Abstract
Objective
To investigate obesogenic co-causing factors, promoting rise of weight in children, associated to local differences in India.
Methods
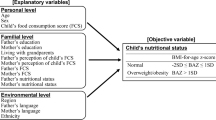
Overall 1,680 children, aged 3–11 and balanced by gender, were recruited in school contexts distributed in seven major Indian cities. All children were weighted and measured in order to calculate their BMI. A validated cultural specific questionnaire was administered to children’s parents for assessing socio-demographic data, eating habits, physical activity, etc. Furthermore children’s brand awareness scores were computed in order to analyze their affiliation towards food-based advertisement. Descriptive statistics of frequencies, duration and intensity of the various factors were performed. Chi-square tests or Wilcoxon signed rank test were used for evaluating significance of differences in factors distribution across Indian cities.
Results
Four factors, promoting rise of children’s weight, were individuated as associated to urban differences, namely meal times consumed in the family, parents’ BMI, brand awareness and physical activity. These aspects exercised a significant impact on children’s body size in Kolkata and Chennai. Hyderabad and Mumbai, instead, were the cities where religion played some role in influencing children’s weight gain.
Conclusions
Such findings underline the need to frame obesity as a situated phenomenon rather than a national problem. Health policies, implemented in treating and preventing obesity, should be therefore specifically focused on locally situated peculiarities.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
WHO. Obesity and overweight. Media centre. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014.
Joshi SR, Mohan V, Joshi SS, Mechanick JI, Marchetti A. Transcultural diabetes nutrition therapy algorithm: the Asian Indian application. Curr Diabetes Rep. 2012;12:204–12.
Gupta R, Gupta KD. Coronary heart disease in low socioeconomic status subjects in India: “an evolving epidemic”. Indian Heart J. 2009;61:358–67.
Evans CA, Selvadurai H, Baur LA, Waters KA. Effects of obstructive sleep apnea and obesity on exercise function in children. Sleep. 2014;37:1103–10.
Deepa M, Anjana RM, Manjula D, Narayan KM, Mohan V. Convergence of prevalence rates of diabetes and cardiometabolic risk factors in middle and low income groups in urban India: 10-year follow-up of the Chennai urban population study. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011;5:918–27.
Misra A, Singhal N, Sivakumar B, Bhagat N, Jaiswal A, Khurana L. Nutrition transition in India: secular trends in dietary intake and their relationship to diet-related non-communicable diseases. J Diabetes. 2011;3:278–92.
Bauman Z. Consuming life. Cambridge: Polity Press; 2007.
Ranasinghe CD, Ranasinghe P, Jayawardena R, Misra A. Physical activity patterns among South-Asian adults: a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013;10:116.
Singh RB, Beegom R, Mehta AS, Niaz MA, De AK, Mitra RK, et al. Social class, coronary risk factors and undernutrition, a double burden of diseases, in women during transition, in five Indian cities. Int J Cardiol. 1999;69:139–47.
Chandra PS, Abbas S, Palmer R. Are eating disorders a significant clinical issue in urban India? A survey among psychiatrists in Bangalore. Int J Eat Disord. 2012;45:443–6.
McMichael AJ. Globalization, climate change, and human health. New Engl J Med. 2013;368:1335–43.
Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C. Rising burden of obesity in Asia. J Obes. 2010. doi:10.1155/2010/868573.
Ramachandran A, Chamukuttan S, Shetty SA, Arun N, Susairaj P. Obesity in Asia–is it different from rest of the world. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2012;28:S47–51.
Chkili W, Nguyen DK. Exchange rate movements and stock market returns in a regime-switching environment: evidence for BRICS countries. Res Int Bus Financ. 2014;31:46–56.
Mantovani G. Exploring borders. Understanding culture and psychology. London: Rootledge; 2000.
Neumark-Sztainer D, Hannan PJ, Story M, Croll J, Perry C. Family meal patterns: associations with sociodemographic characteristics and improved dietary intake among adolescents. J Am Diet Assoc. 2003;103:317–22.
Hook JL. Care in context: men’s unpaid work in 20 countries, 1965–2003. Am Sociol Rev. 2006;71:639–60.
Seliske L, Pickett W, Janssen I. Urban sprawl and its relationship with active transportation, physical activity and obesity in Canadian youth. Health reports/Statistics Canada, Canadian Centre for Health Information = Rapports sur la sante/Statistique Canada, Centre canadien d'information sur la sante. 2012;23:17–25.
Pepe A, Armenti A. Knowledge building processes in blended learning communities: forum usage evaluation from a participatory framework for distance cooperation. Edulearn. Barcelona: IATED; 2009. p. 5075–85.
Kautiainen S, Koivusilta L, Lintonen T, Virtanen SM, Rimpela A. Use of information and communication technology and prevalence of overweight and obesity among adolescents. Int J Obes. 2005;29:925–33.
Ebrahim S, Kinra S, Bowen L, Andersen E, Ben-Shlomo Y, Lyngdoh T, et al. The effect of rural-to-urban migration on obesity and diabetes in India: a cross-sectional study. PLoS Med. 2010;7:e1000268.
Horvath CW. Measuring television addiction. J Broadcast Electron Media. 2004;48:378–98.
Popkin BM, Adair LS, Ng SW. Global nutrition transition and the pandemic of obesity in developing countries. Nutr Rev. 2012;70:3–21.
Rani MA, Sathiyasekaran BW. Behavioural determinants for obesity: a cross-sectional study among urban adolescents in India. J Prev Med Public Health. 2013;46:192–200.
Ghosh A. Rural–urban comparison in prevalence of overweight and obesity among children and adolescents of Asian Indian origin. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2011;23:928–35.
Chadda RK, Deb KS. Indian family systems, collectivistic society and psychotherapy. Indian J Psychiatry. 2013;55:S299–309.
Borradaile KE, Sherman S, Vander Veur SS, McCoy T, Sandoval B, Nachmani J, et al. Snacking in children: the role of urban corner stores. Pediatrics. 2009;124:1293–8.
Taber DR, Chriqui JF, Powell LM, Chaloupka FJ. Banning all sugar-sweetened beverages in middle schools: reduction of in-school access and purchasing but not overall consumption. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2012;166:256–62.
Teevale T, Scragg R, Faeamani G, Utter J. Pacific parents’ rationale for purchased school lunches and implications for obesity prevention. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2012;21:282–90.
Gulati S, Misra A, Colles SL, Kondal D, Gupta N, Goel K, et al. Dietary intakes and familial correlates of overweight/obesity: a four-cities study in India. Ann Nutr Metab. 2013;62:279–90.
Wasir JS, Misra A. The metabolic syndrome in Asian Indians: impact of nutritional and socio-economic transition in India. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2004;2:14–23.
Franchin L, Zobec F, Ghidina M, Stefanini G, Berchialla P, Gregori D. Measuring brand awareness in as a component of eating habits in children: the development of the IBAI (Italian Brand Awareness Instrument). Prog Nutr. 2012. p. 14.
Otten JJ, Hekler EB, Krukowski RA, Buman MP, Saelens BE, Gardner CD, et al. Food marketing to children through toys: response of restaurants to the first U.S. toy ordinance. Am J Prev Med. 2012;42:56–60.
Gregori D, Gulati A, Hochdorn A, Ballali S, Paramesh H, Kumar M, et al. Food packaged with toys: an investigation on potential obesogenic effects in Indian children. Indian J Pediatr. 2014. doi:10.1007/s12098-014-1448-x.
APA. Ethical principles of psychologists and code of conduct. Washington DC: American Psychological Association; 2002.
WHO. Growth reference data for 5–19 years. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2007.
WHO. The WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study (MGRS). Geneva: World Health Organization; 2003.
IAP. IAP growth charts. Patna: Indian Academy of Pediatrics; 2014.
Vecchio MG, Ghidina M, Gulati A, Berchialla P, Paramesh EC, Gregori D. Measuring brand awareness as a component of eating habits in Indian children: the development of the IBAI questionnaire. Indian J Pediatr. 2014. doi:10.1007/s12098-014-1447-y.
Vecchio MG, Berchialla P, Didier N, Cayul O, Valdenegro D, Ghidina M, et al. The IBAI instrument to assess brand awareness toward food in children: the Chile adaptation. Open Obes J. 2013;5:S30–5.
Breiman L. Random forests. Mach Learn. 2001;45:5–32.
Bylander T. Estimating generalization error on two-class datasets using out-of-bag estimates. Mach Learn. 2002;48:287–97.
R Development Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2012.
Liaw A, Wiener M. Classification and regression by random forest. R News. 2002;2:18–22.
Sachs JD, Bajpai N, Ramiah A. Understanding regional economic growth in India*. Asian Econ Pap. 2002;1:32–62.
Cashin P, Ratna S. Internal migration, center-state grants, and economic growth in the states of India. IMF Staff Pap. 1996;43:123–71.
Hammons AJ, Fiese BH. Is frequency of shared family meals related to the nutritional health of children and adolescents? Pediatrics. 2011;127:e1565–74.
Gillman MW, Rifas-Shiman SL, Frazier AL, Rockett HR, Camargo Jr CA, Field AE, et al. Family dinner and diet quality among older children and adolescents. Arch Fam Med. 2000;9:235–40.
Videon TM, Manninf CK. Influence of on adolescents eating patterns: the importance of family meal. J Adolesc Health. 2003;32:365–73.
Shafaghi K, Shariff ZM, Taib MN, Rahman HA, Mobarhan MG, Jabbari H. Parental body mass index is associated with adolescent overweight and obesity in Mashhad, Iran. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2014;23:225–31.
Mandal A, Mandal GC. Prevalence of overweight and obesity among the urban adolescent English medium school girls of Kolkata, India. IJPH. 2012;9:1–6.
Sloutsky VM. From perceptual categories to concepts: what develops? Cogn Sci. 2010;34:1244–86.
Vygotskij LS. Mind and society: the development of higher psychological processes. Cambridge: Haward University Press; 1980.
Borzekowski DL, Robinson TN. The 30-second effect: an experiment revealing the impact of television commercials on food preferences of preschoolers. J Am Diet Assoc. 2001;101:42–6.
Lobstein T, Dibb S. Evidence of a possible link between obesogenic food advertising and child overweight. Obes Rev. 2005;6:203–8.
Boyland EJ, Halford JC. Television advertising and branding. Effects on eating behaviour and food preferences in children. Appetite. 2013;62:236–41.
Forman J, Halford JC, Summe H, MacDougall M, Keller KL. Food branding influences ad libitum intake differently in children depending on weight status. Results of a pilot study. Appetite. 2009;53:76–83.
Ramachandran A, Mary S, Yamuna A, Murugesan N, Snehalatha C. High prevalence of diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors associated with urbanization in India. Diabetes Care. 2008;31:893–8.
Chacko E. From brain drain to brain gain: reverse migration to Bangalore and Hyderabad, India’s globalizing high tech cities. GeoJournal. 2007;68:131–40.
WHO. Global recommendations on physical activity for health: 5–17 years old. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014.
Reaven PD, Barrett-Connor E, Edelstein S. Relation between leisure-time physical activity and blood pressure in older women. Circulation. 1991;83:559–65.
Hamman RF, Wing RR, Edelstein SL, Lachin JM, Bray GA, Delahanty L, et al. Effect of weight loss with lifestyle intervention on risk of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:2102–7.
Willett WC, Koplan JP, Nugent R, Dusenbury C, Puska P, Gaziano TA. Prevention of chronic disease by means of diet and lifestyle changes. In: Jamison DT, Breman JG, Measham AR, Alleyne G, Claeson M, Evans DB, et al., editors. Disease control priorities in developing countries. 2nd ed. Washington (DC): Oxford University Press; 2006. p. 833–50.
Coon KA, Tucker KL. Television and children’s consumption patterns. A review of the literature. Minerva Pediatr. 2002;54:423–36.
Bonne K, Verbeke W. Muslim consumer trust in halal meat status and control in Belgium. Meat Sci. 2008;79:113–23.
Gupta R, Guptha S, Sharma KK, Gupta A, Deedwania P. Regional variations in cardiovascular risk factors in India: India heart watch. World J Cardiol. 2012;4:112–20.
Daniel CR, Prabhakaran D, Kapur K, Graubard BI, Devasenapathy N, Ramakrishnan L, et al. A cross-sectional investigation of regional patterns of diet and cardio-metabolic risk in India. Nutr J. 2011;10:12.
Contributions
DG: Designed the study; AH, DG and AG: Wrote the manuscript; DG and RC: Performed the statistical analysis. AG, IB, HP and ECP critically revised the manuscript and contributed to the discussion. All authors contributed to results interpretation, read and approved the final manuscript. DG will act as guarantor for this paper.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
This work is partially supported by an unrestricted grant from the Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Directorate General for Country Promotion, and from Prochild ONLUS (Italy).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregori, D., Gulati, A., Paramesh, E.C. et al. Cross-Regional Analysis of Multiple Factors Associated with Childhood Obesity in India: A National or Local Challenge?. Indian J Pediatr 81 (Suppl 1), 5–16 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-014-1550-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-014-1550-0