Abstract
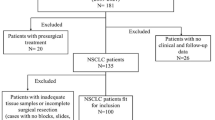
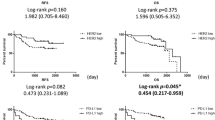
Estrogens and IL-12 play a pivotal role in the development and progression of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC); at the same time, estrogen receptor β2 and (interleukin-12 receptor β2)IL-12Rβ2 are their important receptors, respectively. With the functions of ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ2 explored further in NSCLC, some questions on the relation between ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ2 expression need to be solved. In this study, our aim is to elucidate relationship and roles of ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ2 in NSCLC. The expression of estrogen receptors β2 and IL-12Rβ2 was confirmed by Western blot and RT-PCR analysis in frozen tissues. The correlation between their expression levels and clinical characteristics was evaluated by Mann–Whitney and Kruskal–Wallis test. Using Kaplan–Meier plots and Cox proportional hazard models analyses, overall survival (OS) was evaluated. In contrast to benign pulmonary, ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ2 were over-expressed in NSCLC (p = 0.000). IHC results showed significant correlation between ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ2 (R = 0.382, p = 0.005). By analyzing the relation between ERβ2, IL-12Rβ2 mRNA expression levels and clinical characteristics, it was revealed that ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ2 were significant correlated with regional lymph node metastasis, T stage and clinical stage (p = 0.000/0.000; 0.001/0.000; 0.031/0.003 respectively), and both protein expression levels were lower with TNM stage being higher. In a Kaplan–Meier analysis, compared to both ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ2 or one low expression, high expression levels of ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ2 were identified in a group of patients with the longest overall survival (OS). Cox proportional hazard models revealed that ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ5 had longer OS. This is the first study to uncover that both ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ2 were over-expressed and further show that they were co-expressed in NSCLC. Moreover, we found that high expression levels of ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ2 may be positively correlated with OS and have prognostic values for the progression of NSCLC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pietras RJ, Marquez DC, Chen HW, et al. Estrogen and growth factor receptor interactions in human breast and non-small cell lung cancer cells. Steroids. 2005;70(5–7):372–81.
Kawasaki H, Altieri DC, Lu CD, et al. Inhibition of apoptosis by survivin predicts shorter survival rates in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1998;58(22):5071–4.
Yang XR, Pfeiffer RM, Garcia-Closas M, et al. Hormonal markers in breast cancer: co-expression, relationship with pathologic characteristics, and risk factor associations in a population-based study. Cancer Res. 2007;67(21):10608–17.
Henschke CI, Yip R, Miettinen OS. Women’s susceptibility to tobacco carcinogens and survival after diagnosis of lung cancer. JAMA. 2006;296(2):180–4.
Stabile LP, Davis AL, Gubish CT, et al. Human non-small cell lung tumors and cells derived from normal lung express both estrogen receptor alpha and beta and show biological responses to estrogen. Cancer Res. 2002;62(7):2141–50.
Roman-Blas JA, Castañeda S, Largo R, et al. Osteoarthritis associated with estrogen deficiency. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(5):241.
Davydov MI, Bogush TA, Polotskiĭ BE, et al. Estrogen receptors beta—new target in cellular lung cancer treatment. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2012;2:16–22.
Shaaban AM, Green AR, Karthik S, et al. Nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of ERbeta1, ERbeta2, and ERbeta5 identifies distinct prognostic outcome for breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(16):5228–35.
Chi A. Differential expression of estrogen receptor beta isoforms in human breast cancer tissue. Anticancer Res. 2003;23(1(A)):211–6.
Tang H, Liao Y, Chen G, et al. Estrogen upregulates the IGF-1 signaling pathway in lung cancer through estrogen receptor-β. Med Oncol. 2012;29(4):2640–8.
Presky DH, Yang H, Minetti LJ, Chua AO, Nabavi N, et al. A functional interleukin 12 receptor complex is composed of two beta-type cytokine receptor subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:14002–7.
Airoldi I, Cocco C, Di Carlo E, Disaro S, Ognio E, et al. Methylation of the IL-12Rbeta2 gene as novel tumor escape mechanism for pediatric B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3978–80.
Airoldi I, Di Carlo E. IL-12 Can target human lung adenocarcinoma cells and normal bronchial epithelial cells surrounding tumor lesions. PLoS ONE. 2009;4(7):6119.
Suzuki M, Iizasa T, Nakajima T, et al. Aberrant methylation of IL-12Rβ2 gene in lung cancer. J Thorac oncol. 2007;2(8 suppl 4):s493.
Yan M, Rayoo M, Takano EA, et al. Nuclear and cytoplasmic expressions of ERβ1 and ERβ2 are predictive of response to therapy and alters prognosis in familial breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;126(2):395–405.
Kondo M, Suzuki K, Inoue R, et al. Characterization of T-cell clones specific to ovomucoid from patients with egg-white allergy. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2005;15(2):107–11.
Newton ACS Wong. Malcomson RG, ERβ isoform expression in colorectal carcinoma: an in vivo and in vitro study of clinicopathological and molecular correlates. J Pathol. 2005;207:53–60.
Jarefors S, Janefjord CK, et al. Decreased up-regulation of the interleukin-12Rb2-chain and interferon-g secretion and increased number of forkhead box P3-expressing cells in patients with a history of chronic Lyme borreliosis compared with asymptomatic Borrelia-exposed individuals. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006;147:18–27.
Zhao G, Zhao S, Wang T, et al. Estrogen receptor β signaling regulates the progression of Chinese non-small cell lung cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2011;124(1–2):47–57.
Niikawa H, Suzuki T, Miki Y, et al. Intratumoral estrogens and estrogen receptors in human non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(14):4417–26.
Nose N, Uramoto H, Iwata T, et al. Expression of estrogen receptor beta predicts a clinical response and longer progression-free survival after treatment with EGFR-TKI for adenocarcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer. 2011;71(3):350–5.
Strle K, Zhou JH, Broussard SR, Venters HD, Johnson RW, Freund GG, Dantzer R. Kelley KW.IL-10 promotes survival of microglia without activating Akt. J Neuroimmunol. 2002;122(1–2):9–19.
Kontoyiannis D, Kotlyarov A, Carballo E, Alexopoulou L, Blackshear PJ, Gaestel M, Davis R, Flavell R, Kollias G, et al. Interleukin-10 targets p38 MAPK to modulate ARE-dependent TNF mRNA translation and limit intestinal pathology. EMBO J. 2001;20(14):3760–70.
Fahmi A, Smart N, Punn A, et al. p42/p44-MAPK and PI3 K are sufficient for IL-6 family cytokines/gp130 to signal to hypertrophy and survival in cardiomyocytes in the absence of JAK/STAT activation. Cell Signal. 2013;25(4):898–909.
Gillespie KM, Szeto CC, Betin VM, et al. Role of β1 and β2 subunits of the interleukin-12 receptor in determining T helper 1/T helper 2 responses in vivo in the rat. Immunology. 2000;99:109–12.
Airoldi Irma, Di Carlo Emma, Banelli Barbara, et al. The IL-12Rβ2 gene functions as a tumor suppressor in human B cell malignancies. J. Clin Invest. 2004;113:1651–9.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the contribution of Dr. Xue-ping Lun, Dr. Ke Feng (department of the thoracic surgery, the first hospital of sun sen-yat university) and Long-bin Xiao (department of Gastrointestinal surgery, the first hospital of sun sen-yat university). Dr. Xue-ping Lun and Dr. Ke Feng carried out statistical analyses, Long-bin Xiao performed part of Western-blot experiment.
Conflict of interest
We all read introductions about conflict of interest of medical oncology seriously. All authors declare that: not any data or results were submitted or published in other place; we have no proprietary, financial, professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in. The manuscript has not been published previously by any of the authors and is not under consideration for publication in another journal at the time of this submission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Zg., Lei, Yy., Li, Ww. et al. The co-expression of ERβ2 and IL-12Rβ2 is better prognostic factor in non-small-cell lung cancer progression. Med Oncol 30, 592 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0592-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0592-x