Abstract
Objective
Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) is highly abundant in reactive astrocytes and upregulated in neuroinflammatory processes. However, the age-related change of MAO-B in amyloid-negative cognitively unimpaired elderly subjects has not yet been sufficiently evaluated on positron emission tomography (PET). 18F-THK5351 is a radiotracer with high affinity to MAO-B, which may potentially serve as an imaging biomarker for detecting neuroinflammation. The purpose of this study was to investigate the age-related topographic change of 18F-THK5351 PET in amyloid-negative cognitively unimpaired elderly subjects.
Methods
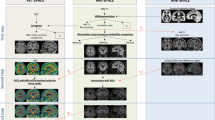
The age-related change of 18F-THK5351 retention was evaluated on the visual analysis, voxel and region of interest (ROI)-based analyses using Statistical Parametric Mapping and PETSurfer tool of FreeSurfer in 31 amyloid-negative cognitively unimpaired elderly subjects.
Results
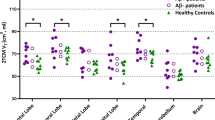
On visual inspection, elderly groups showed the spread of 18F-THK5351 accumulation from the medial to inferolateral temporal and basal frontal lobes, and cingulate gyrus. Additionally, voxel- and ROI-based analysis demonstrated the correlation between 18F-THK5351 accumulation and participants’ age, especially in the inferior temporal lobes.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated age-dependent increase of 18F-THK5351 retention in amyloid-negative cognitively unimpaired subjects, which suggests an increase in MAO-B positive reactive astrocytes with aging.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Damier P, Kastner A, Agid Y, Hirsch EC. Does monoamine oxidase type B play a role in dopaminergic nerve cell death in Parkinson’s disease? Neurology. 1996;46:1262–9.
Riederer P, Konradi C, Schay V, Kienzl E, Birkmayer G, Danielczyk W, Sofic E, Youdim MB. Localization of MAO-A and MAO-B in human brain: a step in understanding the therapeutic action of L-deprenyl. Adv Neurol. 1987;45:111–8.
Saura J, Andrés N, Andrade C, Ojuel J, Eriksson K, Mahy N. Biphasic and region-specific MAO-B response to aging in normal human brain. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18:497–507.
Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Logan J, Pappas N, Shea C, MacGregor R. Age-related increases in brain monoamine oxidase B in living healthy human subjects. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18:431–5.
Alper G, Girgin FK, Ozgönül M, Menteş G, Ersöz B. MAO inhibitors and oxidant stress in aging brain tissue. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 1999;9:247–52.
Palmer AL, Ousman SS. Astrocytes and aging. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:337.
Harada R, Okamura N, Furumoto S, Furukawa K, Ishiki A, Tomita N, Tago T, Hiraoka K, Watanuki S, Shidahara M, Miyake M, Ishikawa Y, Matsuda R, Inami A, Yoshikawa T, Funaki Y, Iwata R, Tashiro M, Yanai K, Arai H, Kudo Y. 18F-THK5351: a Novel PET radiotracer for imaging neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer disease. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:208–14.
Lee H, Seo S, Lee SY, Jeong HJ, Woo SH, Lee KM, Lee YB, Park KH, Heo JH, Yoon CW, Kang JM, Cho J, Okamura N, Furumoto S, Yanai K, Na DL, Ido T, Villemagne VL, Noh Y. [18F]-THK5351 PET imaging in patients with semantic variant primary progressive aphasia. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 2018;32:62–9.
Ng KP, Pascoal TA, Mathotaarachchi S, Therriault J, Kang MS, Shin M, Guiot MC, Guo Q, Harada R, Comley RA, Massarweh G, Soucy JP, Okamura N, Gauthier S, Rosa-Neto P. Monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, selegiline, reduces (18)F-THK5351 uptake in the human brain. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017;9:25.
Harada R, Ishiki A, Kai H, Sato N, Furukawa K, Furumoto S, Tago T, Tomita N, Watanuki S, Hiraoka K, Ishikawa Y, Funaki Y, Nakamura T, Yoshikawa T, Iwata R, Tashiro M, Sasano H, Kitamoto T, Yanai K, Arai H, Kudo Y, Okamura N. Correlations of (18)F-THK5351 PET with postmortem burden of tau and astrogliosis in Alzheimer disease. J Nucl Med. 2018;59:671–4.
Ishibashi K, Kameyama M, Miura Y, Toyohara J, Ishii K. Head-to-head comparison of the two MAO-B radioligands, 18F-THK5351 and 11C-L-deprenyl, to visualize astrogliosis in patients with neurological disorders. Clin Nucl Med. 2021;46:e31–3.
Gulyás B, Pavlova E, Kása P, Gulya K, Bakota L, Várszegi S, Keller E, Horváth MC, Nag S, Hermecz I, Magyar K, Halldin C. Activated MAO-B in the brain of Alzheimer patients, demonstrated by [11C]-L-deprenyl using whole hemisphere autoradiography. Neurochem Int. 2011;58:60–8.
Kang JM, Lee SY, Seo S, Jeong HJ, Woo SH, Lee H, Lee YB, Yeon BK, Shin DH, Park KH, Kang H, Okamura N, Furumoto S, Yanai K, Villemagne VL, Seong JK, Na DL, Ido T, Cho J, Lee KM, Noh Y. Tau positron emission tomography using [(18)F]THK5351 and cerebral glucose hypometabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2017;59:210–9.
Huang CC, Hsiao IT, Huang CY, Weng YC, Huang KL, Liu CH, Chang TY, Wu HC, Yen TC, Lin KJ. Tau PET With (18)F-THK-5351 Taiwan Patients With Familial Alzheimer’s Disease With the APP p. D678H Mutation. Front Neurol. 2019;10:503.
Jeon S, Kang JM, Seo S, Jeong HJ, Funck T, Lee SY, Park KH, Lee YB, Yeon BK, Ido T, Okamura N, Evans AC, Na DL, Noh Y. Topographical heterogeneity of Alzheimer’s disease based on MR imaging, tau PET, and amyloid PET. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019;11:211.
Shigemoto Y, Sone D, Ota M, Maikusa N, Ogawa M, Okita K, Takano H, Kato K, Kimura Y, Morimoto E, Suzuki F, Fujii H, Sato N, Matsuda H. Voxel-based correlation of (18)F-THK5351 accumulation and gray matter volume in the brain of cognitively normal older adults. EJNMMI Res. 2019;9:81.
Jeong HJ, Lee H, Lee SY, Seo S, Park KH, Lee YB, Shin DJ, Kang JM, Yeon BK, Kang SG, Cho J, Seong JK, Okamura N, Villemagne VL, Na DL, Noh Y. [18F]THK5351 PET imaging in patients with mild cognitive impairment. J Clin Neurol. 2020;16:202–14.
Nihashi T, Sakurai K, Kato T, Iwata K, Kimura Y, Ikenuma H, Yamaoka A, Takeda A, Arahata Y, Washimi Y, Suzuki K, Bundo M, Sakurai T, Okamura N, Yanai K, Ito K, Nakamura A. Patterns of distribution of 18F-THK5351 positron emission tomography in Alzheimer’s disease continuum. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;85:223–34.
Iwatsubo T, Iwata A, Suzuki K, Ihara R, Arai H, Ishii K, Senda M, Ito K, Ikeuchi T, Kuwano R, Matsuda H, Sun CK, Beckett LA, Petersen RC, Weiner MW, Aisen PS, Donohue MC. Japanese and north American Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative studies: harmonization for international trials. Alzheimers Dement. 2018;14:1077–87.
Nakamura A, Cuesta P, Kato T, Arahata Y, Iwata K, Yamagishi M, Kuratsubo I, Kato K, Bundo M, Diers K, Fernández A, Maestú F, Ito K. Early functional network alterations in asymptomatic elders at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Sci Rep. 2017;7:6517.
Okada Y, Kato T, Iwata K, Kimura Y, Nakamura A, Hattori H, Toyama H, Ishii K, Ishii K, Senda M, Ito K, Iwatsubo T. Evaluation of PiB visual interpretation with CSF Aβ and longitudinal SUVR in J-ADNI study. Ann Nucl Med. 2020;34:108–18.
Lockhart SN, Baker SL, Okamura N, Furukawa K, Ishiki A, Furumoto S, Tashiro M, Yanai K, Arai H, Kudo Y, Harada R, Tomita N, Hiraoka K, Watanuki S, Jagust WJ. Dynamic PET measures of tau accumulation in cognitively normal older adults and Alzheimer’s disease patients measured using [18F] THK-5351. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0158460.
Greve DN, Svarer C, Fisher PM, Feng L, Hansen AE, Baare W, Rosen B, Fischl B, Knudsen GM. Cortical surface-based analysis reduces bias and variance in kinetic modeling of brain PET data. Neuroimage. 2014;92:225–36.
Tong J, Meyer JH, Furukawa Y, Boileau I, Chang LJ, Wilson AA, Houle S, Kish SJ. Distribution of monoamine oxidase proteins in human brain: implications for brain imaging studies. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2013;33:863–71.
Jang YK, Lyoo CH, Park S, Oh SJ, Cho H, Oh M, Ryu YH, Choi JY, Rabinovici GD, Kim HJ, Moon SH, Jang H, Lee JS, Jagust WJ, Na DL, Kim JS, Seo SW. Head to head comparison of [(18)F] AV-1451 and [(18)F] THK5351 for tau imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;45:432–42.
Soreq L, Rose J, Soreq E, Hardy J, Trabzuni D, Cookson MR, Smith C, Ryten M, Patani R, Ule J. Major shifts in glial regional identity are a transcriptional hallmark of human brain aging. Cell Rep. 2017;18:557–70.
Carter SF, Herholz K, Rosa-Neto P, Pellerin L, Nordberg A, Zimmer ER. Astrocyte biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Mol Med. 2019;25:77–95.
Villemagne VL, Harada R, Dore V, Furumoto S, Mulligan R, Kudo Y, Burnham S, Krishnadas N, Bozinovski S, Huang K, Lopresti BJ, Yanai K, Rowe CC, Okamura N. First-in-human evaluation of (18)F-SMBT-1, a novel (18)F-labeled MAO-B PET tracer for imaging reactive astrogliosis. J Nucl Med. 2022. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.121.263254.
Chinta SJ, Woods G, Rane A, Demaria M, Campisi J, Andersen JK. Cellular senescence and the aging brain. Exp Gerontol. 2015;68:3–7.
Nekrasov PV, Vorobyov VV. Dopaminergic mediation in the brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases: a role of senescent cells. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13:649–50.
Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;82:239–59.
Schöll M, Lockhart SN, Schonhaut DR, O’Neil JP, Janabi M, Ossenkoppele R, Baker SL, Vogel JW, Faria J, Schwimmer HD, Rabinovici GD, Jagust WJ. PET Imaging of tau deposition in the aging human brain. Neuron. 2016;89:971–82.
Pontecorvo MJ, Devous MD Sr, Navitsky M, Lu M, Salloway S, Schaerf FW, Jennings D, Arora AK, McGeehan A, Lim NC, Xiong H, Joshi AD, Siderowf A, Mintun MA. Relationships between flortaucipir PET tau binding and amyloid burden, clinical diagnosis, age and cognition. Brain. 2017;140:748–63.
Lowe VJ, Bruinsma TJ, Min HK, Lundt ES, Fang P, Senjem ML, Boeve BF, Josephs KA, Pandey MK, Murray ME, Kantarci K, Jones DT, Schwarz CG, Knopman DS, Petersen RC, Jack CR Jr. Elevated medial temporal lobe and pervasive brain tau-PET signal in normal participants. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2018;10:210–6.
Lowe VJ, Wiste HJ, Senjem ML, Weigand SD, Therneau TM, Boeve BF, Josephs KA, Fang P, Pandey MK, Murray ME, Kantarci K, Jones DT, Vemuri P, Graff-Radford J, Schwarz CG, Machulda MM, Mielke MM, Roberts RO, Knopman DS, Petersen RC, Jack CR Jr. Widespread brain tau and its association with ageing, braak stage and Alzheimer’s dementia. Brain. 2018;141:271–87.
Son HJ, Oh JS, Roh JH, Seo SW, Oh M, Lee SJ, Oh SJ, Kim JS. Differences in gray and white matter (18)F-THK5351 uptake between behavioral-variant frontotemporal dementia and other dementias. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2019;46:357–66.
Oyama S, Hosoi A, Ibaraki M, McGinnity CJ, Matsubara K, Watanuki S, Watabe H, Tashiro M, Shidahara M. Error propagation analysis of seven partial volume correction algorithms for [(18)F]THK-5351 brain PET imaging. EJNMMI Phys. 2020;7:57.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mr. John Gelblum for his English proofreading.
Funding
This research was supported by AMED (20ae0101077h0003) and an in-house grants in National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology (23–36, 26–30, 27–4, 29–24, 30–3). The authors are grateful to all the staff members of the National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology for their contribution to the MULNIAD and ADSAT studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Prof. Okamura received a research grant from GE Healthcare and own stock in Clino Ltd. Other authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Ethical approval
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the Ethics Committee of NCGG, and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Participants were all fully informed of the study procedures and have signed the informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakurai, K., Nihashi, T., Kimura, Y. et al. Age-related increase of monoamine oxidase B in amyloid-negative cognitively unimpaired elderly subjects. Ann Nucl Med 36, 777–784 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-022-01760-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-022-01760-6