Abstract
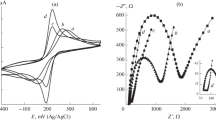
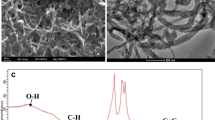
A novel electrochemical method to detect riboflavin was proposed using a multi-walled carbon nanotubes and ionic liquid N-butyl-N-methyl-piperidinium hexafluorophosphate composite film modified glassy carbon electrode (MWNTs-[BMPi]PF6/GCE). A well-defined CV behavior with a pair of sensitive and well-shaped redox peak was observed, and the response value of riboflavin at MWNTs-[BMPi]PF6/GCE is much higher than that at MWNTs/GCE in 0.1 mol L−1 HAc-NaAc buffer solution (pH 4.5). The electrochemical approach based on a sensitive DPV analytical signal exhibits an excellent analytical performance with a wide linear range (2.6 × 10−8 to 1.3 × 10−6 mol L−1) and low detection limit (4.7 × 10−9 mol L−1) for the riboflavin. Moreover, the proposed method possesses a potential practical application value and can be employed for the quantitative analysis of trace riboflavin with a recovery of 95.8–102.4 % in food samples such as milk and soymilk powder.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertollo CM, Oliveira ACP, Rocha LTS, Costa KA, Nascimento Jr EB, Coelho MM (2006) Characterization of the antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of riboflavin in different experimental models. Eur J Pharmacol 547:184–191
Bijad M, Karimi-Maleh H, Khalilzadeh MA (2013) Application of ZnO/CNTs nanocomposite ionic liquid paste electrode as a sensitive voltammetric sensor for determination of ascorbic acid in food samples. Food Anal Methods 6:1639–1647
Chen X, Ren T, Ma M, Wang Z, Zhan G, Li C (2013) Voltammetric sensing of bisphenol A based on a single-walled carbon nanotubes/poly {3-butyl-1-[3-(N-pyrrolyl) propyl] imidazolium ionic liquid} composite film modified electrode. Electrochim Acta 111:49–56
Fukushima T, Kosaka A, Ishimura Y, Yamamoto T, Takigawa T, Ishii N, Aida T (2003) Molecular ordering of organic molten salts triggered by single-walled carbon nanotubes. Science 300:2072–2074
Jin P, Xia L, Li Z, Che N, Zou D, Hu X (2012) Rapid determination of thiamine, riboflavin, niacinamide, pantothenic acid, pyridoxine, folic acid and ascorbic acid in Vitamins with Minerals Tablets by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detector. J Pharmaceut Biomed 70:151–157
Kachoosangi RT, Musameh MM, Abu-Yousef I, Yousef JM, Kanan SM, Xiao L, Davies SG, Russell A, Compton RG (2008) Carbon nanotube-ionic liquid composite sensors and biosensors. Anal Chem 81:435–442
Lavanya N, Radhakrishnan S, Sekar C, Navaneethan M, Hayakawa Y (2013) Fabrication of Cr doped SnO2 nanoparticles based biosensor for the selective determination of riboflavin in pharmaceuticals. Analyst 138:2061–2067
Laviron E (1979) General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J Electroanal Chem 101:19–28
Liu B, Xiao B, Cui L (2015) Electrochemical analysis of carbaryl in fruit samples on graphene oxide-ionic liquid composite modified electrode. J Food Compos Anal 40:14–18
Liu Y, Liu L, Dong S (2007) Electrochemical characteristics of glucose oxidase adsorbed at carbon nanotubes modified electrode with ionic liquid as binder. Electroanal 19:55–59
Majidi MR, Baj RFB, Naseri A (2013) Carbon nanotube-ionic liquid (CNT-IL) nanocamposite modified sol-gel derived carbon-ceramic electrode for simultaneous determination of sunset yellow and tartrazine in food samples. Food Anal Methods 6:1388–1397
Mal P, Ghosh D, Bandyopadhyay D, Dutta K, Bishayi B (2012) Ampicillin alone and in combination with riboflavin modulates Staphylococcus aureus infection induced septic arthritis in mice. Indian J Exp Biol 50:677–689
Maseka A, Chrzescijanska E, Zaborski M, Maciejewska M (2012) Characterisation of the antioxidant activity of riboflavin in an elastomeric composite. CR Chim 15:524–529
Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh A, Pouladsaz P (2014) Voltammetric determination of riboflavin based on electrocatalytic oxidation at zeolite-modified carbon paste electrodes. J Ind Eng Chem 20:2146–2152
Qi H, Cao Z, Hou L (2011) Electrogenerated chemiluminesence method for the determination of riboflavin at an ionic liquid modified gold electrode. Spectrochim Acta A 78:211–215
Riman D, Avgeropoulos A, Hrbac J, Prodromidis MI (2015) Sparked-bismuth oxide screen-printed electrodes for the determination of riboflavin in the sub-nanomolar range in non-deoxygenated solutions. Electrochim Acta 165:410–415
Rodriguez RSJ, Fernández-Ruiz V, Cámara M, Sánchez-Mata MC (2012) Simultaneous determination of vitamin B1 and B2 in complex cereal foods, by reverse phase isocratic HPLC-UV. J Cereal Sci 55:293–299
Sá ÉS, da Silva PS, Jost CL, Spinelli A (2015) Electrochemical sensor based on bismuth-film electrode for voltammetric studies on vitamin B2 (riboflavin). Sensors Actuators B Chem 209:423–430
Safavi A, Maleki N, Ershadifar H, Tajabadi F (2010) Development of a sensitive and selective riboflavin sensor based on carbon ionic liquid electrode. Anal Chim Acta 674:176–181
Salimi A, Kavosi B, Fathi F, Hallaj R (2013) Highly sensitive immunosensing of prostate-specific antigen based on ionic liquid–carbon nanotubes modified electrode: application as cancer biomarker for prostate biopsies. Biosens Bioelectron 42:439–446
Sikorska E, Gliszczyńska-Świgło A, Insińska-Rak M, Khmelinskii I, Keukeleire DD, Sikorski M (2008) Simultaneous analysis of riboflavin and aromatic amino acids in beer using fluorescence and multivariate calibration methods. Anal Chim Acta 613:207–217
Sun Y, Fei J, Hou J, Zhang Q, Liu Y, Hu B (2009) Simultaneous determination of dopamine and serotonin using a carbon nanotubes-ionic liquid gel modified glassy carbon electrode. Microchim Acta 165:373–379
Thomas T, Mascarenhas RJ, D’Souza OJ, Martis P, Dalhalle J, Swamy BEK (2013) Multi-walled carbon nanotube modified carbon paste electrode as a sensor for the amperometric detection of L-tryptophan in biological samples. J Colloid Interface Sci 402:223–229
Voicescu M, Ionita G, Beteringhe A, Vasilescu M, Meghea A (2008) The antioxidative activity of riboflavin in the presence of antipyrin. Spectroscopic studies. J Fluoresc 18:953–959
Wang Y, Zhu PH, Tian T, Tang J, Wang L, Hu XY (2011) Synchronous fluorescence as a rapid method for the simultaneous determination of folic acid and riboflavin in nutritional beverages. J Agric Food Chem 59:12629–12634
Xu T, Zhang L, Yang J, Li N, Yang L, Jiang X (2013) Development of electrochemical method for the determination of olaquindox using multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 109:185–190
Yang J, Dong Y, Wang L, Zhang D, Zhang Z, Zhang L (2015) Highly sensitive detection of faropenem using amino functionalized carbon nanotube modified electrode with ionic liquid as binder: insight into the interaction of faropenem with human serum albumin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 211:59–66
Yan Q, Zhao F, Li G, Zeng B (2006) Voltammetric determination of uric acid with a glassy carbon electrode coated by paste of multiwalled carbon nanotubes and ionic liquid. Electroanal 18:1075–1080
Zhang H, Gao Y, Xiong H, Li X, Zhang S, Shi B, Duan L (2016) Highly sensitive determination of caffeic acid using a multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified electrode with N-butylpyridinium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid and chitosan as binders. Int J Electrochem Sci 11:2971–2981
Zhang H, Zhao J, Liu H, Wang H, Liu R, Liu J (2010) Application of poly (3-methylthiophene) modified glassy carbon electrode as riboflavin sensor. Int J Electrochem Sci 5:295–301
Zhang Y, Shen Y, Li J, Niu L, Dong S, Ivaska A (2005) Electrochemical functionalization of single-walled carbon nanotubes in large quantities at a room-temperature ionic liquid supported three-dimensional network electrode. Langmuir 21:4797–4800
Zhao Y, Gao Y, Zhan D, Liu H, Zhao Q, Kou Y, Shao Y, Li M, Zhuang Q, Zhu Z (2005) Selective detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid by a carbon nanotubes-ionic liquid gel modified electrode. Talanta 66:51–57
Zhao Y, Liu H, Kou Y, Li M, Zhu Z, Zhuang Q (2007) Structural and characteristic analysis of carbon nanotubes-ionic liquid gel biosensor. Electrochem Commun 9:2457–2462
Zheng Q, Yang P, Xu H, Liu J, Jin L (2012) A simple and sensitive method for the determination of 4-n-octylphenol based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified glassy carbon electrode. J Environ Sci China 24:1717–1722
Zougagh M, Ríos Á (2008) Supercritical fluid extraction as an on-line clean-up technique for determination of riboflavin vitamins in food samples by capillary electrophoresis with fluorimetric detection. Electrophoresis 29:3213–3219
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Fundation of China (21367025) and Program for State Ethnic Affairs Commission of the China (2014YNZ012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Fundation of China (21367025) and Program for State Ethnic Affairs Commission of the China (2014YNZ012).
Conflict of Interest
Hongjiao Zhang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Yuntao Gao declares that he has no conflict of interest. Huabin Xiong declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Gao, Y. & Xiong, H. Sensitive and Selective Determination of Riboflavin in Milk and Soymilk Powder by Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes and Ionic Liquid [BMPi]PF6 Modified Electrode. Food Anal. Methods 10, 399–406 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0598-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-016-0598-z