Abstract
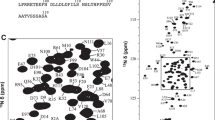
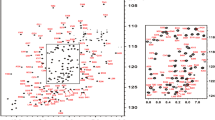
Tissue development requires the expression of a regulated subset of genes, and it is becoming clear that the process of alternative splicing also plays an important role in the production of necessary tissue-specific isoforms. However, only a few of these tissue-specific splicing factors in mammals have so far been discovered. One of these factors is the RNA-binding protein RBM24 which has been recently identified as a major regulator of alternative splicing in cardiac and skeletal muscle development. The RBM24 protein contains an RNA recognition motif (RRM) domain that presumably mediates the binding to target pre-mRNA required for regulation of the splicing patterns. Here we report 1H, 15N and 13C chemical shift assignments of the backbone and sidechain atoms for the RRM domain from human RBM24. Secondary chemical shift analysis and relaxation measurement confirm the canonical architecture of the RRM domain. The data will allow for atomic level studies aimed at understanding splicing regulation of target genes in heart and muscle development and investigation into a separate role of RBM24 in modulating mRNA stability of genes involved in the p53 tumor suppressor pathway.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrane S, Rebora K, Zniber I, Dupuy D, Mackereth CD (2014) Backbone-independent nucleic acid binding by splicing factor SUP-12 reveals key aspects of molecular recognition. Nat Commun 5:4595
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
Fetka I, Radeghieri A, Bouwmeester T (2000) Expression of the RNA recognition motif-containing protein SEB-4 during Xenopus embryonic development. Mech Dev 94:283–286
Grifone R, Xie X, Bourgeois A, Saquet A, Duprez D, Shi D-L (2014) The RNA-binding protein Rbm24 is transiently expressed in myoblasts and is required for myogenic differentiation during vertebrate development. Mech Dev 134:1–15
Jiang Y, Zhang M, Qian Y, Xu E, Zhang J, Chen X (2014) Rbm24, an RNA-binding protein and a target of p53, regulates p21 expression via mRNA stability. J Biol Chem 289:3164–3175
Kong SW, Hu YW, Ho JWK, Ikeda S, Polster S, John R, Hall JL, Bisping E, Pieske B, dos Remedios CG, Pu WT (2010) Heart failure-associated changes in RNA splicing of sarcomere genes. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 3:138–146
Kuwasako K, Takahashi M, Unzai S, Tsuda K, Yoshikawa S, He F, Kobayashi N, Güntert P, Shirouzu M, Ito T, Tanaka A, Yokoyama S, Hagiwara M, Kuroyanagi H, Muto Y (2014) RBFOX and SUP-12 sandwich a G base to cooperatively regulate tissue-specific splicing. Nat Struct Mol Biol 21:778–786
Li HY, Bourdelas A, Carron C, Shi DL (2010) The RNA-binding protein Seb4/RBM24 is a direct target of MyoD and is required for myogenesis during Xenopus early development. Mech Dev 127:281–291
Maragh S, Miller RA, Bessling SL, McGaughey DM, Wessels MW, de Graaf B, Stone EA, Bertoli-Avella AM, Gearhart JD, Fisher S, McCallion AS (2011) Identification of RNA binding motif proteins essential for cardiovascular development. BMC Dev Biol 11:62
Maragh S, Miller RA, Bessling SL, Wang G, Hook PW, McCallion AS (2014) Rbm24a and Rbm24b are required for normal somitogenesis. PLoS ONE 9:e105460
Miyamoto S, Hidaka K, Jin D, Morisaki T (2009) RNA-binding proteins Rbm38 and Rbm24 regulate myogenic differentiation via p21-dependent and -independent regulatory pathways. Genes Cells 14:1241–1252
Poon KL, Tan KT, Wei YY, Ng CP, Colman A, Korzh V, Xu XQ (2012) RNA-binding protein RBM24 is required for sarcomere assembly and heart contractility. Cardiovasc Res 94:418–427
Senn H, Werner B, Messerle BA, Weber C, Traber R, Wüthrich K (1989) Stereospecific assignment of the methyl 1H NMR lines of valine and leucine in polypeptides by nonrandom 13C labelling. FEBS Lett 249:113–118
Shen Y, Delaglio F, Cornilescu G, Bax A (2009) TALOS+: a hybrid method for predicting protein backbone torsion angles from NMR chemical shifts. J Biomol NMR 44:213–223
Tamiola K, Acar B, Mulder FA (2010) Sequence-specific random coil chemical shifts of intrinsically disordered proteins. J Am Chem Soc 132:18000–18003
Xu E, Zhang J, Zhang M, Jiang Y, Cho SJ, Chen X (2014) RNA-binding protein RBM24 regulates p63 expression via mRNA stability. Mol Cancer Res 12:359–369
Yang J, Hung L-H, Licht T, Kostin S, Looso M, Khrameeva E, Bindereif A, Schneider A, Braun T (2014) RBM24 is a major regulator of muscle-specific alternative splicing. Dev Cell 31:87–99
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India. SKU is a recipient of the DST INSPIRE Faculty award [IFA-13 CH-102].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Upadhyay, S.K., Mackereth, C.D. 1H, 15N and 13C backbone and side chain resonance assignments of the RRM domain from human RBM24. Biomol NMR Assign 10, 237–240 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-016-9674-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-016-9674-y