carbonyl compounds in soybean oil during continuous heating. Food Chem 218:518–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.09.036
Ben Hammouda I, Freitas F, Ammar S, Gomes Da Silva MDR, Bouaziz M (2017) Comparison and characterization of volatile compounds as markers of oils stability during frying by HS–SPME-GC/MS and chemometric analysis. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl 1068:322–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.10.063
Berrueta LA, Alonso-Salces RM, Héberger K (2007) Supervised pattern recognition in food analysis. J Chromatogr A 1158:196–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.05.024
Cao J, Zou XG, Deng L, Fan YW, Li H, Li J, Deng ZY (2014) Analysis of nonpolar lipophilic aldehydes/ketones in oxidized edible oils using HPLC-QqQ-MS for the evaluation of their parent fatty acids. Food Res Int 64:901–907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2014.08.042
Cosio MS, Ballabio D, Benedetti S, Gigliotti C (2007) Evaluation of different storage conditions of extra virgin olive oils with an innovative recognition tool built by means of electronic nose and electronic tongue. Food Chem 101:485–491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.02.005
Dias LG, Fernandes A, Veloso AC, Machado AA, Pereira JA, Peres AM (2014) Single-cultivar extra virgin olive oil classification using a potentiometric electronic tongue. Food Chem 160:321–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.03.072
Fernández E, Vidal L, Canals A (2018) Rapid determination of hydrophilic phenols in olive oil by vortex-assisted reversed-phase dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and screen-printed carbon electrodes. Talanta 181:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.12.075
Gambarra-Neto FF, Marino G, Araújo MCU, Galvão RKH, Pontes MJC, de Medeiros EP, Lima RS (2009) Classification of edible vegetable oils using square wave voltammetry with multivariate data analysis. Talanta 77:1660–1666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.10.003
Gázquez-Evangelista D, Pérez-Castaño E, Sánchez-Viñas M, Bagur-González MG (2014) Using offline HPLC-GC-FID 4-desmethylsterols concentration profiles, combined with chemometric tools, to discriminate different vegetable oils. Food Anal Methods 7:912–925. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9773-7
Gebicki J (2016) Application of electrochemical sensors and sensor matrixes for measurement of odorous chemical compounds. Trends Anal Chem 77:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.10.005
Godoy AC, dos Santos PDS, Nakano AY, Bini RA, Siepmann DAB, Schneider R, Gaspar PA, Pfrimer FWD, da Paz RF, Santos OO (2020) Analysis of vegetable oil from different suppliers by chemometric techniques to ensure correct classification of oil sources to deal with counterfeiting. Food Anal Methods 13:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01731-5
Guadarrama A, Rodríguez-Méndez ML, de Saja JA, Ríos JL, Olías JL (2000) Array of sensors based on conducting polymers for the quality control of the aroma of the virgin olive oil. Sensors Actuators B-Chem 69:276–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(00)00507-4
Guillén MD, Uriarte PS (2012) Aldehydes contained in edible oils of a very different nature after prolonged heating at frying temperature: presence of toxic oxygenated α, β unsaturated aldehydes. Food Chem 131:915–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.09.079
Hirri A, Bassbasi M, Platikanov S, Tauler R, Oussama A (2016) FTIR spectroscopy and PLS-DA classification and prediction of four commercial grade virgin olive oils from Morocco. Food Anal Methods 9:974–981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0255-y
Jouan-Rimbaud D, Walczak B, Massart DL, Last IR, Prebble KA (1995) Comparison of multivariate methods based on latent vectors and methods based on wavelength selection for the analysis of near-infrared spectroscopic data. Anal Chim Acta 304:285–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2670(94)00590-I
Jović O, Smolić T, Primožič I, Hrenar T (2016) Spectroscopic and chemometric analysis of binary and ternary edible oil mixtures: qualitative and quantitative study. Anal Chem 88:4516–4524. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b00505
Katragadda HR, Fullana A, Sidhu S, Carbonell-Barrachina ÁA (2010) Emissions of volatile aldehydes from heated cooking oils. Food Chem 120:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.09.070
Kenar A, Cicek B, Arslan FN, Akin G, Elmas ŞNK, Yilmaz I (2019) Electron impact–mass spectrometry fingerprinting and chemometrics for rapid assessment of authenticity of edible oils based on fatty acid profiling. Food Anal Methods 12:1369–1381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01472-0
Khaled AY, Aziz SA, Rokhani FZ (2015) Capacitive sensor probe to assess frying oil degradation. Inf Process Agric 2:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2015.07.002
Kim TS, Yeo J, Kim JY, Kim M, Lee J (2013) Determination of the degree of oxidation in highly oxidized lipids using profile changes of fatty acids. Food Chem 138:1792–1799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.11.119
Kiokias S, Varzakas T (2014) Activity of flavonoids and β-carotene during the auto-oxidative deterioration of model food oil-in water emulsions. Food Chem 150:280–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.112
Kumar R, Bansal V, Patel MB, Sarpal AS (2012) 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) determination of the iodine value in biodiesel produced from algal and vegetable oils. Energy Fuels 26:7005–7008. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef300991n
Li X, Wang S, Shi W, Shen Q (2015) Partial least squares discriminant analysis model based on variable selection applied to identify the adulterated olive oil. Food Anal Methods 9:1713–1718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0355-8
Liland KH (2011) Multivariate methods in metabolomics from pre-processing to dimension reduction and statistical analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 30:827–841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2011.02.007
Liu TB, Zhou Y, Lv J, Chen ZW, Li BB, Shi Y (2013) Authentication of edible vegetable oil and refined recycled cooking oil using a micro-UV spectrophotometer based on chemometrics. J Am Oil Chem Soc 90:1599–1606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-013-2311-3
Liu Y, Wang Y, Cao P, Liu Y (2018) Combination of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and electron spin resonance spectroscopy for analysis of oxidative stability in soybean oil during deep-frying process. Food Anal Methods 11:1485–1492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-1132-7
Man YBC, Abidin SZ, Rohman A (2011) Discriminant analysis of selected edible fats and oils and those in biscuit formulation using FTIR spectroscopy. Food Anal Methods 4:404–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-010-9184-y
Mildner-Szkudlarz S, Jelen HH, Zawirska-Wojtasiak R, Wącasowicz E (2003) Application of headspace-solid phase microextraction and multivariate analysis for plant oils differentiation. Food Chem 83:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00147-X
Miyake Y, Yokomizo K, Matsuzaki N (1998) Rapid determination of iodine value by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Am Oil Chem’ Soc 75:15–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-998-0003-1
Murugappan K, Lee J, Silvester S (2011) Comparative study of screen-printed electrodes for ammonia gas sensing in ionic liquids. Electrochem Commun 13:1435–1438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2011.09.016
Oliveri P, Baldo MA, Daniele S, Forina M (2009) Development of a voltammetric electronic tongue for discrimination of edible oils. Anal Bioanal Chem 395:1135–1143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3070-8
Peng CY, Lan CH, Lin PC, Kuo YC (2017) Effects of cooking method, cooking oil, and food type on aldehyde emissions in cooking oil fumes. J Hazard Mater 324:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.045
Poulli KI, Mousdis GA, Georgiou CA (2005) Classification of edible and lampante virgin olive oil based on synchronous fluorescence and total luminescence spectroscopy. Anal Chim Acta 542:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2005.03.061
Rehman A, Zeng X (2015) Methods and approaches of utilizing ionic liquids as gas sensing materials. RSC Adv 5:58371–58392. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra06754e
Semenov V, Volkov S, Khaydukova M, Fedorov A, Lisitsyna I, Kirsanov D, Legin A (2019) Determination of three quality parameters in vegetable oils using potentiometric e-tongue. J Food Compos Anal 75:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2018.09.015
Seppanen CM, Csallany AS (2001) Simultaneous determination of lipophilic aldehydes by high-performance liquid chromatography in vegetable oil. J Am Oil Chem’ Soc 78:1253–1260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-001-0422-9
Tian L, Zeng Y, Zheng X, Chiu Y, Liu T (2019) Detection of peanut oil adulteration mixed with rapeseed oil using gas chromatography and gas chromatography–ion mobility spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 12:2282–2292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01571-y
Toniolo R, Dossi N, Bortolomeazzi R, Bonazza G, Daniele S (2019) Volatile aldehydes sensing in headspace using a room temperature ionic liquid-modified electrochemical microprobe. Talanta 197:522–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.01.049
Tsopelas F, Konstantopoulos D, Kakoulidou AT (2018) Voltammetric fingerprinting of oils and its combination with chemometrics for the detection of extra virgin olive oil adulteration. Anal Chim Acta 1015:8–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.02.042
Tu D, Li H, Wu Z, Zhao B, Li Y (2013) Application of headspace solid-phase microextraction and multivariate analysis for the differentiation between edible oils and waste cooking oil. Food Anal Methods 7:1263–1270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9743-0
Wu Z, Li H, Tu D (2015) Application of Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy combined with chemometrics for analysis of rapeseed oil adulterated with refining and purificating waste cooking oil. Food Anal Methods 8:2581–2587. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0149-z
Xu L, Yu X, Liu L, Zhang R (2016) A novel method for qualitative analysis of edible oil oxidation using an electronic nose. Food Chem 202:229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.01.144
Zhao X, Dong D, Zheng W, Jiao L, Lang Y (2015) Discrimination of adulterated sesame oil using mid-infrared spectroscopy and chemometrics. Food Anal Methods 8:2308–2314. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0125-7
Zuman P (2006) Aspects of electrochemical behavior of aldehydes and ketones in protic media. Electroanalysis 18:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.200503367
Funding
The authors thank the financial support from Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACyT) (SNI distinction as research membership and scholarship).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M.S. and J.A.R.; methodology, S.R. and J.A.T.; formal analysis, C.A.G.; writing, review, and editing, S.R. and J.A.R.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent to Participate
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
Sandra Ramírez-Montes declares that she has no conflict of interest. Eva M. Santos declares that she has no conflict of interest. Carlos A. Galan-Vidal declares that he has no conflict of interest. J. Andrés Tavizón-Pozos declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jose A. Rodriguez declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramirez-Montes, S., Santos, E.M., Galan-Vidal, C.A. et al. Classification of Edible Vegetable Oil Degradation Using Multivariate Data Analysis From Electrochemical Techniques. Food Anal. Methods 14, 2597–2606 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-021-02083-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-021-02083-4