Abstract
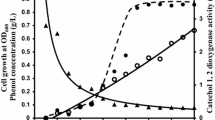
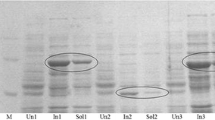
Catechol 1,2-dioxygenase (C12O) was purified to electrophoretic homogeneity from Acinetobacter sp. DS002. The pure enzyme appears to be a homodimer with a molecular mass of 66 kDa. The apparent Km and Vmax for intradiol cleavage of catechol were 1.58 μM and 2 units per mg of protein respectively. Unlike other C12Os reported in the literature, the catechol 1,2-dioxygenase of Acinetobacter showed neither intradiol nor extradiol cleavage activity when substituted catechols were used as substrates. However, it has shown mild intradiol cleavage activity when benzenetriol was used as substrate. As determined by two dimensional electrophoresis (2DE) followed MALDI-TOF/TOF analyses and gel permeation chromatography, no isoforms of C12O was observed in Acinetobacter sp. DS002. Further, the C12O was seen only in cultures grown in benzoate and it was completely absent in succinate grown cultures. Based on the sequence information obtained from MS/MS data, degenerate primers were designed to amplify catA gene from the genomic DNA of Acinetobacter sp. DS002. The sequence of the PCR amplicon and deduced amino acid sequence showed 97% similarity with a catA gene of Acinetobacter baumannii AYE (YP_001713609).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warhurst M, Fewson CA (1994) Biotransformations catalyzed by the genus Rhodococcus. Crit Rev Biotechnol 14:29–73
Bouwer EJ, Zehnder AJB (1993) Bioremediation of organic compounds—putting microbial metabolism to work. Trends Biotechnol 11:360–367
Williams PA, Sayer JR (1994) The evolution of pathways for aromatic hydrocarbon oxidation in Pseudomonas. Biodegradation 5:195–217
Houghton JE, Shanley MS (1994) Catabolic potential of Pseudomonads: a regulatory perspective. In: Chaudhry GR (ed) Biological degradation and bioremediation of toxic chemicals. Dioscorides Press, Portland, pp 11–32
Johnson BF, Stanier RY (1971) Dissimilation of aromatic compounds by Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Bacteriol 107:468–475
Hayaishi O, Katagiri M, Rothberg S (1957) Studies on oxygenases: pyrocatechase. J Biol Chem 229:905–9207
Patel RN, Hou CT, Felix A, Lillard MO (1976) Catechol 1,2-dioxygenase from Acinetobacter calcoaceticus: purification and properties. J Bacteriol 127:536–544
Aoki K, Konohana T, Shinke R, Nishira H (1984) Purification and characterization of catechol 1,2-dioxygenase from aniline-assimilating Rhodococcus erythropolis AN- 13. Agric Biol Chem 48:2087–2095
Aoki K, Konohana T, Shinke R, Nishira H (1984) Two catechol 1,2-dioxygenases from aniline-assimilating bacterium, Frateuria species ANA-18. Agric Biol Chem 48:2097–2104
Dorn E, Knackmuss HJ (1978) Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds: two catechol 1,2-dioxygenases from a 3- chlorobenzoate grown pseudomonad. Biochem J 174:73–84
Fujiwara M, Golovleva LA, Saeki Y, Nozaki M, Hayaishi O (1975) Extradiol cleavage of 3-substituted catechols by an intradiol dioxygenase, pyrocatechase, from a pseudomonad. J Biol Chem 250:4848–4855
Suresh BP, Purushotham G, Pijari AB, Krovidi RK, Baru R, Yanamandra M, Merrick M, Siddavattam D (2006) Biodegradation of methyl parathion and p-nitrophenol: evidence for the presence of a p-nitrophenol 2–hydroxylase in a Gram negative Serratia sp. strain DS001. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:1452–1462
Briganti Fabrizio, Pessione Enrica, Giunta Carlo, Scozzafava Andrea (1997) Purification, biochemical properties and substrate specificity of a catechol 1,2-dioxygenase from a phenol degrading Acinetobacter radioresistens. FEBS Lett 416:61–6414
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 772:248–254
Stothard P (2000) The sequence manipulation suite: JavaScript programs for analyzing and formatting protein and DNA sequences. Biotechniques 28:1102–1104
Strachan PD, Freer AA, Fewson CA (1998) Purification and characterization of catechol 1,2-dioxygenase from Rhodococcus rhodochrous NCIMB 13259 and cloning and sequencing of its catA gene. Biochem J 333(3):741–747
Ridder L, Briganti F, Boersma MG, Boeren S, Vis EH, Scozzafava A, Veeger C, Rietjens IMCM (1998) Quantitative structure/activity relationship for the rate of conversion of C4-substituted catechols by catechol 1,2-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) C1. Eur J Biochem 257:92–100
Wang C, You S, Wang S (2006) Purification and characterization of a novel catechol 1,2-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa with benzoic acid as a carbon source. Proc Biochem 41:1594–1601
Briganti F, Pessione E, Giunta C, Mazzoli R, Scozzafava A (2000) Purification and catalytic properties of two catechol 1,2-dioxygenase isozymes from benzoate grown cells of Acinetobacter radioresistens. J Protein Chem 19:709–716
Murakami S, Wang CL, Naito A, Shinke R, Aoki K (1998) Purification and characterization of four catechol 1,2-dioxygenase isozymes from the benzamide assimilating bacterium Arthrobacter species BA-5–17. Microbiol Res 153(2):163–171
Nakai C, Kagamiyama H, Saeki Y, Nozaki M (1979) Nonidentical subunits of pyrocatechase from Pseudomonas arvilla C-1. Arch Biochem Biophys 195:12–22
Canovas JL, Stanier RY (1967) Regulation of the enzymes of the β-ketoadipate pathway in Moraxella calcoaceticus. Eur J Biochem 1:289–300
Ornston LN (1971) Regulation of catabolic pathways in Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev 35:87–116
Acknowledgments
PEVP is a recipient of Senior Research Fellowship (SRF) from Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi. Research work in the laboratory of DS is supported by Dept. of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. of India and CSIR, New Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandeeti, E.V.P., Siddavattam, D. Purification and Characterization of Catechol 1,2-Dioxygenase from Acinetobacter sp. DS002 and Cloning, Sequencing of Partial catA Gene. Indian J Microbiol 51, 312–318 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-011-0123-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-011-0123-4