Abstract
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) represent the host immune response to cancer. CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (CTLs) have a central role in the elimination of tumors, while regulatory T cells (Tregs) can suppress the immune reaction. The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic value of TILs, especially Tregs and CTLs, in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients after resection. CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, and FoxP3+ TILs were assessed by immunohistochemistry in tumor tissue from 141 randomly selected HCC patients. Prognostic effects of low- or high-density TIL subsets were evaluated by Kaplan–Meier and Cox regression analysis using the median values as cutoff. The density of intratumoral Tregs (P = 0.040) and peritumoral CTLs (P = 0.004) were an independent factor for overall survival (OS), but not for disease-free survival (DFS). The density of CD3+ and CD4+ TILs, and the prevalence of Tregs and CTLs were associated with neither OS nor DFS. The presence of low intratumoral Tregs with high intratumoral CTLs was a negative independent prognostic factor for OS (P = 0.001), while that of low intratumoral Tregs and low peritumoral CTLs independently correlated with improved DFS (P = 0.008). Moreover, the combined analysis of Tregs and CTLs displayed better prognostic performances than any of them alone. Additionally, higher density of intratumoral Tregs correlated with both the presence of liver cirrhosis (P = 0.025) and increased tumor size (P = 0.050). Tregs within tumor environment are promising prognostic parameters for HCC patients, and their combination with CTLs can predict prognosis more effectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jochems C, Schlom J. Tumor-infiltrating immune cells and prognosis: the potential link between conventional cancer therapy and immunity. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2011;236(5):567–79. doi:10.1258/ebm.2011.011007.
Wada Y, Nakashima O, Kutami R, Yamamoto O, Kojiro M. Clinicopathological study on hepatocellular carcinoma with lymphocytic infiltration. Hepatology. 1998;27(2):407–14. doi:10.1002/hep.510270214.
Galon J, Costes A, Sanchez-Cabo F, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Lagorce-Pages C et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science. 2006;313(5795):1960–4. doi:10.1126/science.1129139.
Zou W. Regulatory T cells, tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(4):295–307.
Fu J, Xu D, Liu Z, Shi M, Zhao P, Fu B, et al. Increased regulatory T cells correlate with CD8 T-cell impairment and poor survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(7):2328–39.
Unitt E, Rushbrook SM, Marshall A, Davies S, Gibbs P, Morris LS, et al. Compromised lymphocytes infiltrate hepatocellular carcinoma: the role of T-regulatory cells. Hepatology. 2005;41(4):722–30.
Yang XH, Yamagiwa S, Ichida T, Matsuda Y, Sugahara S, Watanabe H, et al. Increase of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T-cells in the liver of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2006;45(2):254–62.
Kryczek I, Liu R, Wang G, Wu K, Shu X, Szeliga W, et al. FOXP3 defines regulatory T cells in human tumor and autoimmune disease. Cancer Res. 2009;69(9):3995–4000.
Salama P, Phillips M, Grieu F, Morris M, Zeps N, Joseph D, et al. Tumor-infiltrating FOXP3+ T regulatory cells show strong prognostic significance in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(2):186–92.
Wilke CM, Wu K, Zhao E, Wang G, Zou W. Prognostic significance of regulatory T cells in tumor. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(4):748–58. doi:10.1002/ijc.25464.
Alvaro T, Lejeune M, Salvado MT, Bosch R, Garcia JF, Jaen J et al. Outcome in Hodgkin’s lymphoma can be predicted from the presence of accompanying cytotoxic and regulatory T cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(4):1467–73. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1869.
Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang XY, Xiao YS, et al. Intratumoral balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(18):2586–93.
Ju MJ, Qiu SJ, Gao Q, Fan J, Cai MY, Li YW et al. Combination of peritumoral mast cells and T-regulatory cells predicts prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2009;100(7):1267–74. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01182.x.
Varotti G, Ramacciato G, Ercolani G, Grazi GL, Vetrone G, Cescon M et al. Comparison between the fifth and sixth editions of the AJCC/UICC TNM staging systems for hepatocellular carcinoma: multicentric study on 393 cirrhotic resected patients. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2005;31(7):760–7. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2005.04.008.
Schepke M, Roth F, Fimmers R, Brensing KA, Sudhop T, Schild HH et al. Comparison of MELD, Child-Pugh, and Emory model for the prediction of survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003;98(5):1167–74. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2003.07515.x.
Zhu XD, Zhang JB, Zhuang PY, Zhu HG, Zhang W, Xiong YQ et al. High expression of macrophage colony-stimulating factor in peritumoral liver tissue is associated with poor survival after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(16):2707–16. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.6521.
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, et al. Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med. 2004;10(9):942–9.
Hiraoka N, Onozato K, Kosuge T, Hirohashi S. Prevalence of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells increases during the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its premalignant lesions. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(18):5423–34. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0369.
Badoual C, Hans S, Rodriguez J, Peyrard S, Klein C, Agueznay Nel H et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating CD4+ T-cell subpopulations in head and neck cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(2):465–72. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1886.
Grabenbauer GG, Lahmer G, Distel L, Niedobitek G. Tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic T cells but not regulatory T cells predict outcome in anal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(11 Pt 1):3355–60. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2434.
Kobayashi N, Hiraoka N, Yamagami W, Ojima H, Kanai Y, Kosuge T, et al. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells affect the development and progression of hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(3):902–11.
Zhang L, Conejo-Garcia JR, Katsaros D, Gimotty PA, Massobrio M, Regnani G et al. Intratumoral T cells, recurrence, and survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(3):203–13. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa020177
Nakano O, Sato M, Naito Y, Suzuki K, Orikasa S, Aizawa M, et al. Proliferative activity of intratumoral CD8(+) T-lymphocytes as a prognostic factor in human renal cell carcinoma: clinicopathologic demonstration of antitumor immunity. Cancer Res. 2001;61(13):5132–6.
Zhou J, Ding T, Pan W, Zhu LY, Li L, Zheng L. Increased intratumoral regulatory T cells are related to intratumoral macrophages and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(7):1640–8. doi:10.1002/ijc.24556.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program (NO.2009CB522407), the Major National S&T Program (NO. 2008ZX10002-026), and the Program for Innovative Research Team of Zhejiang Province of China (NO. 2009R50038).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling EiC: Peter Wiernik.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12032_2011_6_MOESM1_ESM.tif
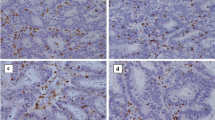
Fig. 1 Peritumoral tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) outnumbered intratumoral TILs. (a) A typical tissue disk. T, tumor tissue; P, peritumor tissue. (b) Peritumoral lymphocytes form an aggregate. In a representative case, (c) in the peritumoral noncancerous area, lymphocytic infiltration was more abundant than that of (d) the intratumoral area. In each case, positive lymphocytes were stained brown (a, x100; b, x200; c and d, x400). (e) The density of FoxP3+ cells in intratumoral area was close to that in peritumoral area. (magnification, x200) (TIFF 10588 kb)
12032_2011_6_MOESM2_ESM.tif
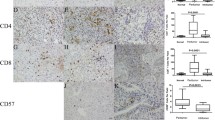
Fig. 2 Kaplan–Meier analyses of disease-free survival and overall survival for intratumoral CD3+ (CD3I; a and b) and CD4+ (CD4I; c and d) TILs, and the prevalence of intratumoral CTLs among intratumoral CD3+ TILs (CD8I/CD3I; e and f) and intratumoral Tregs among intratumoralCD4+ TILs (FoxP3I/CD4I; g and h). None of them was associated with survival and recurrence (TIFF 2311 kb)
12032_2011_6_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Fig. 3 Kaplan–Meier pairwise analyses of disease-free survival and overall survival for the combination of intratumoral Tregs (FoxP3I) with intratumoral CTLs (CD8I) and with peritumoral CTLs (CD8P) (TIFF 1924 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Kj., Zhou, L., Xie, Hy. et al. Intratumoral regulatory T cells alone or in combination with cytotoxic T cells predict prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. Med Oncol 29, 1817–1826 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-0006-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-011-0006-x