Abstract
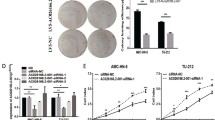
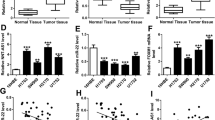
Increasing evidence demonstrates that many long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are implicated with the development of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC). As shown by bioinformatics analysis, lncRNA non-catalytic region of tyrosine kinase adaptor protein 1-antisense 1 (NCK1-AS1) is upregulated in tissues of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. The study aimed to explore the role and mechanism of NCK1-AS1 in LSCC. NCK1-AS1 expression in LSCC cells was evaluated by reverse transcription qPCR. The viability, proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis of LSCC cells with indicated transfection were evaluated by CCK-8 assays, Ethynyl deoxyuridine incorporation assays, Transwell assays, wound healing assays, and TUNEL assays, respectively. Subcellular fractionation assays were performed to evaluate the cellular distribution of NCK1-AS1 and NCK1. NCK1 protein level in LSCC cells with indicated transfection was quantified by western blotting. The binding relation between miR-137 and NCK1-AS1 (or NCK1) were determined using RNA immunoprecipitation assays and luciferase reporter assays. NCK1-AS1 was highly expressed in LSCC cell lines. NCK1-AS1 depletion suppressed LSCC cell viability, proliferation, invasion, and migration while enhancing cell apoptosis. NCK1, an adjacent gene of NCK1-AS1, is also highly expressed in LSCC cells and was positively regulated by NCK1-AS1. Moreover, NCK1-AS1 interact with miR-137 to upregulate NCK1 expression. NCK1 was the downstream target of miR-137 and was negatively correlated to miR-137. In addition, overexpressed NCK1 reversed the suppressive impact of NCK1-AS1 depletion on malignant behaviors of LSCC cells. NCK1-AS1 contributes to LSCC cellular behaviors by upregulating NCK1 via interaction with miR-137.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are available in the published article.
Change history
22 March 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00478-0
References
Kyurkchiyan, S. G., Popov, T. M., Mitev, V. I., & Kaneva, R. P. (2020). The role of miRNAs and lncRNAs in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma—a mini-review. Folia Medica (Plovdiv), 62(2), 244–252. https://doi.org/10.3897/folmed.62.e49842
Xu, Z., & Xi, K. (2019). LncRNA RGMB-AS1 promotes laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells progression via sponging miR-22/NLRP3 axis. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 118, 109222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109222
Jiang, Q., Liu, S., Hou, L., Guan, Y., Yang, S., & Luo, Z. (2020). The implication of LncRNA MALAT1 in promoting chemo-resistance of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis, 34(4), e23116. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.23116
Bhan, A., Soleimani, M., & Mandal, S. S. (2017). Long noncoding RNA and cancer: A new paradigm. Cancer Research, 77(15), 3965–3981. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2634
Liu, H., Sun, Y., Tian, H., Xiao, X., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., & Yu, F. (2019). Characterization of long non-coding RNA and messenger RNA profiles in laryngeal cancer by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Aging (Albany), 11(22), 10074–10099. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102419
Zhang, G., Fan, E., Zhong, Q., Feng, G., Shuai, Y., Wu, M., Chen, Q., & Gou, X. (2019). Identification and potential mechanisms of a 4-lncRNA signature that predicts prognosis in patients with laryngeal cancer. Human Genomics, 13(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40246-019-0230-6
Ali, T., & Grote, P. (2020). Beyond the RNA-dependent function of LncRNA genes. eLife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.60583
Yang, Q., Sun, J., Ma, Y., Zhao, C., & Song, J. (2019). LncRNA DLX6-AS1 promotes laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma growth and invasion through regulating miR-376c. American Journal of Translational Research, 11(11), 7009–7017.
Li, Y., Xu, J., Guo, Y. N., & Yang, B. B. (2019). LncRNA SNHG20 promotes the development of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-140. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 23(8), 3401–3409. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201904_17704
Qi, X., Zhang, D. H., Wu, N., Xiao, J. H., Wang, X., & Ma, W. (2015). ceRNA in cancer: Possible functions and clinical implications. Journal of medical genetics, 52(10), 710–718. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103334
Cheng, D. L., Xiang, Y. Y., Ji, L. J., & Lu, X. J. (2015). Competing endogenous RNA interplay in cancer: Mechanism, methodology, and perspectives. Tumour Biology, 36(2), 479–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3093-z
Wang, N., Wang, L., & Pan, X. (2020). Long Non-Coding RNA TRPM2-AS promotes cell migration and invasion by serving as a ceRNA of miR-138 and inducing SOX4-mediated EMT in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Management Research, 12, 7805–7812. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.S265412
Liu, T., Meng, W., Cao, H., Chi, W., Zhao, L., Cui, W., Yin, H., & Wang, B. (2020). lncRNA RASSF8-AS1 suppresses the progression of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting the miR-664b-3p/TLE1 axis. Oncology Reports, 44(5), 2031–2044. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2020.7771
Hui, L., Wang, J., Zhang, J., & Long, J. (2019). lncRNA TMEM51-AS1 and RUSC1-AS1 function as ceRNAs for induction of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and prediction of prognosis. PeerJ, 7, e7456. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7456
Hu, H., Li, H., & Feng, X. (2019). Downregulation of lncRNA NCK1-AS1 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by upregulating miR-135a. Cancer Management and Research, 11, 10531–10537. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S221326
Zhang, W. Y., Liu, Y. J., He, Y., & Chen, P. (2019). Suppression of long noncoding RNA NCK1-AS1 increases chemosensitivity to cisplatin in cervical cancer. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234(4), 4302–4313. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27198
Huang, L., Li, X., Ye, H., Liu, Y., Liang, X., Yang, C., Hua, L., Yan, Z., & Zhang, X. (2020). Long non-coding RNA NCK1-AS1 promotes the tumorigenesis of glioma through sponging microRNA-138-2-3p and activating the TRIM24/Wnt/β-catenin axis. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 39(1), 63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01567-1
Livak, K. J., & Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods, 25(4), 402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Tang, Z., Li, C., Kang, B., Gao, G., Li, C., & Zhang, Z. (2017). GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic acids research, 45(W1), W98-w102. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx247
Li, J. H., Liu, S., Zhou, H., Qu, L. H., & Yang, J. H. (2014). starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic acids research, 42, D92-97. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1248
Cao, Z., Pan, X., Yang, Y., Huang, Y., & Shen, H. B. (2018). The lncLocator: A subcellular localization predictor for long non-coding RNAs based on a stacked ensemble classifier. Bioinformatics, 34(13), 2185–2194. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty085
Bardou, P., Mariette, J., Escudié, F., Djemiel, C., & Klopp, C. (2014). jvenn: An interactive venn diagram viewer. BMC Bioinformatics, 15(1), 293. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-15-293
Cossu, A. M., Mosca, L., Zappavigna, S., Misso, G., Bocchetti, M., De Micco, F., Quagliuolo, L., Porcelli, M., Caraglia, M., & Boccellino, M. (2019). Long non-coding RNAs as important biomarkers in laryngeal cancer and other head and neck tumours. International Journal of Molecular Science. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143444
Fan, C. N., Ma, L., & Liu, N. (2018). Systematic analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network identifies four-lncRNA signature as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. Journal of Translational Medicine, 16(1), 264. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-018-1640-2
Yang, G., & Lu, X. (1839). Yuan L (2014) LncRNA: A link between RNA and cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 11, 1097–1109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.08.012
Chang, H., Li, B., Zhang, X., & Meng, X. (2020). NCK1-AS1 promotes NCK1 expression to facilitate tumorigenesis and chemo-resistance in ovarian cancer. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 522(2), 292–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.11.014
Luo, X., Zhou, J., Quan, L., Liang, Y., Huang, P., Chen, F., & Liu, S. (2020). LncRNA NCK1-AS1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression via regulating miR-512-5p/p21 axis. Pathology Research and Practice, 216(11), 153157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2020.153157
Li, W., Duan, J., Shi, W., Lei, L., & Lv, P. (2020). Long non-coding RNA NCK1-AS1 serves an oncogenic role in gastric cancer by regulating miR-137/NUP43 axis. Oncotargets and Therapy, 13, 9929–9939. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S259336
Huang, L., Gan, X., He, L., Wang, L., & Yu, J. (2019). Silencing of long non-coding RNA NCK1-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation and migration via inhibition of microRNA-134 in cervical cancer. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 18(3), 2314–2322. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7799
Li, J., Wu, X., Cao, W., & Zhao, J. (2020). Long non-coding RNA NCK1-AS1 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells by acting as a ceRNA of miR-137. American Journal of Translational Research, 12(10), 6908–6920.
Zhang, F., Lu, Y. X., Chen, Q., Zou, H. M., Zhang, J. M., Hu, Y. H., Li, X. M., Zhang, W. J., Zhang, W., Lin, C., & Li, X. N. (2017). Identification of NCK1 as a novel downstream effector of STAT3 in colorectal cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. Cellular signalling, 36, 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.04.020
Guo, Q., Wang, H., Xu, Y., Wang, M., & Tian, Z. (2021). miR-374a-5p inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and migration via targeting NCK1. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 22(3), 943. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2021.10375
Mohr, A. M., & Mott, J. L. (2015). Overview of microRNA biology. Seminars in Liver Disease, 35(1), 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1397344
Lu, T. X., & Rothenberg, M. E. (2018). MicroRNA. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 141(4), 1202–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034
Li, Y., Liu, J., Hu, W., Zhang, Y., Sang, J., Li, H., Ma, T., Bo, Y., Bai, T., Guo, H., Lu, Y., Xue, X., Niu, M., Ge, S., Wen, S., Wang, B., Gao, W., & Wu, Y. (2019). miR-424-5p promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotargets and Therapy, 12, 10441–10453. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S224325
Luo, M., Sun, G., & Sun, J. W. (2019). MiR-196b affects the progression and prognosis of human LSCC through targeting PCDH-17. Auris Nasus Larynx, 46(4), 583–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2018.10.020
Yungang, W., Xiaoyu, L., Pang, T., Wenming, L., & Pan, X. (2014). miR-370 targeted FoxM1 functions as a tumor suppressor in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC). Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 68(2), 149–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2013.08.008
Ma, Y., Bu, D., Long, J., Chai, W., & Dong, J. (2019). LncRNA DSCAM-AS1 acts as a sponge of miR-137 to enhance tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 234(3), 2880–2894. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27105
Duan, J., Lu, G., Li, Y., Zhou, S., Zhou, D., & Tao, H. (2019). miR-137 functions as a tumor suppressor gene in pituitary adenoma by targeting AKT2. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 12(5), 1557–1564.
Lv, N., Hao, S., Luo, C., Abukiwan, A., Hao, Y., Gai, F., Huang, W., Huang, L., Xiao, X., Eichmüller, S. B., & He, D. (2018). miR-137 inhibits melanoma cell proliferation through downregulation of GLO1. Science China Life Science, 61(5), 541–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-017-9138-9
Guo, L., Chen, J., Liu, D., & Liu, L. (2020). OIP5-AS1/miR-137/ZNF217 Axis promotes malignant behaviors in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Management and research, 12, 6707–6717. https://doi.org/10.2147/cmar.S237726
Liu, P. J., Pan, Y. H., Wang, D. W., & You, D. (2020). Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes cell proliferation of pancreatic cancer through miR-137 and Notch1 pathway. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 24(23), 12161–12170. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202012_24005
Xu, J., Wu, G., Zhao, Y., Han, Y., Zhang, S., Li, C., & Zhang, J. (2020). Long noncoding RNA DSCAM-AS1 facilitates colorectal cancer cell proliferation and migration via miR-137/Notch1 axis. Journal of Cancer, 11(22), 6623–6632. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.46562
Lu, Y., Guo, G., Hong, R., Chen, X., Sun, Y., Liu, F., Zhang, Z., Jin, X., Dong, J., Yu, K., Yang, X., Nan, Y., & Huang, Q. (2021). LncRNA HAS2-AS1 promotes glioblastoma proliferation by sponging miR-137. Frontiers in Oncology, 11, 634893. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.634893
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LW and XJ: were the main designers of this study. All authors conducted experiments and performed data analysis. LW: finished the manuscript. The final manuscript was approved by all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
The article does not include studies with human or animal subjects.
Consent for publication
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, L., Gu, D. & Jin, X. LncRNA NCK1-AS1 Promotes Malignant Cellular Phenotypes of Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma via miR-137/NCK1 Axis. Mol Biotechnol 64, 888–901 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00469-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-022-00469-1