Abstract
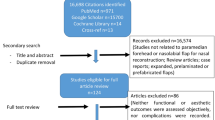
The nose is a key aesthetic element of face. Nasal defect reconstruction by forehead flap has been done since ancient times. The aim of this study is to review our experience of the outcomes of two- stage paramedian forehead flap in nasal defects of various aetiologies in the local population. This prospective study was done from January 2020 to December 2022 in the Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at SMS Medical College and Hospital. A total of 29 patients were included in this study who were candidates for a forehead flap for nose reconstruction due to any aetiology. After informed and written consent, two- stage paramedian forehead flap was done and patients were followed up to 6 months for analysis of outcomes. 29 participants were included in the study. Age range was 18–72 years (mean age 38.5 ± 16.78). 21 (72.4%) were male and 8 (27.6%) were female.23 (79.3%) patients had multiple subunit involvement, 4 (13.8%) patients had single subunit defect and 2 (6.9%) had total nasal defect. Most common aetiology was trauma (58.7%). Early complications including flap and donor site healing related complications were present in 8 (27.5%) patients. Delayed complications were grouped into cosmetic and functional complications and were seen in 22 (75.8%) patients. Cosmetic dissatisfaction was high with the two- stage paramedian forehead flap. Forehead flap is an established gold standard reconstructive option for nasal defects. In a two stage paramedian forehead flap, flap and donor site related issues are minor but cosmetic dissatisfaction is high. With some additional stages, satisfaction among patients increases significantly.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Samuel B (2021) Determination of soft tissue thickness of face for facial reconstruction–an autopsy study. J Evol Med Dent Sci 10(37):3267–3271
Burget GC, Menick FJ (1985) The subunit principle in nasal reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 76:239–247
Ang TW, Juniat V, O’Rourke M et al (2023) The use of the paramedian forehead flap alone or in combination with other techniques in the reconstruction of periocular defects and orbital exenterations. Eye 37:560–565
Ribeiro RDA, Pagotto VPF, Takahashi GG, Tutihashi RMC, Camargo CP, Busnardo FF, Gemperli R (2022) Paramedian forehead flap in the treatment of nasal, non-melanoma skin cancer: a cross-sectional study. Rev Col Bras Cir 2:49
Rohrich RJ, Griffin JR, Ansari M, Beran SJ, Potter JK (2004) Nasal reconstruction–beyond aesthetic subunits: a 15-year review of 1334 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 114(6):1405-16–1417-19
Cerci F, Kubo E (2020) Nasal reconstruction after Mohs micrographic surgery: analysis of 208 cases. Surg Cosmet Dermatol 12:42–50
Schmidt C, Nightingale J, Ioannou C, Grigg R (2021) Forehead flap nasal reconstruction: oncologic and functional outcomes in a regional centre. Aust J Otolaryngol 4:30
Ibrahim A, Ijekeye FO, Asuku ME (2014) Experience with a two-stage nasal reconstruction with the paramedian forehead flap. Niger J Plast Surg 10:21–23
Thornton JF (2013) A note on surgical revisions. Semin Plast Surg 27(2):126
Correa BJ, Weathers WM, Wolfswinkel EM, Thornton JF (2013) The forehead flap: the gold standard of nasal soft tissue reconstruction. Semin Plast Surg 27(2):96–103
Boyd CM, Baker SR, Fader DJ, Wang TS, Johnson TM (2000) The forehead flap for nasal reconstruction. Arch Dermatol 136(11):1365–1370
Schreiber NT, Mobley SR (2011) Elegant solutions for complex paramedian forehead flap reconstruction. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 19:465–479
Quatela VC, Sherris DA, Rounds MF (1995) Esthetic refinements in forehead flap nasal reconstruction. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 121(10):1106–1113
Garg S, Dahiya N, Gupta S (2014) Surgical scar revision: an overview. J Cutan Aesthet Surg 7(1):3–13
Riyat H, Touil LL, Briggs M, Shokrollahi K (2017) Autologous fat grafting for scars, healing and pain: a review. Scars Burn Heal 18(3):2059513117728200
Ibrahim SM, Saudi WM, Abozeid MF, Elsaie ML (2019) Early fractional carbon dioxide laser intervention for postsurgical scars in skin of color. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 4(12):29–34
Oleck NC, Hernandez JA, Cason RW, Glener AD, Shammas RL, Avashia YJ, Marcus JR (2021) Two or three? Approaches to staging of the paramedian forehead flap for nasal reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 9(5):e3591
Hsiao Y-C, Chang C-S, Zelken J (2017) Aesthetic refinements in forehead flap reconstruction of the Asian nose. Plast Surg 25(2):71–77
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None to disclose.
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval was provided by institutional ethical committee.
Informed Consent
Written and informed consent taken from the patients in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khushalani, A., Thakurani, S. & Garg, P. Outcome Analysis of Two-Stage Paramedian Forehead Flap for Nasal Defects Reconstruction in Local Population: Experience of 3 Years at Our Center. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 76, 559–566 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-04212-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-04212-3