Abstract
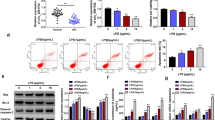
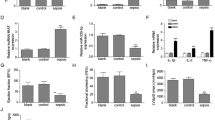
Sepsis is a life-threatening syndrome that can result in multi-organ dysfunction. MicroRNA (miR)-483-3p was previously demonstrated to be upregulated in sepsis patients; however, its specific functions in sepsis-triggered intestinal injury remain unclarified. Human intestinal epithelial NCM460 cell line was stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to mimic sepsis-induced intestinal injury in vitro. Terminal-deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining was utilized for examining cell apoptosis. Western blotting and real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) were used for detecting molecular protein and RNA levels. LPS-induced cytotoxicity was determined by measuring concentrations of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), diamine oxidase (DAO) and fatty acid binding protein 2 (FABP2). Luciferase reporter assay was utilized for verifying the interaction between miR-483-3p and homeodomain interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2). Inhibiting miR-483-3p alleviates LPS-triggered NCM460 cell apoptosis and cytotoxicity. miR-483-3p targeted HIPK2 in LPS-stimulated NCM460 cells. Knockdown of HIPK2 reversed the above effects mediated by miR-483-3p inhibitor. Inhibiting miR-483-3p ameliorates LPS-triggered apoptosis and cytotoxicity by targeting HIPK2.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Singer, M., Deutschman, C. S., Seymour, C. W., Shankar-Hari, M., Annane, D., Bauer, M., Bellomo, R., Bernard, G. R., Chiche, J. D., Coopersmith, C. M., Hotchkiss, R. S., Levy, M. M., Marshall, J. C., Martin, G. S., Opal, S. M., Rubenfeld, G. D., van der Poll, T., Vincent, J. L., & Angus, D. C. (2016). The Third International consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). Jama, 315, 801–810.
Rudd, K. E., Johnson, S. C., Agesa, K. M., Shackelford, K. A., Tsoi, D., Kievlan, D. R., Colombara, D. V., Ikuta, K. S., Kissoon, N., Finfer, S., Fleischmann-Struzek, C., Machado, F. R., Reinhart, K. K., Rowan, K., Seymour, C. W., Watson, R. S., West, T. E., Marinho, F., Hay, S. I., … Naghavi, M. (2020). Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global burden of disease study. Lancet, 395, 200–211.
Zhang, Y. Y., & Ning, B. T. (2021). Signaling pathways and intervention therapies in sepsis. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 6, 407.
Rello, J., Valenzuela-Sánchez, F., Ruiz-Rodriguez, M., & Moyano, S. (2017). Sepsis: A Review of Advances in Management. Advances in Therapy, 34, 2393–2411.
Fay, K. T., Ford, M. L., & Coopersmith, C. M. (2017). The intestinal microenvironment in sepsis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, Molecular Basis of Disease, 1863, 2574–2583.
Zhu, Y., Wang, Y., Teng, W., Shan, Y., Yi, S., Zhu, S., & Li, Y. (2019). Role of Aquaporin-3 in intestinal injury induced by sepsis. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 42, 1641–1650.
Wang, Y. F., Li, J. W., Wang, D. P., Jin, K., Hui, J. J., & Xu, H. Y. (2022). Anti-hyperglycemic agents in the adjuvant treatment of sepsis: Improving intestinal barrier function. Drug Design, Development and Therapy, 16, 1697–1711.
Lu, T. X., & Rothenberg, M. E. (2018). MicroRNA. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 141, 1202–1207.
Harrill, A. H., McCullough, S. D., Wood, C. E., Kahle, J. J., & Chorley, B. N. (2016). MicroRNA biomarkers of toxicity in biological matrices. Toxicological Sciences, 152, 264–272.
Zhou, S. S., Jin, J. P., Wang, J. Q., Zhang, Z. G., Freedman, J. H., Zheng, Y., & Cai, L. (2018). miRNAS in cardiovascular diseases: potential biomarkers, therapeutic targets and challenges. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 39, 1073–1084.
Yu, J., Xue, J., Liu, C., Zhang, A., Qin, L., Liu, J., & Yang, Y. (2022). MiR-146a-5p accelerates sepsis through dendritic cell activation and glycolysis via targeting ATG7. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 36, e23151.
Du, X., Tian, D., Wei, J., Yan, C., Hu, P., Wu, X., Yang, W., & Zhu, Z. (2020). miR-199a-5p exacerbated intestinal barrier dysfunction through inhibiting surfactant protein D and activating NF-κB pathway in sepsis. Mediators of Inflammation, 2020, 8275026.
Qiu, G., Fan, J., Zheng, G., He, J., Lin, F., Ge, M., Huang, L., Wang, J., Xia, J., Huang, R., Shu, Q., & Xu, J. (2022). Diagnostic potential of plasma extracellular vesicle miR-483-3p and Let-7d-3p for sepsis. Frontiers Molecular Bioscience, 9, 814240.
Yuan, T., Zhang, L., Yao, S., Deng, S. Y., & Liu, J. Q. (2020). miR-195 promotes LPS-mediated intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis via targeting SIRT1/eIF2a. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 45, 510–518.
Li, J. H., Liu, S., Zhou, H., Qu, L. H., & Yang, J. H. (2014). starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Research, 42, D92–D97.
Pérez-Hernández, E. G., Delgado-Coello, B., Luna-Reyes, I., & Mas-Oliva, J. (2021). New insights into lipopolysaccharide inactivation mechanisms in sepsis. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 141, 111890.
Gu, J., Hu, J., Qian, H., Shi, Y., Zhang, E., Guo, Y., Xiao, Z., Fang, Z., Zhong, M., Zhang, H., & Meng, W. (2016). Intestinal barrier dysfunction: A novel therapeutic target for inflammatory response in acute stanford type a aortic dissection. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 21, 64–69.
Wang, M., Guo, S., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Zhang, H. (2021). Remifentanil attenuates sepsis-induced intestinal injury by inducing autophagy. Bioengineered, 12, 9575–9584.
Kuang, Z. S., Leng, Y. X., Yang, N., Li, Z. Q., Zong, Y. N., Han, D. Y., Li, Y., He, J. D., Mi, X. N., Cong, Z. K., Zhu, X., Wu, C. Y., & Guo, X. Y. (2022). Inhibition of visfatin alleviates sepsis-induced intestinal damage by inhibiting Hippo signaling pathway. Inflammation Research, 71, 911–922.
Tan, F., Cao, Y., Zheng, L., Wang, T., Zhao, S., Chen, J., Pang, C., Xia, W., Xia, Z., Li, N., & Chi, X. (2022). Diabetes exacerbated sepsis-induced intestinal injury by promoting M1 macrophage polarization via miR-3061/Snail1 signaling. Frontiers Immunology, 13, 922614.
Li, Z., Gao, M., Yang, B., Zhang, H., Wang, K., Liu, Z., Xiao, X., & Yang, M. (2018). Naringin attenuates MLC phosphorylation and NF-κB activation to protect sepsis-induced intestinal injury via RhoA/ROCK pathway. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 103, 50–58.
Formosa, A., Turgeon, P., & Dos Santos, C. C. (2022). Role of miRNA dysregulation in sepsis. Molecular Medicine, 28, 99.
Du, X., Tian, D., Wei, J., Yan, C., Hu, P., Wu, X., & Yang, W. (2020). MEG3 alleviated LPS-induced intestinal injury in sepsis by modulating miR-129-5p and surfactant protein D. Mediators Inflammation, 2020, 8232734.
Wang, Z., Zhong, C., Cao, Y., Yin, H., Shen, G., Lu, W., & Ding, W. (2021). LncRNA DANCR improves the dysfunction of the intestinal barrier and alleviates epithelial injury by targeting the miR-1306-5p/PLK1 axis in sepsis. Cell Biology International, 45, 1935–1944.
Zhang, H., Wang, J., Du, A., & Li, Y. (2020). MiR-483-3p inhibition ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting the MDM4/p53 pathway. Molecular Immunology, 125, 9–14.
Zhou, J., Lin, J., Zhao, Y., & Sun, X. (2022). Deregulated expression of miR-483-3p serves as a diagnostic biomarker in severe pneumonia children with respiratory failure and its predictive value for the clinical outcome of patients. Molecular Biotechnology, 64, 311–319.
Huang, X., Zhou, Y., Sun, Y., & Wang, Q. (2022). Intestinal fatty acid binding protein: A rising therapeutic target in lipid metabolism. Progress in Lipid Research, 87, 101178.
Dang, S., Shen, Y., Yin, K., & Zhang, J. (2012). TREM-1 Promotes Pancreatitis-Associated Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction. Gastroenterol Res Pract., 2012, 720865.
Chipman, L. B., & Pasquinelli, A. E. (2019). miRNA Targeting: Growing beyond the Seed. Trends in Genetics, 35, 215–222.
Wang, Y., Hou, L., Yuan, X., Xu, N., Zhao, S., Yang, L., & Zhang, N. (2020). miR-483-3p promotes cell proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting IGF-1. Biomedicine & Pharmacotheraphy, 130, 110519.
Zhou, B., Peng, K., Wang, G., Chen, W., Liu, P., Chen, F., & Kang, Y. (2020). miR4833p promotes the osteogenesis of human osteoblasts by targeting Dikkopf 2 (DKK2) and the Wnt signaling pathway. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 46, 1571–1581.
Yu, Q., Liu, L., Zhang, X., Chang, H., Ma, S., Xie, Z., Tang, S., Ju, X., Zhu, H., Shen, B., & Zhang, Q. (2022). MiR-221-3p targets HIPK2 to promote diabetic wound healing. Microvascular Research, 140, 104306.
Li, R., Shang, J., Zhou, W., Jiang, L., Xie, D., & Tu, G. (2018). Overexpression of HIPK2 attenuates spinal cord injury in rats by modulating apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 103, 127–134.
Jiang, Z., Bo, L., Meng, Y., Wang, C., Chen, T., Wang, C., Yu, X., & Deng, X. (2018). Overexpression of homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2) attenuates sepsis-mediated liver injury by restoring autophagy. Cell Death & Disease, 9, 847.
Zhang, F., Qi, L., Feng, Q., Zhang, B., Li, X., Liu, C., Li, W., Liu, Q., Yang, D., Yin, Y., Peng, C., Wu, H., Tang, Z. H., Zhou, X., Xiang, Z., Zhang, Z., Wang, H., & Wei, B. (2021). HIPK2 phosphorylates HDAC3 for NF-κB acetylation to ameliorate colitis-associated colorectal carcinoma and sepsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 118, e2021798118.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Anhui Province (Grant no. KJ2021ZD0099) and Horizontal Scientific Research Project of Yijishan Hospital, The First Affiliated Hospital of Wannan Medical College (Grant no. 662202204007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZW and XQ: conceived and designed the experiments. ZW, XQ, JY, HY, RQ, CZ and WD: carried out the experiments. ZW, XQ and WD: drafted the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Qin, X., Yuan, J. et al. MicroRNA-483-3p Inhibitor Ameliorates Sepsis-Induced Intestinal Injury by Attenuating Cell Apoptosis and Cytotoxicity Via Regulating HIPK2. Mol Biotechnol 66, 233–240 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00734-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-023-00734-x