Abstract
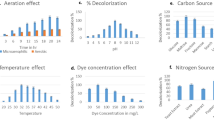
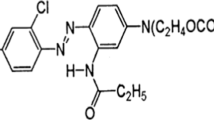
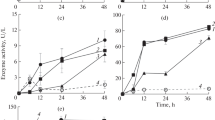
A high exhaust reactive dye, Green HE4B (GHE4B) was 98% degraded in nutrient medium by Pseudomonas desmolyticum NCIM 2112 (pd2112) within 72 h at static condition. Decolorization time in synthetic 10 g/l molasses. Addition of 5 g/l peptone to NaCl medium had reduced decolorization time from 108 to 72 h. Beef extract do not contribute more to the inducing effect of peptone, however it is a good co-substrate in sucrose or urea containing NaCl medium. Intracellular lignin peroxidase (Lip), laccase and tyrosinase activities were induced by 150, 355 and 212%, respectively till maximum dye removal took place. Aminopyrine N-demethylase (AND) and dichlorophenol indophenol reductase (DCIP-reductase) activities in pd2112 were induced by 130 and 20%, respectively at 72 h of incubation during GHE4B decolorization. By high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis, 4-hydroxybenzene sulfonic acid and 4-amino, 6-hydroxynaphthalene 2-sulfonic acids were identified as metabolites formed during 24–72 h incubation. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis supports the formation of these aromatic amines. pd2112, aerobically degraded GHE4B metabolites (formed at static condition) showing stationary phase of 6 days. There was no germination inhibition of Sorghum bicolor and Triticum aestivum by GHE4B metabolites at 3,000 ppm concentration however untreated dye showed germination inhibition at the same concentration. GHE4B metabolites did not show any microbial toxicity at 10,000 ppm concentration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pearce CI, Lloyd JR and Guthrie JT (2003) The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: a review. Dyes Pigments 58:179–196
Grover IS, Kaur A and Mahajan RK (1996) Mutagenicity of some dye effluents. Nat Aca Sci Lett India 19:149–158
Jadhav SU, Kalme SD and Govindwar SP (2008) Biodegradation of Methyl red by Galactomyces geotrichum MTCC 1360. Inter Biodete Biodeg 62:135–142
Moosvi S, Kcharia H and Madamwar D (2005) Decolorization of textile dye Reactive Violet 5 by a newly isolated bacterial consortium RVM 11.1. W J Microiol Biotechnol 21: 667–672
Supaka N, Juntongjin K, Damronglerd S, Delia M and Strehaiano P (2004) Microbial decolorization of reactive azo dyes in a sequential anaerobic-aerobic system. Chem Eng J 99:169–176
Kalme SD, Parshetti GK, Jadhav SU and Govindwar SP (2007) Biodegradation of benzidine based dye Direct Blue-6 by Pseudomonas desmolyticum NCIM 2112. Biores Technol 98:1405–1410
American Public Health Association (1995) Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater. 19th edition, APHA, AWWA and WPCF, Washington, DC, USA
Saratale GD, Kalme SD and Govindwar SP (2006) Decolorization of textile dyes by Aspergillus ochraceus. Ind J Biotechnol 5:407–410
Kalme S, Ghodake G and Govindwar S (2007) Red HE7B degradation using desulfonation by Pseudomonas desmolyticum NCIM 2112. Int Biodet Biodeg 60:327–333
Kalme S (2006) Role of microbes in biotransformation of chemicals, Ph.D. Thesis, Shivaji University, Kolhapur, India, pp 47
Hatvani N and Mecs I (2001) Production of laccase and manganese peroxidase by Lentinus edodes on malt containing by product of the brewing process. Process Biochem 37: 491–496
Zhang X and Flurkey W (1997) Phenoloxidases in Portabella mushrooms. J Food Sci 62:97–100
Kalme SD, Parshetti GK, Gomare SS and Govindwar SP (2008) Diesel and Kerosene degradation by diesel and kerosene degradation by Pseudomonas desmolyticum NCIM 2112 and Nocardia hydrocarbonoxydans NCIM 2386. Curr Microbiol 56:581–586
Parshetti G, Kalme S, Saratale G and Govindwar S (2006) Biodegradation of malachite green by Kocuria rosea MTCC 1532. Acta Chim Slov 53:492–498
Nicholas DJD and Fisher DJ (1960) Nitrogen fixation in extracts of Azotobacter vinelandii. Nature 186:735–736
Dean SM, Jin Y, Cha DK, Wilson SV and Radosevich M (2001) Phenanthrene degradation in soils co-inoculated with phenanthrene-degrading and biosurfactant-producing bacteria. J Environ Qual 30:1126–1133
Jadhav SU, Jadhav UU, Dawkar W and Govindwar SP (2008) Biodegradation of Disperse Dye Brown 3REL by 14. microbial consortium of Galactomyces geotrichum MTCC 1360 and Bacillus sp. VUS. Biotechnol Biopro Engg 13:232–239
Lee TH, Aoki H, Sugano Y and Shoda M (2000) Effect of molasses on the production and activity of dye-decolorizing peroxidase from Geotrichum candidum Dec l. J Biosci Bioeng 89:545–549
Dong X, Zhou J and Liu Y (2003) Peptone-induced biodecolorization of Reactive Brilliant Blue (KN-R) by Rhodocyclus gelatinosus XL-1. Process Biochem 39:89–94
Kalyani DC, Patil PS, Jadhav JP and Govindwar SP (2008) Biodegradation of reactive textile dye Red BLI by an isolated bacterium Pseudomonas sp. SUK1. Biores Technol 99:4635–4641
Nachiyar CV and Rajkumar GS (2003) Degradation of a tannery and textile dye, Navitan Fast Blue S5R by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. W J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:609–614
Yuri L, Park C, Lee B, Han E-J, Kim T-H, Lee J and Kim S (2006) Effect of nutrients on the production of extracellular enzymes for decolorization of Reactive Blue 19 and Reactive Black 5. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:226–231
McMahon AM, Doyle EM, Brooks S and O’Connor KE (2007) Biochemical characterisation of the coexisting tyrosinase and laccase in the soil bacterium Pseudomonas putida F6. Enz Microb Technol 40:1435–1441
Kandelbauer A, Erlacher A, Cavaco-Paulo A and Guebitz G (2004) Laccase-catalyzed decolorization of the synthetic azo dye Diamond Black PV 200 and of some structurally related derivatives. Biocat Biotrans 22:331–339
Maier J, Kandelbauer A, Erlacher A, Cavaco-Paulo A and Gübitz G (2004) A new alkali-thermostable azoreductase from Bacillus sp. strain SF. Appl Env Microbiol 70: 837–844
Kneifel H, Elmendorff K, Hegewald E and Soeder CJ (1997) Biotransformation of 1-naphthalenesulfonic acid by the green alga Scenedesmus obliquus. Arch Microbiol 167:32–37
Ekiei P, Leupold G and Parlar H (2001) Degradability of selected azo dye metabolite in activated sludge systems. Chemosphere 44:721–728
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalme, S.D., Jadhav, S.U., Parshetti, G.K. et al. Biodegradation of Green HE4B: Co-substrate effect, biotransformation enzymes and metabolite toxicity analysis. Indian J Microbiol 50, 156–164 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-010-0001-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-010-0001-5