Abstract
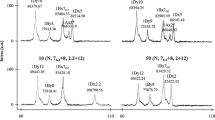
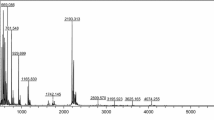
Durum wheat (Triticum turgidum L.) flour is instrumental for the production of pasta worldwide. The quality of this food rests on flour processing and on its protein content and composition. Gluten proteins as high and low-molecular weight glutenins (GS) are important to predict the flour technological property in pasta making. Different methods were compared to separate, identify and quantify GS in flours from two wheat cultivars. Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrilamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gave in a fast way information about the GS assets. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2D-GE) allowed for the highest resolution in detecting and quantifying single GS, subsequently identified by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS). Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) is a non-gel alternative system for separation and quantification of single GS that when combined with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF/MS) gave information about their exact masses. This method gives also quantitative indications of each individual GS. Different GS patterns and contents were detected in the flour of the two cultivars, underlining the importance of these analytical methods before determining the best flour processing procedure in pasta making. The different methods were evaluated with a modular approach consisting of a grid of different parameters and a non-linear score within each module.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GS:
-
Glutenins
- SDS-PAGE:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrilamide gel electrophoresis
- 2D-GE:
-
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
- LC-ESI-MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
- RP-HPLC:
-
Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography
- MALDI-TOF/MS:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry
References
Brites C, Carrillo MJ (2001) Influence of high molecular weight (HMW) and low molecular weight (LMW) glutenin subunits controlled by Glu-1 and Glu-3 loci on durum wheat quality. Cereal Chem 78:59–63
Cunsolo V, Foti S, Saletti R, Gilbert S, Tatham AS, Shewry PR (2003) Structural studies of glutenin subunits 1Dy10 and 1Dy12 by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometry and high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 17:442–454
D’Ovidio R, Simeone M, Masci S, Porceddu E (1997) Molecular characterization of a LMW-GS gene located on chromosome 1B and the development of primers specific for the Glu-B3 complex locus in durum wheat. Theor Appl Gen 95:1119–1126
D’Ovidio R, Masci S (2004) The low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits of wheat gluten. J Cereal Sci 39:321–339
De Vita P, Nicosia OLD, Nigro F, Platani C, Riefolo C, Di Fonzo N et al (2007) Breeding progress in morpho-physiological, agronomical and qualitative traits of durum wheat cultivars released in Italy during 20th century. Eur J Agron 26:39–53
El-Khayat GH, Samaan J, Manthey FA, Fuller MP, Brennan CS (2006) Durum wheat quality I: correlations between physical and chemical characteristics of Syrian durum wheat cultivars. Int J Food Sci Technol 41:22–29
Foti S, Maccarrone G, Saletti R, Roepstorff P, Gilbert S, Tatham AS et al (2000) Verification of the cDNA deduced sequence of glutenin subunit 1Dx5 and an Mr 58000 repetitive peptide by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS). J Cereal Sci 31:173–183
Gao L, Ma W, Chen J, Wang K, Li J, Wang S et al (2010) Characterization and comparative analysis of wheat high molecular weight glutenin subunits by SDS-PAGE, RP-HPLC, HPCE, and MALDI-TOF-MS. J Agric Food Chem 58:2777–2786
Gianibelli MC, Larroque OR, MacRitchie F, Wringley W (2001) Biochemical, genetic, and molecular characterization of wheat glutenin and its component subunits. Cereal Chem 78:635–646
Kawka A, Ng PKW, Bushuk W (1992) Equivalence of high molecular weight glutenin subunits prepared by reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Cereal Chem 69:92–96
Lagrain B, Brunnbauer M, Rombouts I, Koehler P (2013) Identification of intact high molecular weight glutenin subunits from the wheat proteome using combined liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Plos One 8:1–10
Liu L, Ikeda MT, Branlard G, Peña RJ, Rogers WJ, Lerner SE et al (2010) Comparison of low molecular weight glutenin subunits identified by SDS-PAGE, 2-DE, MALDI-TOF-MS and PCR in common wheat. BMC Plant Biol 10:124
Liu L, Wang A, Appels R, Ma J, Xia X, Lan P et al (2009) A MALDI-TOF based analysis of high molecular weight glutenin subunits for wheat breeding. J Cereal Sci 50:295–301
Martinez MC, Ruiz M, Carrillo MJ (2005) Effects of different prolamin alleles on durum wheat quality proprieties. J Cereal Sci 41:123–131
Shevchenko A, Tomas H, Havliš J, Olsen JV, Mann M (2006) In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat Protoc 1:2856–2860
Shewry RP, Halford GN (2002) Cereal seed storage proteins: structures, proprieties and role in grain utilization. J Exp Bot 370:947–958
Singh KN, Shepherd WK, Cornish BG (1991) A simplified SDS-PAGE procedure for separating LMW subunits of glutenin. J Cereal Sci 14:203–208
Sissons JM (2008) Role of durum wheat composition on the quality of pasta and bread. Food 2:75–90
Zhang Q, Dong Y, An X, Wang A, Zhang Y, Li X et al (2008) Characterization of HMW glutenin subunits in common wheat and related species by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS). J Cereal Sci 47:252–261
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the University of Parma, Regione Elimia-Romagna (IT) SITEA.PARMA Technopole (POR FESR 2007–2013) (MN) and the Interdepartmental Measure Centre “Giuseppe Casnati” (CIM) for accessing to MS facilities. The contribution of COST action FA0905, coordinated by Prof. Bal Ram Singh (Norwegian University of Life sciences, Norway), is also acknowledged.
Funding
This work was funded by AGER grant 2010–0278 “Environmental and economic sustainability for yield and quality production of durum wheat supply chain”.
Conflict of Interest
Dr. Giovanna Visioli declares that she has no conflict of interest. Dr. Alessia Comastri declares that she has no conflict of interest. Dr. Davide Imperiale declares that he has no conflict of interest. Dr. Gianluca Paredi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Dr. Andrea Faccini declares that he has no conflict of interest. Prof. Nelson Marmiroli declares that he has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or living animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Visioli, G., Comastri, A., Imperiale, D. et al. Gel-Based and Gel-Free Analytical Methods for the Detection of HMW-GS and LMW-GS in Wheat Flour. Food Anal. Methods 9, 469–476 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0218-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-015-0218-3