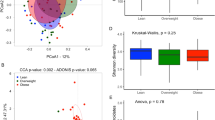
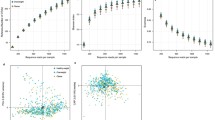
Abstract
Obesity is a consequence of a complex interplay between the host genome and the prevalent obesogenic factors among the modern communities. The role of gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of the disorder was recently discovered; however, 16S-rRNA-based surveys revealed compelling but community-specific data. Considering this, despite unique diets, dietary habits and an uprising trend in obesity, the Indian counterparts are poorly studied. Here, we report a comparative analysis and quantification of dominant gut microbiota of lean, normal, obese and surgically treated obese individuals of Indian origin. Representative gut microbial diversity was assessed by sequencing fecal 16S rRNA libraries for each group (n = 5) with a total of over 3000 sequences. We detected no evident trend in the distribution of the predominant bacterial phyla, Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes. At the genus level, the bacteria of genus Bacteroides were prominent among the obese individuals, which was further confirmed by qPCR (P < 0.05). In addition, a remarkably high archaeal density with elevated fecal SCFA levels was also noted in the obese group. On the contrary, the treated-obese individuals exhibited comparatively reduced Bacteroides and archaeal counts along with reduced fecal SCFAs. In conclusion, the study successfully identified a representative microbial diversity in the Indian subjects and demonstrated the prominence of certain bacterial groups in obese individuals; nevertheless, further studies are essential to understand their role in obesity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashelford KE, Chuzhanova NA, Fry JC, Jones AJ and Weightman AJ 2006 New screening software shows that most recent large 16S rRNA gene clone libraries contain chimeras. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72 5734–5741
Avgustin G, Wallace RJ and Flint HJ 1997 Phenotypic diversity among ruminal isolates of Prevotella ruminicola: proposal of Prevotella brevis sp. nov., Prevotella bryantii sp. nov. and Prevotella albensis sp. nov. and redefinition of Prevotella ruminicola. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47 284–288
Backhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, Semenkovich CF and Gordon JI 2004 The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101 15718–15723
Balamurugan R, Chittaranjan SP, Chandragunasekaran AM and Ramakrishna BS 2009 Molecular detection of the ruminal bacterium, Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens, in feces from rural residences of Southern India.. Microb. Ecolo. Health Dis. 21 38–43
Ben-Dov E, Shapiro OH, Siboni N and Kushmaro A 2006 Advantage of using inosine at the 3' termini of 16S rRNA gene universal primers for the study of microbial diversity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72 6902–6906
Choban PS, Jackson B, Poplawski S and Bistolarides P 2002 Bariatric surgery for morbid obesity: why, who, when, how, where, and then what?. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 69 897–903
Cole JR, Chai B, Farris RJ, Wang Q, Kulam SA, McGarrell DM, Garrity GM and Tiedje JM 2005 The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP-II): sequences and tools for high-throughput rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 33 D294–D296
Collado MC, Isolauri E, Laitinen K and Salminen S 2008 Distinct composition of gut microbiota during pregnancy in overweight and normal-weight women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 88 894–899
Cummings DE and Schwartz MW 2003 Genetics and pathophysiology of human obesity. Annu. Rev. Med. 54 453–471
Deepa M, Farooq S, Deepa R, Manjula D and Mohan V 2009 Prevalence and significance of generalized and central body obesity in an urban Asian Indian population in Chennai, India (CURES: 47). Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 63 259–267
DeSantis TZ, Jr., Hugenholtz P, Keller K, Brodie EL, Larsen N, Piceno YM, Phan R and Andersen GL 2006 NAST: a multiple sequence alignment server for comparative analysis of 16S rRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 34 W394-W399
Duncan SH, Lobley GE, Holtrop G, Ince J, Johnstone AM, Louis P and Flint HJ 2008 Human colonic microbiota associated with diet, obesity and weight loss. Int. J. Obes. (London) 32 1720–1724
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M, Gill SR, Nelson KE and Relman DA 2005 Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308 1635–1638
Einen J, Thorseth IH and Ovreas L 2008 Enumeration of Archaea and Bacteria in seafloor basalt using real-time quantitative PCR and fluorescence microscopy. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 282 182–187
Ewing B, Hillier L, Wendl MC and Green P 1998 Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res. 8 175–185
Fierer N, Jackson JA, Vilgalys R and Jackson RB 2005 Assessment of soil microbial community structure by use of taxon-specific quantitative PCR assays. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71 4117–4120
Flint HJ, Bayer EA, Rincon MT, Lamed R and White BA 2008 Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6 121–131
Flint HJ, Duncan SH, Scott KP and Louis P 2007 Interactions and competition within the microbial community of the human colon: links between diet and health. Environ. Microbiol. 9 1101–1111
Haslam DW and James WP 2005 Obesity. Lancet 366 1197–1209
Hill JO and Peters JC 1998 Environmental contributions to the obesity epidemic. Science 280 1371–1374
Huycke MM and Gaskins HR 2004 Commensal bacteria, redox stress, and colorectal cancer: mechanisms and models. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood. ) 229 586–597
Langer FB, Reza Hoda MA, Bohdjalian A, Felberbauer FX, Zacherl J, Wenzl E, Schindler K, Luger A, Ludvik B and Prager G 2005 Sleeve gastrectomy and gastric banding: effects on plasma ghrelin levels. Obes. Surg. 15 1024–1029
Layton A, McKay L, Williams D, Garrett V, Gentry R and Sayler G 2006 Development of Bacteroides 16S rRNA gene TaqMan-based real-time PCR assays for estimation of total, human, and bovine fecal pollution in water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72 4214–4224
Ley RE, Backhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD and Gordon JI 2005 Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102 11070–11075
Ley RE, Hamady M, Lozupone C, Turnbaugh PJ, Ramey RR, Bircher JS, Schlegel ML, Tucker TA, Schrenzel MD, Knight R and Gordon JI 2008 Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 320 1647–1651
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S and Gordon JI 2006 Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 444 1022–1023
Lintsi M, Kaarma H and Kull I 2004 Comparison of hand-to-hand bioimpedance and anthropometry equations versus dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for the assessment of body fat percentage in 17–18-year-old conscripts. Clin. Physiol Funct. Imaging 24 85–90
Lozupone C and Knight R 2005 UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71 8228–8235
Lucke K, Miehlke S, Jacobs E and Schuppler M 2006 Prevalence of Bacteroides and Prevotella spp. in ulcerative colitis. J. Med. Microbiol. 55 617–624
Murphy KG and Bloom SR 2006 Gut hormones and the regulation of energy homeostasis. Nature 444 854–859
Nadal I, Santacruz A, Marcos A, Warnberg J, Garagorri M, Moreno LA, Martin-Matillas M, Campoy C, et al. 2009 Shifts in clostridia, bacteroides and immunoglobulin-coating fecal bacteria associated with weight loss in obese adolescents. Int. J. Obes. (Lond) 33 758–767
Noverr MC and Huffnagle GB 2004 Does the microbiota regulate immune responses outside the gut? Trends Microbiol. 12 562–568
Raghavachari TN S 1961 Cow dung and Insanitary Flooring. JAMA 178 680
Rakoff-Nahoum S, Paglino J, Eslami-Varzaneh F, Edberg S and Medzhitov R 2004 Recognition of commensal microflora by toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell 118 229–241
Rautava S and Isolauri E 2002 The development of gut immune responses and gut microbiota: effects of probiotics in prevention and treatment of allergic disease. Curr. Iss. Intest. Microbiol. 3 15–22
Roesch LF, Lorca GL, Casella G, Giongo A, Naranjo A, Pionzio AM, Li N, Mai V, et al. 2009 Culture-independent identification of gut bacteria correlated with the onset of diabetes in a rat model. ISME J. 3 536–548
Romualdi C, Bortoluzzi S, D'Alessi F and Danieli GA 2003 IDEG6: a web tool for detection of differentially expressed genes in multiple tag sampling experiments. Physiol Genomics 12 159–162
Samuel BS and Gordon JI 2006 A humanized gnotobiotic mouse model of host-archaeal-bacterial mutualism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 103 10011–10016
Schloss PD and Handelsman J 2005 Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71 1501–1506
Schneider BE and Mun EC 2005 Surgical management of morbid obesity. Diabetes Care 28 475–480
Shamseddeen H, Getty JZ, Hamdallah IN and Ali MR 2011 Epidemiology and economic impact of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Surg. Clin. North Am. 91 1163–72, vii
Sinha R, Anderson DE, McDonald SS and Greenwald P 2003 Cancer risk and diet in India. J. Postgrad. Med. 49 222–228
Sokol H, Pigneur B, Watterlot L, Lakhdari O, Bermudez-Humaran LG, Gratadoux JJ, Blugeon S, Bridonneau C, et al. 2008 Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. US A 105 16731–16736
Stappenbeck TS, Hooper LV and Gordon JI 2002 Developmental regulation of intestinal angiogenesis by indigenous microbes via Paneth cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 15451–15455
Stevens CE and Hume ID 1998 Contributions of microbes in vertebrate gastrointestinal tract to production and conservation of nutrients. Physiol. Rev. 78 393–427
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M and Kumar S 2007 MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 24 1596–1599
Terranova L, Busetto L, Vestri A and Zappa MA 2012 Bariatric surgery: cost-effectiveness and budget impact. Obes. Surg. 22 646–653
Thompson D and Wolf AM 2001 The medical-care cost burden of obesity. Obes. Rev. 2 189–197
Turnbaugh PJ, Hamady M, Yatsunenko T, Cantarel BL, Duncan A, Ley RE, Sogin ML, Jones WJ, et al. 2009 A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 457 480–484
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER and Gordon JI 2006 An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444 1027–1031
Walker AW, Duncan SH, Leitch EC M, Child MW and Flint HJ 2005 pH and peptide supply can radically alter bacterial populations and short-chain fatty acid ratios within microbial communities from the human colon. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71 3692–3700
Wexler HM 2007 Bacteroides: the good, the bad and the nitty-gritty. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 20 593–621
Wood J, Scott KP, Avgustin G, Newbold CJ and Flint HJ 1998 Estimation of the relative abundance of different Bacteroides and Prevotella ribotypes in gut samples by restriction enzyme profiling of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA gene sequences. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64 3683–3689
Yost WM, Young JW, Schmidt SP and McGilliard AD 1977 Gluconeogenesis in ruminants: propionic acid production from a high-grain diet fed to cattle. J. Nutr. 107 2036–2043
Zhang H, DiBaise JK, Zuccolo A, Kudrna D, Braidotti M, Yu Y, Parameswaran P, Crowell MD, Wing R, Rittmann BE and Krajmalnik-Brown R 2009 Human gut microbiota in obesity and after gastric bypass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106 2365–2370
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the volunteers for their participation in the study. We also thank Ms Tulika M Jaokar for proofreading the manuscript. We also gratefully acknowledge the active support and encouragement provided by the former Director of National Centre for Cell Science (NCCS) Padmashree Dr GC Mishra.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Sudha Bhattacharya
MS received 12 March 2012; accepted 29 June 2012
Corresponding editor: sudha bhattacharya
[Patil DP, Dhotre DP, Chavan SG, Sultan A, Jain DS, Lanjekar VB, Gangawani J, Shah PS, Todkar JS, Shah S, Ranade DR, Patole MS and Shouche YS 2012 Molecular analysis of gut microbiota in obesity among Indian individuals. J. Biosci. 37 1–11] DOI
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, D.P., Dhotre, D.P., Chavan, S.G. et al. Molecular analysis of gut microbiota in obesity among Indian individuals. J Biosci 37, 647–657 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-012-9244-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-012-9244-0