Abstract
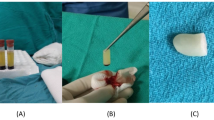
Being rich in growth factors platelet rich fibrin (PRF) has been used for decades for its healing properties in cosmetic surgeries but its use in transcanal myringoplasty is a novel approach that remains unexplored. In todays era of minimally invasive surgery not only does it provide as a great alternative to conventional myringoplasty but also outshines it. It reduces post operative pain, hospital stay and unlike the conventional technique that uses termporalis fascia as a graft material, PRF myringoplasty if required can be reperformed on the same patient multiple times with minimal risk. This procedure comes as a boon for patients with recurrent graft defects because after multiple revision surgeries, temporalis fascia can be deficient and other graft materials like cartilage/perichondrium or fascia lata etc. have to be harvested surgically for myringoplasty. In PRF myringoplasty there is no upper limit in the number of times the PRF membrane can be made and also it does not entail any surgical incision for graft harvest. A prospective study involving 41 patients was conducted at Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose Medical College, Jabalpur where in the tympanic membrane perforations were repaired using PRF membrane with a successful outcome in 85.4% of the patients included in this study.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seddik Abd El-Gelil A, Mohamed Dawod Y (2020) Effect of platelet rich plasma-enriched gelfoam on chronic tympanic membrane perforation. Al-Azhar Med J 49(1):173–180
Kumar RD (2019) Application of platelet rich fibrin matrix to repair traumatic tympanic membrane perforations: a pilot study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71(2):1126–1134
Sinkkonen ST, Jero J, Aarnisalo AA (2014) Tympanic membrane perforation. Duodecim; laaketieteellinen aikakauskirja 130(8):810–818
Amoils CP, Jackler RK, Lustig LR (1992) Repair of chronic tympanic membrane perforations using epidermal growth factor. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 107(5):669–683
Imamoglu M, Isik AU, Acuner O, Harova G, Bahadir O (1998) Fat-plug and paper-patch myringoplasty in rats. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 27(6):318
Zaman A, Omar S (2019) Myringoplasty using temporalis fascia and its clinical outcome. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 5(6):1539
Ringenberg JC (1962) Fat graft tympanoplasty. Laryngoscope 72(2):188–192
Mitchell RB, Pereira KD, Lazar RH (1997) Fat graft myringoplasty in children—a safe and successful day-stay procedure. J Laryngol Otol 111(2):106–108
Landsberg R, Fishman G, DeRowe A, Berco E, Berger G (2006) Fat graft myringoplasty: results of a long-term follow-up. J Otolaryngol 35(1):44–47
Golz A, Goldenberg D, Netzer A, Fradis M, Westerman ST, Westerman LM, Joachims HZ (2003) Paper patching for chronic tympanic membrane perforations. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128(4):565–570
Dursun E, Dogru S, Gungor A, Cincik H, Poyrazoglu E, Ozdemir T (2008) Comparison of paper-patch, fat, and perichondrium myringoplasty in repair of small tympanic membrane perforations. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 138(3):353–356
Puterman M, Leiberman A (2005) Gelfoam plug tympanostomy concomitant with removal of retained ventilation tubes. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 69:57–60
Lou ZC, He JG (2011) A randomised controlled trial comparing spon- taneous healing, gelfoam patching and edge-approximation plus gelfoam patching in traumatic tympanic membrane perforation with inverted or everted edges. Clin Otolaryngol 36:221–226
Park MK, Kim KH, Lee JD, Lee BD (2011) Repair of large traumatic tympanic membrane perforation with a Steri-strips patch. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 145:581–585
Choukroun J, Adda F, Schoeffler C, Vervelle A (2001) Une opportunité en paro-implantologie: le PRF. Implantodontie 42:55–62
Dohan DM, Choukroun J, Diss A, Dohan SL, Dohan AJ, Mouhyi J et al (2006) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part II: Platelet-related biologic features. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 101:e45–e50
Dohan DM, Rasmusson L, Albrektsson T (2009) Classification of plate- let concentrates from pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol 27:158–167
Tang XB, Dong PL, Wang J, Zhou HY, Zhang HX, Wang SZ (2015) Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on the chondrogenic differentiation of rabbit adipose-derived stem cells in vitro. Exp Therap Med 10(2):477–483
Gür ÖE, Ensari N, Öztürk MT, Boztepe OF, Gün T, Selçuk ÖT, Renda L (2016) Use of a platelet-rich fibrin membrane to repair traumatic tympanic membrane perforations: a comparative study. Acta Oto-laryngol 136(10):1017–1023
Sengupta A, Basak B, Ghosh D, Basu D, Adhikari D, Maity K (2012) A study on outcome of underlay, overlay and combined techniques of myringoplasty. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 64(1):63–66
Nair NP, Alexander A, Abhishekh B, Hegde JS, Ganesan S, Saxena SK (2019) Safety and efficacy of autologous platelet-rich fibrin on graft uptake in myringoplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 23(01):077–082
Habesoglu M, Oysu C, Sahin S, Sahin-Yilmaz A, Korkmaz D, Tosun A, Karaaslan A (2014) Platelet-rich fibrin plays a role on healing of acute-traumatic ear drum perforation. J Craniofac Surg 25(6):2056–2058
Garin P, Mullier F, Gheldof D, Dogne JM, Putz L, Van Damme JP (2014) Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): an autologous packing material for middle ear microsurgery. B-ENT 10(01):27–34
Sharma D, Mohindroo S, Azad RK (2018) Efficacy of platelet rich fibrin in myringoplasty. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 4:677–681
Karimi K, Rockwell H (2019) The benefits of platelet-rich fibrin. Facial Plast Surg Clin 27(3):331–340
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shukla, A., Kaurav, Y.S. & Vatsyayan, R. Novel Use of Platelet Rich Fibrin Membrane in Transcanal Myringoplasty: A Prospective Study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 72, 355–362 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-01851-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-01851-8