Abstract
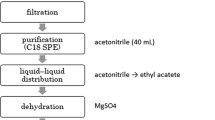
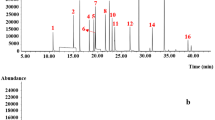
To investigate multi-residual pesticide monitoring data in commercial Chinese herbal medicines on major markets, an easy, rapid, and selective gas chromatography with mass spectrometry (GC/MS/MS) method was established for simultaneously determining multi-residual pesticides including organochlorine, pyrethroid, carbamate, and organophosphorus pesticides in Chinese herbal medicines. The analytical method was based on an efficient extraction procedure and further cleanup steps by solid-phase extraction columns, yielding recovery rates in the range of 70.0–120.0 % for the majority of pesticides, except for hexachlorobenze, diazinon, β-HCH, δ-HCH, and omethoate, with precision values expressed as relative standard deviation of 0.1–14.7 %. The limits of detection of the established GC/MS/MS method for all investigated pesticides ranged from 0.01 to 3.6 μg kg−1 and limits of quantification from 0.03 to 11.88 μg kg−1. With this validated method, multi-residual pesticides of 132 Chinese herbal medicine samples were analyzed. The monitoring results indicated that pesticide residue was found in 74 samples. In total, 51 pesticides were found with detection rate ranging from 0.76 to 18.94 %. An 82.3 % of positive pesticides were found in less than 6 % of samples. Hexachlorobenzene was found in 25 samples, quintozene in 15 samples, and acephate and simazine in 13 samples. Concentrations of pesticide residue from monitoring data obtained ranged from 0.5 to 203.5 μg kg−1. The simple and rapid method can be used as routine analysis method in multi-residual pesticide monitoring of Chinese herbal medicines.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aquino A, Wanderley KA, Paiva-Santos CDO, de Sá GF, Alexandre MDR, Júnior SA, Navickiene S (2010) Talanta 83:631
Chan K (2003) Chemosphere 52:1361
Chen L, Song F, Liu Z, Zheng Z, Xing J, Liu S (2012) J Chromatogr A 1225:132
Du G, Xiao Y, Yang H, Wang L, Song Y, Wang Y (2012) J Sep Sci 35:1922
Guo Q, Deng M, Yu B, Tan L (2010) J AOAC Int 93:295
Hao LL, Xue J (2005) J Chin Med Mater 30:405
Harris ESJ, Cao S, Littlefield BA, Craycroft JA, Scholten R, Kaptchuk T, Fu Y, Wang W, Liu Y, Chen H, Zhao Z, Clardy J, Woolf AD, Eisenberg DM (2011) Sci Total Environ 409:4297
Hu Y, Wan L, Zhang J, Yang F, Cao J (2012) Acta Pharm Sin B 2:286
Hwang B, Lee M (2000) J Chromatogr A 898:245
Ilias Y, Rudaz S, Christen P, Veuthey J (2006) Chimia 60:846
Jia Z, Mao X, Chen K, Wang K, Ji S (2010a) J AOAC Int 93:1570
Jia ZW, Mao XH, Miao S, Lu JW, Chen K, Wang K, Ji S (2010b) Acta Pharm Sin 45:353
Lee K, Jo E (2012) Food Chem 134:2497
Liu HT, Zhang BG, Chen JM, Xue J (2006) J Chin Med Mater 31:1841
Liu D, Xue J, Wu X (2011) J Chin Med Mater 36:396
Liu Q, Kong W, Qiu F, Wei J, Yang S, Zheng Y, Yang M (2012) J Chromatogr B 885–886:90
Mao XJ, Wan YQ, Yan AP, Shen MY, Wei YL (2012) Talanta 97:131
Rodrigues MVN, Reyes FGR, Rehder VLG, Rath S (2005) Chromatographia 61:291
Rodrigues MVN, Reyes FGR, Magalhães PM, Rath S (2007) J Brazil Chem Soc 18:135
SANCO (2009) European Council, Document No. SANCO/10684/2009
Słowik-Borowiec M, Szpyrka E, Walorczyk S (2012) B Environ Contam Tox 89:633
Tang F, YueY D, Hua RM, Cao HQ (2006) J AOAC Int 89:498
Xu R, Wu J, Liu Y, Zhao R, Chen B, Yang M, Chen J (2011) Chemosphere 84:908
Zhuang W, Gong Z (2012) Am J Anal Chem 3:24
Zuin VG, Yariwake JH, Bicchi C (2003) J Chromatogr A 985:159
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by the National S&T Major Special Project on Major New Drug Innovation, item number 2009ZX09502-027. This work is financially supported by the National Science and Technology Major Special Project on Major New Drug Innovation (no. 2009ZX09502-027) sponsored by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China only.
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest exists between our institute (Institute of Medicinal Plant Development, Chinese Academy of Medical Science and Peking Union Medical College) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China. All authors have read and approved this version of the article. All authors have agreed to the submission. No conflict of interest exists in the submission of this manuscript. Hefang Tong declares that she has no conflict of interest. Yanling Tong declares that she has no conflict of interest. Jian Xue declares that she has no conflict of interest. Dongjing Liu declares that she has no conflict of interest. Xiaobo Wu declares that he has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hefang Tong and Yanling Tong contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, H., Tong, Y., Xue, J. et al. Multi-residual Pesticide Monitoring in Commercial Chinese Herbal Medicines by Gas Chromatography–Triple Quadrupole Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 7, 135–145 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9609-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9609-5