Abstract
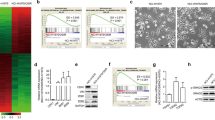
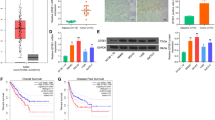
EGFR-targeted therapies are reported to yield modest effect in OSCC. Activation of NFκB signaling is considered as molecular driver of EGFR inhibitor resistance in various cancers. In this scenario, present study focused on the molecular crosstalk between EGFR and NFκB signaling pathways and its therapeutic importance in OSCC. The EGFR- NFκB p65 co-expressed human OSCC cell lines UPCI:SCC066, UPCI:SCC040 and UM-SCC083B were used for in vitro studies. Recombinant human EGF, siRNAs, Western blot and qRT-PCR were used to dissect the molecular crosstalk between EGFR-NFκB signaling pathways in OSCCs. The effect of NFκB p65 knockdown on cancer hallmarks was studied by respective functional assays and RNA-Seq analysis was performed to identify the differentially expressed genes upon NFκB p65 knockdown. Gefitinib and Bay 11-7085 combination treatment was done to study the chemotherapeutic potential of EGFR- NFκB axis. Significant positive correlation between EGFR and NFκB p65 expression was observed in Head and Neck TCGA data set. EGFR induction or knockdown respectively stimulate or impair the NFκB signaling in EGFR- NFκB p65 co-expressed OSCC cell lines. NFκB p65 knockdown causes apoptosis and suppresses the viability, colony formation, migration, invasion, and spheroid formation. Using RNA-seq analysis, we identified PIK3CD as the NFκB target gene, which is commonly involved in these functions. Gefitinib and Bay 11-7085 combination treatment was found to be useful in chemosensitizing the Gefitinib-resistant OSCC cells by capitulating the EGFR- NFκB signaling axis. Combination treatment using Gefitinib and Bay 11-7085 enhanced the apoptosis and reduced cell viability and colony formation in a synergistic way. Our data demonstrated that EGFR-NFκB signaling axis plays a key role in the pathogenesis of OSCCs. Therefore, simultaneous therapeutic intervention of these pathways may be a good alternative approach for the management of OSCCs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Miranda-Filho A, Bray F. Global patterns and trends in cancers of the lip, tongue and mouth. Oral Oncol. 2020;102:104551.
Gupta B, Johnson NW, Kumar N. Global epidemiology of head and neck cancers: a continuing challenge. Oncology. 2016;91:13–23.
Rivera C, Venegas B. Histological and molecular aspects of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2014;8:7–11.
Gupta N, Gupta R, Acharya AK, Patthi B, Goud V, Reddy S, Garg A, Singla A. Changing Trends in oral cancer-a global scenario. Nepal J Epidemiol. 2016;6:613.
Falzone L, Salomone S, Libra M. Evolution of cancer pharmacological treatments at the turn of the third millennium. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1300.
Bonomi M, Patsias A, Posner M, Sikora A. The role of inflammation in head and neck cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;816:107–27.
Baldwin AS. Control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-κB. J Clin Investig. 2001;107:241–6.
Ling J, Kumar R. Crosstalk between NFkB and glucocorticoid signaling: a potential target of breast cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2012;322:119–26.
Perkins ND. The diverse and complex roles of NF-κB subunits in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:121–32.
Alberti C, Pinciroli P, Valeri B, Ferri R, Ditto A, Umezawa K, Sensi M, Canevari S, Tomassetti A. Ligand-dependent EGFR activation induces the co-expression of IL-6 and PAI-1 via the NFkB pathway in advanced-stage epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31:4139–49.
De S, Dermawan JKT, Stark GR. EGF receptor uses SOS1 to drive constitutive activation of NFκB in cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111:11721–6.
Saxon JA, Sherrill TP, Polosukhin VV, Sai J, Zaynagetdinov R, McLoed AG, Gulleman PM, Barham W, Cheng D-S, Hunt RP. Epithelial NF-κB signaling promotes EGFR-driven lung carcinogenesis via macrophage recruitment. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5:e1168549.
Martinez-Useros J, Garcia-Foncillas J. The challenge of blocking a wider family members of EGFR against head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2015;51:423–30.
Hartmann S, Neckel N, Seher A, Mutzbauer G, Brands RC, Linz C, Kübler AC, Müller-Richter UD. Erlotinib and gefitinib responsiveness in head and neck cancer cell lines—a comparing analysis with cetuximab. Clin Oral Invest. 2016;20:759–69.
Freudlsperger C, Burnett JR, Friedman JA, Kannabiran VR, Chen Z, Van Waes C. EGFR–PI3K–AKT–mTOR signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas: attractive targets for molecular-oriented therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2011;15:63–74.
Roshan VD, Sinto M, Thomas S, Kannan S. Cyclin D1 overexpression associated with activation of STAT3 in oral carcinoma patients from South India. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018;14:403.
Le Page C, Koumakpayi IH, Lessard L, Mes-Masson AM, Saad F. EGFR and Her-2 regulate the constitutive activation of NF-kappaB in PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 2005;65:130–40.
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Song H, Li D. Expression and prognostic influence of NF-κB and EGFR in esophageal cancer. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14:16819–26.
Nottingham LK, Yan CH, Yang X, Si H, Coupar J, Bian Y, Cheng T-F, Allen C, Arun P, Gius D. Aberrant IKKα and IKKβ cooperatively activate NF-κB and induce EGFR/AP1 signaling to promote survival and migration of head and neck cancer. Oncogene. 2014;33:1135–47.
Cahill KE, Morshed RA, Yamini B. Nuclear factor-κB in glioblastoma: insights into regulators and targeted therapy. Neuro Oncol. 2015;18:329–39.
Frank CJ, McClatchey KD, Devaney KO, Carey TE. Evidence that loss of chromosome 18q is associated with tumor progression. Can Res. 1997;57:824–7.
Scott ML, Fujita T, Liou H-C, Nolan GP, Baltimore D. The p65 subunit of NF-kappa B regulates I kappa B by two distinct mechanisms. Genes Dev. 1993;7:1266–76.
Sun S-C, Ganchi PA, Ballard DW, Greene WC. NF-kappa B controls expression of inhibitor I kappa B alpha: evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science. 1993;259:1912–5.
Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Turpin P, Rodriguez M, Thomas D, Hay RT, Virelizier J-L, Dargemont C. Nuclear localization of I kappa B alpha promotes active transport of NF-kappa B from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:369–78.
White JS, Weissfeld JL, Ragin CC, Rossie KM, Martin CL, Shuster M, Ishwad CS, Law JC, Myers EN, Johnson JT. The influence of clinical and demographic risk factors on the establishment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Oral Oncol. 2007;43:701–12.
Chen Z, Yan B, Van Waes C. Role of the NF-κB transcriptome and proteome as biomarkers in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Biomark Med. 2008;4:409–26.
Hynes NE, MacDonald G. ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21:177–84.
Klinger B, Sieber A, Fritsche-Guenther R, Witzel F, Berry L, Schumacher D, Yan Y, Durek P, Merchant M, Schafer R, Sers C, Bluthgen N. Network quantification of EGFR signaling unveils potential for targeted combination therapy. Mol Syst Biol. 2013;9:673.
Roskoski R Jr. The ErbB/HER family of protein-tyrosine kinases and cancer. Pharmacol Res. 2014;79:34–74.
Han W, Lo H-W. Landscape of EGFR signaling network in human cancers: biology and therapeutic response in relation to receptor subcellular locations. Cancer Lett. 2012;318:124–34.
Xia L, Tan S, Zhou Y, Lin J, Wang H, Oyang L, Tian Y, Liu L, Su M, Wang H. Role of the NFκB-signaling pathway in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2018;11:2063.
Qu Y, Zhang X, Wu R. Knockdown of NF-κB p65 subunit expression suppresses growth of nude mouse lung tumor cell xenografts by activation of Bax apoptotic pathway. Neoplasma. 2015;62:34–40.
Tian F, Fan T, Jiang Y, Zhang X, Wang X. A small interfering RNA targeting NF-κB p65 alone or combined with 5-FU inhibits growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in nude mice. Pathol Res Pract. 2012;208:32–8.
Zhang Y, Lapidus RG, Liu P, Choi EY, Adediran S, Hussain A, Wang X, Liu X, Dan HC. Targeting IκB kinase β/NF-κB signaling in human prostate cancer by a novel IκB kinase β inhibitor CmpdA. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15:1504–14.
Pan X, Arumugam T, Yamamoto T, Levin PA, Ramachandran V, Ji B, Lopez-Berestein G, Vivas-Mejia PE, Sood AK, McConkey DJ, Logsdon CD. Nuclear factor-kappaB p65/relA silencing induces apoptosis and increases gemcitabine effectiveness in a subset of pancreatic cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:8143–51.
Zakaria N, Mohd YN, Zakaria Z, Widera D, Yahaya BH. Inhibition of NF-κB signaling reduces the stemness characteristics of lung cancer stem cells. Front Oncol. 2018;8:166. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00166
Song L, Liu L, Wu Z, Li Y, Ying Z, Lin C, Wu J, Hu B, Cheng S-Y, Li M, Li J. TGF-β induces miR-182 to sustain NF-κB activation in glioma subsets. J Clin Investig. 2012;122:3563–78.
Zhu J, Li Y, Chen C, Ma J, Sun W, Tian Z, Li J, Xu J, Liu CS, Zhang D, Huang C, Huang H. NF-κB p65 overexpression promotes bladder cancer cell migration via FBW7-mediated degradation of RhoGDIα protein. Neoplasia. 2017;19:672–83.
Hoxhaj G, Manning BD. The PI3K-AKT network at the interface of oncogenic signalling and cancer metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20:74–88.
Pires BRB, Mencalha AL, Ferreira GM, de Souza WF, Morgado-Díaz JA, Maia AM, Corrêa S, Abdelhay ESFW. NF-kappaB is involved in the regulation of EMT genes in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0169622–e0169622.
Vanhaesebroeck B, Leevers SJ, Panayotou G, Waterfield MD. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases: a conserved family of signal transducers. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997;22:267–72.
Ikeda H, Hideshima T, Fulciniti M, Perrone G, Miura N, Yasui H, Okawa Y, Kiziltepe T, Santo L, Vallet S, Cristea D, Calabrese E, Gorgun G, Raje NS, Richardson P, Munshi NC, Lannutti BJ, Puri KD, Giese NA, Anderson KC. PI3K/p110{delta} is a novel therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Blood. 2010;116:1460–8.
Han SS, Yun H, Son DJ, Tompkins VS, Peng L, Chung ST, Kim JS, Park ES, Janz S. NF-kappaB/STAT3/PI3K signaling crosstalk in iMyc E mu B lymphoma. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:97.
Whitehead MA, Bombardieri M, Pitzalis C, Vanhaesebroeck B. Isoform-selective induction of human p110δ PI3K expression by TNFα: identification of a new and inducible PIK3CD promoter. Biochem J. 2012;443:857–67.
Cassell A, Grandis JR. Investigational EGFR-targeted therapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010;19:709–22.
Sharafinski ME, Ferris RL, Ferrone S, Grandis JR. Epidermal growth factor receptor targeted therapy of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Head Neck. 2010;32:1412–21.
Noro R, Gemma A, Kosaihira S, Kokubo Y, Chen M, Seike M, Kataoka K, Matsuda K, Okano T, Minegishi Y, Yoshimura A, Kudoh S. Gefitinib (IRESSA) sensitive lung cancer cell lines show phosphorylation of Akt without ligand stimulation. BMC Cancer. 2006;6:277.
Blakely CM, Pazarentzos E, Olivas V, Asthana S, Yan JJ, Tan I, Hrustanovic G, Chan E, Lin L, Neel DS, Newton W, Bobb KL, Fouts TR, Meshulam J, Gubens MA, Jablons DM, Johnson JR, Bandyopadhyay S, Krogan NJ, Bivona TG. NF-κB-activating complex engaged in response to EGFR oncogene inhibition drives tumor cell survival and residual disease in lung cancer. Cell Rep. 2015;11:98–110.
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Dr. VG Deepak Roshan, Division of Genetics and Cytogenetics, Malabar Cancer Centre, Kannur, 670103, Kerala, India for his support and kind suggestions.
Funding
This work was supported by the Kerala State Council for Science, Technology & Environment, Government of Kerala through their grant, No. 723/2014/KSCSTE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinto, M.S., Thomas, S. & Kannan, S. Combinatorial treatment with Gefitinib and Bay11-7085 sensitizes primary Gefitinib-resistant OSCC cells by influencing the EGFR- NFκB signaling axis. Med Oncol 38, 110 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-021-01557-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-021-01557-z