Abstract
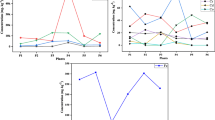
Minerals and heavy metal concentrations of 23 plants (arial parts, leaves, bark, stem, root, rhizome, dried berries, seeds) possessing health-promoting effects and used in indigenous medicines (as medicinal food) were determined using inductively coupled plasma atomic spectrometry. Vital essential minerals and heavy metals were present in all the samples analyzed. The majority of the plant materials were rich in some of the essential minerals like Na, K, Ca, Fe, Mg, Cu, Mn, and Zn, which are known to be beneficial for health. The plant material of Vitiveria zizinalis had highest concentration of toxic heavy metals, including arsenic (53.1 mg/100 g), chromium (6.74 mg/100 g), cobalt (10.2 mg/100 g), mercury (3.6 mg/100 g), and nickel (3.28 mg/100 g). Results of the present study provide vital data on the availability of some essential minerals, which can be useful to provide dietary information for designing value-added foods and for food biofortification. Apart from this, data on the contaminant levels of heavy metals highlights the necessity on the quality and safety concerns about their use.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberoumand A, Deokule SS (2009) Determination of elements profile of some wild edible plants. Food Anal Methods 2:116–119
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis of the Association of Official Agricultural Chemists, 15th edn. AOAC, Washington
Bhat R, Sridhar KR (2008) Nutritional quality evaluation of electron beam-irradiated lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) seeds. Food Chem 107:174–184
Bhat R, Karim AA (2009) Exploring the nutritional potential of wild and underutilized legumes. Comp Rev Food Sci Food Safety (in press)
Brody T (1994) Nutritional biochemistry. Academic, San Diego, pp 555–556
Chaturvedi VC, Shrivastava R, Upreti RK (2004) Viral infections and trace elements: a complex interaction. Curr Sci 87:1536–1554
Chopra RN, Nayar SL, Chopra IC (1956) Glossary of Indian medicinal plants. Council of Scientific Industrial Research, New Delhi, pp 1–330
COMA, Committee on medical aspects of food policy (1991) Dietary reference values for Food Energy and Nutrients in the United Kingdom. Department of Health, HSMO, London
Dahanukar SA, Thatte UM, Rege NN (1998) Pharmacology in Ayurveda: VI. Adverse reactions to Ayurvedic drugs. Indian Pract 51:815–821
FAO/WHO (1989) Joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives: Evaluation of certain food additives and contaminants, 33rd Report, Tech Rep Series 776. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 27–38
Galgano F, Favati F, Caruso M, Scarpa T, Palma A (2008) Analysis of trace elements in southern Italian wines and their classification according to provenance. LWT - Food Sci Technol 41:1808–1815
Hemalatha S, Patel K, Srinivasan K (2007) Zinc and iron contents and their bioaccessibility in cereals and pulses consumed in India. Food Chem 102:1328–1336
Januz M, Danutra W, Jerzy K, Robart R, Krysztof L, Jerzy C (1994) The occurrence of Pb, Cd, Cu, Mn, Ni, Co, and Cr in selected species of medicinal plants in Poland. Bromatol Toksypol 28:363–368
Jorhem L, Svensson K, Thuvander A, Glynn WA, Grawé PK (1996) Nickel in foodstuffs and nickel allergy (in Swedish). SLV-Rapport 8/96. National Food Administration, Uppsala
Kabelitz L (1998) Heavy metals in herbal drugs. Eur J Herbal Med 4:25–29
Kalǎc P, Svoboda L (2000) A review of trace element concentrations in edible mushrooms. Food Chem 69:273–281
Knapp G (1991) Mechanized techniques for sample decomposition and element pre-concentration. Microcemica Acta 2:445–455
Lavilla I, Filgueiras AV, Bendicho C (1999) Comparison of digestion methods for determination of trace and minor metals in plant samples. J Agric Food Chem 47:5072–5077
Liang W-L, Lin S-W, Yen K-Y, Yang L-L (1998) Metal element analysis of commercial Chinese medicines. Taiwan Kexue 51:37–56
Mayer ML, Vyklicky L (1989) The action of Zinc on synaptic transmission of mouse neuronal excitability in culture of mouse hippocampus. The J Physiol 415:351–365
Mazzanti G, Battinelli L, Daniele C, Costantini S, Ciaralli L, Evandri MG (2008) Purity control of some Chinese crude herbal drugs marketed in Italy. Food Chem Toxicol 46:3043–3047
Mertz W (1982) Trace minerals and atherosclerosis. J Food Process 41:2807–2812
Miller-Cebert RL, Sistani NA, Cebert E (2009) Comparative mineral composition among canola cultivars and other cruciferous leafy greens. J Food Comp Anal 22:112–116
Özcan M, Akgül A (1998) Influence of species, harvest date and size on composition of capers (Capparis spp.) flower buds. Nahrung 42:102–105
Perry HM (1972) Hypertension and true geochemical environments in relation to health and diseases. Academic, New York
Sanchez-Castillo CP, Dewey PJS, Aguirre A, Lara JJ, Vaca R, Leon de la Barra P, Ortiz M, Escamilla I, James WPT (1998) The mineral content of Mexican fruits and vegetables. J Food Comp Anal 1:340–356
Schilcher H, Peters H, Wank H (1987) Pestiszide and Schmermretalle in Arzneipmanzen and Arzneiplanzen Zubereitungen. Pharmazeutische Industrie 49:202–211
Schumacher M, Bosque MA, Domingo JL, Corbella J (1991) Dietary intake of lead and cadmium from foods in Tarragona Province, Spain. Bull of Environ Contam Toxicol 46:320–328
Shetty BV, Kaveriappa KM, Bhat GK (2002) Plant resources of Western Ghats and lowlands of Dakshina Kannada and Udupi districts Published in 2002. Pilikula Nisarga Dhama Society, Mangalore, p 264
Smith KT (1988) Trace minerals in foods. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–430
Strickland GT, Beckner WM, Leu ML, O'Reilly S (1972) Turnover studies of copper in homozygotes and heterozygotes for Wilson's disease and controls: isotope tracer studies with 27Cu. Clinical Sci 43:605–615
Talwar GP, Srivastava LM, Mudgil KD (1989) Textbook of biochemistry and human biology (2nd edition). Prentice Hall of India Private Ltd, India, p 1292
Tuzen M, Sesli E, Soylak M (2007) Trace element levels of mushroom species from East Black Sea region of Turkey. Food Cont 18:806–810
Vasant L (1998) The complete book of ayurvedic home remedies. Harmony, New York, p 325
Wong MK, Tan P, Wee YC (1993) Heavy metals in some Chinese herbal plants. Biol Trace Elem Res 36:135–142
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhat, R., Kiran, K., Arun, A.B. et al. Determination of Mineral Composition and Heavy Metal Content of Some Nutraceutically Valued Plant Products. Food Anal. Methods 3, 181–187 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-009-9107-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-009-9107-y