Abstract
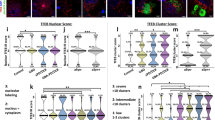
α-Synuclein (αSyn), the major constituent of Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites, is generally expressed in presynapses and is involved in synaptic function. However, we previously demonstrated that some neurons, including those in the olfactory bulb, show high αSyn expression levels in the cell body under normal conditions. αSyn is also known to be important for adult neurogenesis. Thus, in present study, we examined the role of αSyn in juxtaglomerular neurons (JGNs) with high αSyn expression in the mouse olfactory bulb. Most αSyn-enriched JGNs expressed sex-determining region Y-box 2 (Sox2), which functions to maintain neural immature identity. Interestingly, in αSyn homozygous (-/-) knockout (KO) mice, Sox2-positive JGNs were significantly increased compared with heterozygous (+/-) KO mice. Following global brain ischemia using wild-type mice, there was also a significant decrease in Sox2-positive JGNs, and in the co-expression ratio of Sox2 in αSyn-enriched JGNs. By contrast, the co-expression ratio of neuronal nuclei (NeuN, mature neuronal marker) was significantly increased in αSyn-enriched JGNs. However, this ischemia-induced decrease of Sox2-positive JGNs was not observed in αSyn homozygous KO mice. Overall, these data suggest that αSyn functions to promote the maturation of immature JGNs in the mouse olfactory bulb.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeliovich A, Schmitz Y, Farinas I, Choi-Lundberg D, Ho WH, Castillo PE, Shinsky N, Verdugo JM et al (2000) Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 25(1):239–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80886-7
Aungst JL, Heyward PM, Puche AC, Karnup SV, Hayar A, Szabo G, Shipley MT (2003) Centre-surround inhibition among olfactory bulb glomeruli. Nature 426(6967):623–629. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02185nature02185
Benito N, Gaborieau E, Sanz Diez A, Kosar S, Foucault L, Raineteau O, De Saint JD (2018) A pool of postnatally generated interneurons persists in an immature stage in the olfactory bulb. J Neurosci 38(46):9870–9882. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1216-18.2018JNEUROSCI.1216-18.2018
Boldrini M, Fulmore CA, Tartt AN, Simeon LR, Pavlova I, Poposka V, Rosoklija GB, Stankov A, Arango V, Dwork AJ, Hen R, Mann JJ (2018) Human hippocampal neurogenesis persists throughout aging. Cell Stem Cell 22 (4):589-599 e585. doi:S1934-5909(18)30121-8 [pii]10.1016/j.stem.2018.03.015
Bonfanti L, Nacher J (2012) New scenarios for neuronal structural plasticity in non-neurogenic brain parenchyma: the case of cortical layer II immature neurons. Prog Neurobiol 98(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.05.002S0301-0082(12)00069-X
Bylund M, Andersson E, Novitch BG, Muhr J (2003) Vertebrate neurogenesis is counteracted by Sox1-3 activity. Nat Neurosci 6(11):1162–1168. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1131nn1131
Dickson DW (2001) Alpha-synuclein and the Lewy body disorders. Curr Opin Neurol 14(4):423–432. https://doi.org/10.1097/00019052-200108000-00001
Doty RL (2012) Olfaction in Parkinson’s disease and related disorders. Neurobiol Dis 46(3):527–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2011.10.026S0969-9961(11)00358-5
Duda JE (2010) Olfactory system pathology as a model of Lewy neurodegenerative disease. J Neurol Sci 289(1-2):49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2009.08.042S0022-510X(09)00821-1
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, Gage FH (1998) Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 4(11):1313–1317. https://doi.org/10.1038/3305
Goedert M (2015) Neurodegeneration. Alzheimer’s and Parkinson's diseases: the prion concept in relation to assembled Abeta, tau, and alpha-synuclein. Science 349 (6248):1255555. doi:10.1126/science.12555551255555 [pii]349/6248/1255555
Graham V, Khudyakov J, Ellis P, Pevny L (2003) SOX2 functions to maintain neural progenitor identity. Neuron 39(5):749–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00497-5
Herrera DG, Robertson HA (1996) Activation of c-fos in the brain. Prog Neurobiol 50(2-3):83–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-0082(96)00021-4
Kim T, Mehta SL, Kaimal B, Lyons K, Dempsey RJ, Vemuganti R (2016) Poststroke induction of alpha-synuclein mediates ischemic brain damage. J Neurosci 36(26):7055–7065. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1241-16.201636/26/7055
Knoth R, Singec I, Ditter M, Pantazis G, Capetian P, Meyer RP, Horvat V, Volk B et al (2010) Murine features of neurogenesis in the human hippocampus across the lifespan from 0 to 100 years. PLoS One 5(1):e8809. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0008809
Kosaka T, Kosaka K (2011) “Interneurons” in the olfactory bulb revisited. Neurosci Res 69(2):93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2010.10.002S0168-0102(10)02814-2
Kosaka T, Kosaka K (2016) Neuronal organization of the main olfactory bulb revisited. Anat Sci Int 91(2):115–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-015-0309-710.1007/s12565-015-0309-7
Kosaka K, Toida K, Aika Y, Kosaka T (1998) How simple is the organization of the olfactory glomerulus?: the heterogeneity of so-called periglomerular cells. Neurosci Res 30(2). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-0102(98)00002-9
Langenfurth A, Gu S, Bautze V, Zhang C, Neumann JE, Schuller U, Stock K, Wolf SA et al (2016) Decreased demand for olfactory periglomerular cells impacts on neural precursor cell viability in the rostral migratory stream. Sci Rep 6:32203. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32203srep32203
Le Grand JN, Gonzalez-Cano L, Pavlou MA, Schwamborn JC (2015) Neural stem cells in Parkinson’s disease: a role for neurogenesis defects in onset and progression. Cell Mol Life Sci 72(4):773–797. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1774-1
Luk KC, Kehm V, Carroll J, Zhang B, O’Brien P, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2012) Pathological alpha-synuclein transmission initiates Parkinson-like neurodegeneration in nontransgenic mice. Science 338(6109):949–953. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1227157338/6109/949
Ming GL, Song H (2011) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron 70(4):687–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.001S0896-6273(11)00348-5
Mochizuki H, Choong CJ, Masliah E (2018) A refined concept: alpha-synuclein dysregulation disease. Neurochem Int 119:84–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2017.12.011
Okano HJ, Darnell RB (1997) A hierarchy of Hu RNA binding proteins in developing and adult neurons. J Neurosci 17(9):3024–3037. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-09-03024.1997
Parrish-Aungst S, Shipley MT, Erdelyi F, Szabo G, Puche AC (2007) Quantitative analysis of neuronal diversity in the mouse olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol 501(6):825–836. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.21205
Piumatti M, Palazzo O, La Rosa C, Crociara P, Parolisi R, Luzzati F, Levy F, Bonfanti L (2018) Non-newly generated, “immature” neurons in the sheep brain are not restricted to cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 38(4):826–842. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1781-17.2017JNEUROSCI.1781-17.2017
Pontarelli F, Ofengeim D, Zukin RS, Jonas EA (2012) Mouse transient global ischemia two-vessel occlusion model. Bio Protoc 2(18). https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.262
Spillantini MG, Crowther RA, Jakes R, Hasegawa M, Goedert M (1998) alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(11):6469–6473
Stefanis L (2012) alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2 (2):a009399. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009399a009399
Taguchi K, Watanabe Y, Tsujimura A, Tatebe H, Miyata S, Tokuda T, Mizuno T, Tanaka M (2014) Differential expression of alpha-synuclein in hippocampal neurons. PLoS One 9(2):e89327. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089327PONE-D-13-41043
Taguchi K, Watanabe Y, Tsujimura A, Tanaka M (2016) Brain region-dependent differential expression of alpha-synuclein. J Comp Neurol 524(6):1236–1258. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.23901
Taguchi K, Watanabe Y, Tsujimura A, Tanaka M (2018) Expression of alpha-synuclein is regulated in a neuronal cell type-dependent manner. Anat Sci Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12565-018-0464-810.1007/s12565-018-0464-8
Totterdell S, Meredith GE (2005) Localization of alpha-synuclein to identified fibers and synapses in the normal mouse brain. Neuroscience 135(3):907–913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.06.047
Totterdell S, Hanger D, Meredith GE (2004) The ultrastructural distribution of alpha-synuclein-like protein in normal mouse brain. Brain Res 1004(1-2):61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2003.10.072S0006899304000873
Vivacqua G, Casini A, Vaccaro R, Fornai F, Yu S, D'Este L (2011) Different sub-cellular localization of alpha-synuclein in the C57BL\6J mouse’s central nervous system by two novel monoclonal antibodies. J Chem Neuroanat 41(2):97–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2010.12.003S0891-0618(10)00173-0
Winner B, Lie DC, Rockenstein E, Aigner R, Aigner L, Masliah E, Kuhn HG, Winkler J (2004) Human wild-type alpha-synuclein impairs neurogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63(11):1155–1166. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/63.11.1155
Winner B, Regensburger M, Schreglmann S, Boyer L, Prots I, Rockenstein E, Mante M, Zhao C et al (2012) Role of alpha-synuclein in adult neurogenesis and neuronal maturation in the dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 32(47):16906–16916. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2723-12.201232/47/16906
Withers GS, George JM, Banker GA, Clayton DF (1997) Delayed localization of synelfin (synuclein, NACP) to presynaptic terminals in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 99(1):87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-3806(96)00210-6
Yoon DK, Hwang IK, Yoo KY, Lee YB, Lee JJ, Kim JH, Kang TC, Lee BH et al (2006) Comparison of alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity and protein levels in ischemic hippocampal CA1 region between adult and aged gerbils and correlation with Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase. Neurosci Res 55(4):434–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2006.04.014 https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2006.260194
Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH (2008) Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 132(4):645–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.033S0092-8674(08)00134-7
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Kanji Yoshimoto (Department of Food Sciences and Biotechnology, Faculty of Life Sciences, Hiroshima Institute of Technology, Japan) for instruction on basic surgical techniques for the two-vessel occlusion model.
Funding
This study was supported by a scientific research grant from the Japan Society for Promotion of Science (KT; Grant number 16K21283).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KT and MT: conceived and designed the experiments, and wrote the manuscript; KT: performed the experiments; YW and AT: contributed to data analysis and discussion.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. Animal experiments were performed in accordance with the Guidelines for Animal Experiments, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine and national regulations as described in the section of materials and methods.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 6748 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taguchi, K., Watanabe, Y., Tsujimura, A. et al. α-Synuclein Promotes Maturation of Immature Juxtaglomerular Neurons in the Mouse Olfactory Bulb. Mol Neurobiol 57, 1291–1304 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01814-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01814-3