Abstract
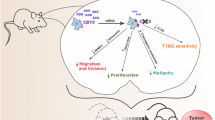
Glioblastomas (GBMs), the most common and lethal primary brain tumor, show inherent infiltrative nature and high molecular heterogeneity that make complete surgical resection unfeasible and unresponsive to conventional adjuvant therapy. Due to their fast growth rate even under hypoxic and acidic conditions, GBM cells can conserve the intracellular pH at physiological range by overexpressing membrane-bound carbonic anhydrases (CAs). The synthetic sulfonamide E7070 is a potent inhibitor of CAs that harbors putative anticancer properties; however, this drug has still not been tested in GBMs. The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of E7070 on CA9 and CA12 enzymes in GBM cells as well as in the tumor cell growth, migration, invasion, and resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. We found that E7070 treatment significantly reduced tumor cell growth and increased radio- and chemotherapy efficacy against GBM cells under hypoxia. Our data suggests that E7070 has therapeutic potential as a radio-chemo-sensitizing in drug-resistant GBMs, representing an attractive strategy to improve the adjuvant therapy. We showed that CA9 and CA12 represent potentially valuable therapeutic targets that should be further investigated as useful diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for GBM tailored therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are included within the article and additional files.
References
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJB, Janzer RC et al (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10:459–466
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WB et al (2016) The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Acta Neuropathol 131:803–820
Johannessen TCA, Bjerkvig R (2012) Molecular mechanisms of temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 12(5):635–642
Singh N, Miner A, Hennis L, Mittal S (2021) Mechanisms of temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma - a comprehensive review. Cancer Drug Resist 4:17–43
Kesari S (2011) Understanding glioblastoma tumor biology: the potential to improve current diagnosis and treatments. Semin Oncol 38(Suppl 4):S2-10
Soda Y, Myskiw C, Rommel A, Verma IM (2013) Mechanisms of neovascularization and resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies in glioblastoma multiforme. J Mol Med (Berl) 91(4):439–448
Ho IAW, Shim WSN (2017) Contribution of the microenvironmental niche to glioblastoma heterogeneity. Biomed Res Int 2017:9634172
Nejad AE, Najafgholian S, Rostami A, Sistani A, Shojaeifar S, Esparvarina M et al (2021) The role of hypoxia in the tumor microenvironment and development of cancer stem cell: a novel approach to developing treatment. Cancer Cell Int 21:62
Supuran CT (2018) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors as emerging agents for the treatment and imaging of hypoxic tumors. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 27:963–970
Haapasalo J, Nordfors K, Haapasalo H, Parkkila S (2020) The expression of carbonic anhydrases II, IX and XII in brain tumors. Cancers (Basel) 12(7):1723
Agnihotri S, Burrell KE, Wolf A, Jalali S, Hawkins C, Rutka JT et al (2013) Glioblastoma, a brief review of history, molecular genetics, animal models and novel therapeutic strategies. Arch Immunol Ther Exp 61:25–41
Muz B, de la Puente P, Azab F, Azab AK (2015) The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia (Auckl) 11(3):83–92
Uribe D, Torres Á, Rocha JD, Niechi I, Oyarzún C, Sobrevia L et al (2017) Multidrug resistance in glioblastoma stem-like cells: role of the hypoxic microenvironment and adenosine signaling. Mol Aspects Med 55:140–151
Angeli A, Carta F, Nocentini A, Winum J-Y, Zaluboskis R, Akdemir A et al (2020) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors targeting metabolism and tumor microenvironment. Metabolites 10(10):412
Wang B, Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Zheng Z, Liu S et al (2021) Targeting hypoxia in the tumor microenvironment: a potential strategy to improve cancer immunotherapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 40(1):24
Becker HM, Deitmer JW (2021) Proton transport in cancer cells: the role of carbonic anhydrases. Int J Mol Sci 22(6):3171
Swayampakula M, McDonald PC, Vallejo M, Coyaud E, Chafe SC, Westerback A et al (2017) The interactome of metabolic enzyme carbonic anhydrase IX reveals novel roles in tumor cell migration and invadopodia/MMP14-mediated invasion. Oncogene 36:6244–6261
Pastorekova S, Gillies RJ (2019) The role of carbonic anhydrase IX in cancer development: links to hypoxia, acidosis, and beyond. Cancer Metastasis Rev 38(1–2):65–77
Sedlakova O (2014) Carbonic anhydrase IX, a hypoxia-induced catalytic component of the pH regulating machinery in tumors. Front Physiol 4:400
Pastorek J, Pastorekova S, Zatovicova M (2008) Cancer-associated carbonic anhydrases and their inhibition. Curr Pharm Des 14:685–698
Haapasalo J, Hilvo M, Nordfors K et al (2008) Identification of an alternatively spliced isoform of carbonic anhydrase XII in diffusely infiltrating astrocytic gliomas. Neuro Oncol 10:131–138
Supuran CT (2008) Carbonic anhydrases–an overview. Curr Pharm Des 14:603–614
Said HM, Supuran CT, Hageman C, Staab A, Polat B, Katzer A et al (2010) Modulation of carbonic anhydrase 9 (CA9) in human brain cancer. Curr Pharm Des 16:3288–3299
Lou Y, McDonald PC, Oloumi A, Chia S, Ostlund AA, Kyle A et al (2011) Targeting tumor hypoxia: suppression of breast tumor growth and metastasis by novel carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors. Cancer Res 71:3364–3376
Scrideli CA, Carlotti CG, Okamoto OK, Andrade VS, Cortez MAA, Motta FJN et al (2008) Gene expression profile analysis of primary glioblastomas and non-neoplastic brain tissue: identification of potential target genes by oligonucleotide microarray and real-time quantitative PCR. J Neurooncol 88(3):281–291
Ameis HM, Drenckhan A, Freytag M, Izbicki JR, Supuran CT, Reinshagen K et al (2016) Influence of hypoxia-dependent factors on the progression of neuroblastoma. Pediatr Surg Int 32:187–192
McDonald PC, Chafe SC, Brown WS, Saberi S, Swayampakula GV, Nemirosvky O et al (2019) Regulation of pH by carbonic anhydrase 9 mediates survival of pancreatic cancer cells with activated KRAS in response to hypoxia. Gastroenterology 157:823–837
Pérez-Sayáns M, Suárez-Peñaranda JM, Pilar G-D, Supuran CT, Pastorekova S, Barros-Angueira F et al (2012) Expression of CA-IX is associated with advanced stage tumors and poor survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. J Oral Pathol Med 41:667–674
Hsieh M-J, Chen K-S, Chiou H-L, Hsieh Y-S (2010) Carbonic anhydrase XII promotes invasion and migration ability of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Eur J Cell Biol 89:598–606
Ilie M, Hofman V, Zangari J, Chiche J, Mouroux J, Mazure NM et al (2013) Response of CAIX and CAXII to in vitro re-oxygenation and clinical significance of the combined expression in NSCLC patients. Lung Cancer 82:16–23
Winum JY, Innocenti A, Nasr J, Montero J, Scozzafava A, Vullo D, Supuran C (2005) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: synthesis and inhibition of cytosolic/tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase isozymes I, II, IX, and XII with N-hydroxysulfamides - a new zinc-binding function in the design of inhibitors. Bioorganic Med Chem Lett 15:2353–2358
Kopecka J, Campia I, Jacobs A, Frei AP, Ghigo D, Wollscheid B et al (2015) Carbonic anhydrase XII is a new therapeutic target to overcome chemoresistance in cancer cells. Oncotarget 6:6776–6793
Supuran CT (2016) How many carbonic anhydrase inhibition mechanisms exist? J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 31:345–360
Said HM, Hagemann C, Carta F, Katzer A, Polat B, Staab A et al (2013) Hypoxia induced CA9 inhibitory targeting by two different sulfonamide derivatives including acetazolamide in human glioblastoma. Bioorg Med Chem 21:3949–3957
McDonald PC, Chia S, Bedard PL, Chu Q, Lyle M, Tang L et al (2020) A phase 1 study of SLC-0111, a novel inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase IX, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Am J Clin Oncol Cancer Clin Trials 43:484–490
Yamada Y, Yamamoto N, Shimoyama T, Horiike A, Fujisaka Y, Takayama K et al (2005) Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacogenomic study of E7070 administered once every 21 days. Cancer Sci 96:721–728
D’Ambrosio K, Vitale RM, Dogné JM, Masereel B, Innocenti A, Scozzafava A et al (2008) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: bioreductive nitro-containing sulfonamides with selectivity for targeting the tumor associated isoforms IX and XII. J Med Chem 51:3230–3237
Abbate F, Casini A, Owa T, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT (2004) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: E7070, a sulfonamide anticancer agent, potently inhibits cytosolic isozymes I and II, and transmembrane, tumor-associated isozyme IX. Bioorganic Med Chem Lett 14:217–223
Supuran CT (2008) Carbonic anhydrases: novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:168–181
Fukuoka K, Usuda J, Iwamoto Y, Fukumoto H, Nakamura T, Yoneda T et al (2001) Mechanisms of action of the novel sulfonamide anticancer agent E7070 on cell cycle progression in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Invest New Drugs 19:219–227
Franken N a P, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman J, van Bree C (2006) Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc 1:2315–2319
Tao Y, Zhang P, Frascogna V, Lecluse Y, Auperin A, Bourhis J et al (2007) Enhancement of radiation response by inhibition of Aurora-A kinase using siRNA or a selective Aurora kinase inhibitor PHA680632 in p53-deficient cancer cells. Br J Cancer 97:1664–1672
Agudelo-Garcia PA, Jesus JK De, Williams SP, Nowicki MO, Chiocca EA, Liyanarachchi S et al (2011) Glioma cell migration on three-dimensional nanofiber scaffolds is regulated by substrate topography and abolished by inhibition of STAT3 signaling. Neoplasia 13:831–840
Valente V, Teixeira SA, Neder L, Okamoto OK, Oba-Shinjo SM, Marie SKN et al (2009) Selection of suitable housekeeping genes for expression analysis in glioblastoma using quantitative RT-PCR. BMC Mol Biol 10:17
Ozawa Y, Sugi NH, Nagasu T, Owa T, Watanabe T, Koyanagi N et al (2001) E7070, a novel sulphonamide agent with potent antitumour activity in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Cancer 37:2275–2282
Hu B, Thirtamara-Rajamani KK, Sim H, Viapiano MS (2009) Fibulin-3 is uniquely upregulated in malignant gliomas and promotes tumor cell motility and invasion. Mol Cancer Res 7:1756–1770
Wan YW, Allen GI, Liu Z (2016) TCGA2STAT: simple TCGA data access for integrated statistical analysis in R. Bioinformatics 32:952–954
Chiche J, Ilc K, Laferrière J, Trottier E, Dayan F, Mazure NM et al (2009) Hypoxia-inducible carbonic anhydrase IX and XII promote tumor cell growth by counteracting acidosis through the regulation of the intracellular pH. Cancer Res 69:358–368
Mboge MY, McKenna RC, Frost S (2016) Advances in anti-cancer drug development targeting carbonic anhydrase IX and XII. Topics in Anti-Cancer Research 5:3–42
Zamanova S, Shabana AM, Mondal UK, Ilies MA (2019) Carbonic anhydrases as disease markers. Expert Opin Ther Pat 29(7):509–533
Neri D, Supuran CT (2011) Interfering with pH regulation in tumours as a therapeutic strategy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:767–777
Parks SK, Chiche J, Pouyssegur J (2011) pH control mechanisms of tumor survival and growth. J Cell Physiol 226:299–308
Ward C, Meehan J, Gray M, Kunkler IH, Langdon SP, Argyle DJ et al (2018) Carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX), cancer, and radiation responsiveness. Metabolites 8:1–13
Chiche J, Ricci JE, Pouysségur J (2013) Tumor hypoxia and metabolism - towards novel anticancer approaches. Ann Endocrinol 74:111–114
Gondi G, Mysliwietz J, Hulikova A, Jen JP, Swietach P, Kremmer E, Zeidler R (2013) Antitumor efficacy of a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the activity of cancer-associated carbonic anhydrase XII. Cancer Res 73:6494–6503
Conklin KA (2004) Chemotherapy-associated oxidative stress: impact on chemotherapeutic effectiveness. Integr Cancer Ther 3(4):294–300
Owa T, Yoshino H, Yoshimatsu K, Nagasu T (2001) Cell cycle regulation in the G1 phase: a promising target for the development of new chemotherapeutic anticancer agents. Curr Med Chem 8:1487–1503
Owa T, Yoshino H, Okauchi T, Okabe T, Ozawa Y, Hata Sugi N et al (2002) Synthesis and biological evaluation of N-(7-indolyl)-3-pyridinesulfonamide derivatives as potent antitumor agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 12:2097–2100
Ozawa Y, Kusano K, Owa T, Yokoi A, Asada A, Yoshimatsu K (2012) Therapeutic potential and molecular mechanism of a novel sulfonamide anticancer drug, indisulam (E7070) in combination with CPT-11 for cancer treatment. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 69:1353–1362
Baur M, Gneist M, Owa T, Dittrich C (2007) Clinical complete long-term remission of a patient with metastatic malignant melanoma under therapy with indisulam (E7070). Melanoma Res 17:329–331
Talbot DC, von Pawel J, Cattell E, Yule SM, Johnston C, Zandvliet AS et al (2007) A randomized phase II pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of indisulam as second-line therapy in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 13:1816–1822
Morris JC, Chiche J, Grellier C, Lopez M, Bornaghi LF, Maresca A et al (2011) Targeting hypoxic tumor cell viability with carbohydrate-based carbonic anhydrase IX and XII inhibitors. J Med Chem 54:6905–6918
Parkkila S, Rajaniemi H, Parkkila AK, Kivela J, Waheed A, Pastorekova S et al (2000) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor suppresses invasion of renal cancer cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:2220–2224
Ward C, Langdon SP, Mullen P, Harris A, Harrison D, Supuran C, Kunkler I (2013) New strategies for targeting the hypoxic tumour microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 39:171–179
Gieling R, Williams K (2013) Carbonic anhydrase IX as a target for metastatic disease. Bioorg Med Chem 21:1470–1476
Boyd NH, Walker K, Fried J, Hackney JR, McDonald GAB, Spina R et al (2017) Addition of carbonic anhydrase 9 inhibitor SLC-0111 to temozolomide treatment delays glioblastoma growth in vivo. JCI insight 2(24):e92928
Vartanian A, Singh SK, Agnihotri S, Jalali S, Burrell K, Aldape KD et al (2014) GBM’s multifaceted landscape: highlighting regional and microenvironmental heterogeneity. Neuro Oncol 16(9):1167–1175
Sethi KK, Verma SM, Tanç M, Purper G, Calafato G, Carta F, Supuran CT (2014) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: synthesis and inhibition of the human carbonic anhydrase isoforms I, II, IX and XII with benzene sulfonamides incorporating 4- and 3-nitrophthalimide moieties. Bioorganic Med Chem 22:1586–1595
Dubois L, Peeters SGJA, Van Kuijk SJA, Yaromina A, Lieuwes NG, Saraya R et al (2013) Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX by nitroimidazole based sulfamides enhances the therapeutic effect of tumor irradiation: a new concept of dual targeting drugs. Radiother Oncol 108:523–528
Andreucci E, Ruzzolini J, Peppicelli S, Bianchini AL, Carta F, Supuran CT, Calorini L (2019) The carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitor SLC-0111 sensitises cancer cells to conventional chemotherapy. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 34:117–123
McIntyre A, Patiar S, Wigfield S, Ledaki I, Turley H, Leek R et al (2012) Carbonic anhydrase IX promotes tumor growth and necrosis in vivo and inhibition enhances anti-VEGF therapy. Clin Cancer Res 18:3100–3111
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2013) The definition of primary and secondary glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 19:764–772
Stupp R, Dietrich PY, Kraljevic SO, Pica A, Maillard I, Maeder P et al (2002) Promising survival for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme treated with concomitant radiation plus temozolomide followed by adjuvant temozolomide. J Clin Oncol 20:1375–1382
Hegi ME, Diserens A-C, Gorlia T, Hamou M-F, de Tribolet N, Weller M et al (2005) MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:997–1003
Qiu ZK, Shen D, Chen YS, Yang QY, Guo CC, Feng BH et al (2014) Enhanced MGMT expression contributes to temozolomide resistance in glioma stem-like cells. Chin J Cancer 33:115–122
Boyd NH, Tran AN, Bernstock JD, Etminam T, Jones AB, Gillespie GY et al (2021) Glioma stem cells and their roles within the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Theranostics 11(2):665–683
Giannini C (2005) Patient tumor EGFR and PDGFRA gene amplifications retained in an invasive intracranial xenograft model of glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro Oncol 7:164–176
Gkogkou C, Frangia K, Saif MW, Trigidou R, Syrigos K (2014) Necrosis and apoptotic index as prognostic factors in non-small cell lung carcinoma: a review. Springerplus 3:120
Dittrich C, Zandvliet a S, Gneist M, Huitema AD, King AA, Wanders J (2007) A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of indisulam in combination with carboplatin. Br J Cancer 96:559–566
Assi R, Kantarjian HM, Kadia TM, Pemmaraju N, Jabbour E, Jain N et al (2018) Final results of a phase 2, open-label study of indisulam, idarubicin, and cytarabine in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Cancer 124:2758–2765
Kil WJ, Tofilon PJ, Camphausen K (2012) Post-radiation increase in VEGF enhances glioma cell motility in vitro. Radiat Oncol 7:25
Yano S, Miwa S, Mii S, Hiroshima Y, Uehara F, Yamamoto M et al (2014) Invading cancer cells are predominantly in G0/G1 resulting in chemoresistance demonstrated by real-time FUCCI imaging. Cell Cycle 13:953–960
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Dr. Aguinaldo Luiz Simões for providing the authentication of the cell lines. We thank Prof. Dr. Eduardo Magalhães Rego, Cleide Lúcia Araújo Silva, and Prajna Behera for providing animal assistance.
Funding
This research was supported by grants from The São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP), process numbers 2011/05957–6, 2011/07448–1, and 2014/08899–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Silvia A. Teixeira, Augusto F. Andrade, Julia A. Pezuk, and Veridiana K. Suazo designed, performed, and analyzed in vitro experiments. Silvia Teixeira, Augusto F. Andrade, Julia A. Pezuk, Mariano S. Viapiano, and Mohan S. Nandhu designed, and provided assistance with animal surgery and reagent preparation. Mariano S. Viapiano and Mohan S. Nandhu provided assistance to cell migration and radiotherapy experiments and orthotopic models. Aline P. Becker and Luciano Neder analyzed H&E slides. Lucas T. Bidinotto performed in silico analysis. The manuscript was written or reviewed by Silvia A. Teixeira, Augusto F. de Andrade, Mariano Sebastian Viapiano, Carlos G. Carlotti, Luiz G. Tone, and Carlos Alberto Scrideli. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All procedures involving animals were performed in accordance Institutional Commission of Ethics in Animal Research (CETEA) at the Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo (São Paulo, SP, Brazil) and Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees at Harvard Medical School/Brigham and Women's Hospital (HMA-IACUC—Boston, MA, USA). The study was carried out in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines.
Consent for Publication
All authors consent to the publication of current data.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 710 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teixeira, S.A., Viapiano, M.S., Andrade, A.F. et al. The Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor E7070 Sensitizes Glioblastoma Cells to Radio- and Chemotherapy and Reduces Tumor Growth . Mol Neurobiol 58, 4520–4534 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02437-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02437-3