Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the outcomes and risk factors of patients treated with stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR) delivered by image-guided helical tomotherapy (HT) for extracranial oligometastases.
Methods
From August 2006 through July 2011, 42 consecutive patients (median age 69 years [range 16–87]) with oligometastases (≤3) received HT to all known cancer sites (lung, n = 28; liver, n = 12; adrenal, n = 2). Prognostic factors were assessed by Cox’s proportional hazards regression analysis.
Results
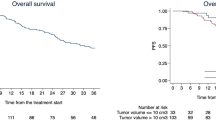
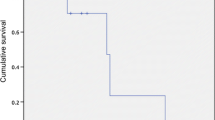
A total of 60 lesions were treated with hypofractionated HT (median dose 39 Gy [range 36–72.5]; median dose per fraction 12 Gy [range 5–20]). Complete or partial response was observed in 40 (54 %) patients. With a median follow-up period of 15 months, 1- and 2-year overall survival (OS) was 84 and 63 %, respectively; and 1- and 2-year local control (LC) was 92 and 86 %, respectively. Four patients had pneumonitis Grade ≥2 and two patients had lower gastrointestinal toxicity Grade ≥2. Only the lack of complete/partial response was associated with higher risk of mortality on univariate (HR = 3.8, P = 0.04) and multivariate (HR = 6.6, P = 0.01) analyses.
Conclusions
SABR delivered by image-guided HT is well tolerated and offers adequate LC with low acute morbidity in patients with extracranial oligometastatic disease. We found that the response to HT was the only predictor for OS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID et al (2002) Lung. In: AJCC cancer staging manual, 6th edn. Springer, New York
Weichselbaum RR, Hellman S (2011) Oligometastases revisited. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8:378–382
Lopes JC, Navarro A, Solé JM, Martínez M, Guedea F (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for spinal metastases. Clin Transl Oncol 12:639–642
Norihisa Y, Nagata Y, Takayama K et al (2008) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastatic lung tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72:398–403
Tomita N, Soga N, Ogura Y et al (2012) Preliminary results of intensity-modulated radiation therapy with helical tomotherapy for prostate cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. doi:10.1007/s00432-012-1277-0
Hoyer M, Swaminath A, Bydder S et al (2012) Radiotherapy for liver metastases: a review of evidence. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:1047–1057
Cárdenes HR, Price TR, Perkins SM et al (2010) Phase I feasibility trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol 12:218–225
Oshiro Y, Aruga T, Tsuboi K et al (2010) Stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung tumors at the pulmonary hilum. Strahlenther Onkol 186:274–279
Siva S, MacManus M, Ball D (2010) Stereotactic radiotherapy for pulmonary oligometastases: a systematic review. J Thorac Oncol 5:1091–1099
Ohtakara K, Hayashi S, Mizuta K et al (2012) Clinical outcomes of single or oligo-fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for head and neck tumors using micromultileaf collimator-based dynamic conformal arcs. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 138:1511–1522
Lagerwaard FJ, Van Sornsen de Koste JR, Nijssen-Visser MR et al (2001) Multiple “slow” CT scans for incorporating lung tumor mobility in radiotherapy planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 51:932–937
Timmerman R, Galvin J, Michalski J et al (2006) Accreditation and quality assurance for radiation therapy oncology group: multicenter clinical trials using stereotactic body radiation therapy in lung cancer. Acta Oncol 45:779–786
Timmerman RD (2008) An overview of hypofractionation and introduction to this issue of seminars in radiation oncology. Semin Radiat Oncol 18:215–222
Bentzen SM, Constine LS, Deasy JO et al (2010) Quantitative analyses of normal tissue effects in the clinic (QUANTEC): an introduction to the scientific issues. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76:S3–S9
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247
Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program (2003) Common terminology criteria for adverse events VB, MD, National Cancer Institute
Feuvret L, Noel G, Mazeron JJ, Bey P (2006) Conformity index: a review. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:333–342
Paddick I (2000) A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans. Technical note. J Neurosurg 93:219–222
Casamassima F, Livi L, Masciullo S et al (2012) Stereotactic radiotherapy for adrenal gland metastases: university of Florence experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 82:919–923
Milano MT, Katz AW, Schell MC et al (2008) Descriptive analysis of oligometastatic lesions treated with curative-intent stereotactic body radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 72:1516–1522
Rusthoven KE, Kavanagh BD, Burri SH et al (2009) Multi-institutional phase I/II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for lung metastases. J Clin Oncol 27:1579–1584
Chi A, Jang SY, Welsh JS et al (2011) Feasibility of helical tomotherapy in stereotactic body radiation therapy for centrally located early stage nonsmall-cell lung cancer or lung metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:856–862
Iwata H, Shibamoto Y, Baba F et al (2011) Correlation between the serum KL-6 level and the grade of radiation pneumonitis after stereotactic body radiotherapy for stage I lung cancer or small lung metastasis. Radiother Oncol 101(267–270):22
Fumagalli I, Bibault JE, Dewas S et al (2012) A single-institution study of stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with unresectable visceral pulmonary or hepatic oligometastases. Radiat Oncol 7:164
Engels B, Gevaert T, Everaert H et al (2012) Phase II study of helical tomotherapy in the multidisciplinary treatment of oligometastatic colorectal cancer. Radiat Oncol 7:34
Verellen D, De Ridder M, Linthout N et al (2007) Innovations in image-guided radiotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 7:949–960
Engels B, Everaert H, Gevaert T et al (2011) Phase II study of helical tomotherapy for oligometastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol 22:362–368
Langenhoff BS, Oyen WJ, Jager GJ et al (2002) Efficacy of fluorine-18-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography in detecting tumor recurrence after local ablative therapy for liver metastases: a prospective study. J Clin Oncol 20:4453–4458
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sole, C.V., Lopez Guerra, J.L., Matute, R. et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy delivered by image-guided helical tomotherapy for extracranial oligometastases. Clin Transl Oncol 15, 484–491 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-012-0956-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-012-0956-2