Abstract
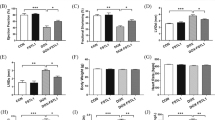
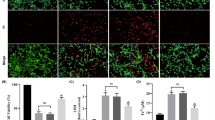
Redox impairment, inflammation, and increased rates of cell death are central players during neurodegeneration. In that context, activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (Nrf2) has been viewed as an interesting strategy in order to reduce the impact of redox dysfunction and neuroinflammation on cell fate. There is evidence indicating that the benefits caused by natural products in the brain may be due to the ability of these agents in upregulating Nrf2. Gastrodin (GAS) induces anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic actions in brain cells. Nonetheless, the mechanisms underlying such effects are not clear yet. Therefore, we investigated here whether GAS would affect apoptosis and inflammation in the human neuroblastoma cell line (SH-SY5Y) exposed to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). GAS at 1–25 μM was administrated to the cells during 30 min before a challenge with H2O2 at 300 μM for additional 24 h. GAS prevented the activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway by modulating the levels of Bcl-2 and Bax, causing a decrease in the release of cytochrome c to the cytosol. GAS also prevented the activation of the pro-apoptotic enzymes caspase-9 and caspase-3. Consequently, GAS abrogated poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage and DNA fragmentation in the H2O2-treated SH-SY5Y cells. Moreover, GAS reduced the levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and the activity of nuclear factor-κB in H2O2-treated cells. Silencing of Nrf2 by small interfering RNA (siRNA) suppressed the GAS-induced cytoprotection. Thus, GAS elicited anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects by a mechanism involving Nrf2 in SH-SY5Y cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcaraz MJ, Fernández P, Guillén MI (2003) Anti-inflammatory actions of the heme oxygenase-1 pathway. Curr Pharm Des 9:2541–2551
Amor S, Peferoen LA, Vogel DY, Breur M, van der Valk P, Baker D, van Noort JM (2014) Inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases--an update. Immunology 142:151–166. https://doi.org/10.1111/imm.12233
Buendia I, Michalska P, Navarro E, Gameiro I, Egea J, León R (2016) Nrf2-ARE pathway: an emerging target against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol Ther 157:84–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.11.003
Cappellano G, Carecchio M, Fleetwood T, Magistrelli L, Cantello R, Dianzani U, Comi C (2013) Immunity and inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Am J Neurodegener Dis 2:89–107
Chen WW, Zhang X, Huang WJ (2016) Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases (review). Mol Med Rep 13:3391–3396. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.4948
Chen J, Gu YT, Xie JJ, Wu CC, Xuan J, Guo WJ, Yan YZ, Chen L, Wu YS, Zhang XL, Xiao J, Wang XY (2017) Gastrodin reduces IL-1β-induced apoptosis, inflammation, and matrix catabolism in osteoarthritis chondrocytes and attenuates rat cartilage degeneration in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother 97:642–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.067
Cuadrado A, Martín-Moldes Z, Ye J, Lastres-Becker I (2014) Transcription factors NRF2 and NF-κB are coordinated effectors of the Rho family, GTP-binding protein RAC1 during inflammation. J Biol Chem 289:15244–15258. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.540633
de Oliveira MR, Ferreira GC, Schuck PF, Dal Bosco SM (2015) Role for the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway in the protective effects of carnosic acid against methylglyoxal-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Chem Biol Interact 242:396–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2015.11.003
de Oliveira MR, Peres A, Ferreira GC, Schuck PF, Bosco SM (2016) Carnosic acid affords mitochondrial protection in chlorpyrifos-treated Sh-Sy5y cells. Neurotox Res 30:367–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-016-9620-x
de Oliveira MR, Peres A, Ferreira GC, Schuck PF, Gama CS, Bosco SMD (2017a) Carnosic acid protects mitochondria of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells exposed to paraquat through activation of the Nrf2/HO-1Axis. Mol Neurobiol 54:5961–5972. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0100-3
de Oliveira MR, Brasil FB, Andrade CMB (2017b) Naringenin attenuates H2O2-induced mitochondrial dysfunction by an Nrf2-dependent mechanism in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurochem Res 42:3341–3350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2376-8
de Oliveira MR, Schuck PF, Bosco SMD (2017c) Tanshinone I induces mitochondrial protection through an Nrf2-dependent mechanism in paraquat-treated human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Mol Neurobiol 54:4597–4608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0009-x
de Oliveira MR, de Souza IC, Fürstenau CR (2017d) Carnosic acid induces anti-inflammatory effects in paraquat-treated SH-SY5Y cells through a mechanism involving a crosstalk between the Nrf2/HO-1 axis and NF-κB. Mol Neurobiol 55:890–897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0389-6
de Oliveira MR, da Costa Ferreira G, Brasil FB, Peres A (2017e) Pinocembrin suppresses H2O2-induced mitochondrial dysfunction by a mechanism dependent on the Nrf2/HO-1 axis in SH-SY5Y cells. Mol Neurobiol 55:989–1003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0380-7
de Oliveira MR, de Bittencourt Brasil F, Fürstenau CR (2017f) Sulforaphane promotes mitochondrial protection in SH-SY5Y cells exposed to hydrogen peroxide by an Nrf2-dependent mechanism. Mol Neurobiol 55:4777–4787. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0684-2
Du F, Wang X, Shang B, Fang J, Xi Y, Li A, Diao Y (2016) Gastrodin ameliorates spinal cord injury via antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Acta Biochim Pol 63:589–593. https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2016_1272
Dunham J, van de Vis R, Bauer J, Wubben J, van Driel N, Laman JD, ‘t Hart BA, Kap YS (2017) Severe oxidative stress in an acute inflammatory demyelinating model in the rhesus monkey. PLoS One 12:e0188013. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188013
Foresti R, Bains SK, Pitchumony TS, de Castro Brás LE, Drago F, Dubois-Randé JL, Bucolo C, Motterlini R (2013) Small molecule activators of the Nrf2-HO-1 antioxidant axis modulate heme metabolism and inflammation in BV2 microglia cells. Pharmacol Res 76:132–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2013.07.010
González H, Pacheco R (2014) T-cell-mediated regulation of neuroinflammation involved in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuroinflammation 11:201. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-014-0201-8
González H, Elgueta D, Montoya A, Pacheco R (2014) Neuroimmune regulation of microglial activity involved in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuroimmunol 274:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2014.07.012
Hulsmans M, Holvoet P (2010) The vicious circle between oxidative stress and inflammation in atherosclerosis. J Cell Mol Med 14:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00978.x
Hussain T, Tan B, Liu G, Murtaza G, Rahu N, Saleem M, Yin Y (2017) Modulatory mechanism of polyphenols and Nrf2 signaling pathway in LPS challenged pregnancy disorders. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2017:8254289. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8254289
Jiang G, Hu Y, Liu L, Cai J, Peng C, Li Q (2014) Gastrodin protects against MPP(+)-induced oxidative stress by up regulates heme oxygenase-1 expression through p38 MAPK/Nrf2 pathway in human dopaminergic cells. Neurochem Int 75:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2014.06.003
Jones JT, Qian X, van der Velden JL, Chia SB, McMillan DH, Flemer S, Hoffman SM, Lahue KG, Schneider RW, Nolin JD, Anathy V, van der Vliet A, Townsend DM, Tew KD, Janssen-Heininger YM (2016) Glutathione S-transferase pi modulates NF-κB activation and pro-inflammatory responses in lung epithelial cells. Redox Biol 8:375–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2016.03.005
Kallaur AP, Lopes J, Oliveira SR, Simão AN, Reiche EM, de Almeida ER, Morimoto HK, de Pereira WL, Alfieri DF, Borelli SD, Kaimen-Maciel DR, Maes M (2016) Immune-inflammatory and oxidative and nitrosative stress biomarkers of depression symptoms in subjects with multiple sclerosis: increased peripheral inflammation but less acute neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol 53:5191–5202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9443-4
Kobayashi EH, Suzuki T, Funayama R, Nagashima T, Hayashi M, Sekine H, Tanaka N, Moriguchi T, Motohashi H, Nakayama K, Yamamoto M (2016) Nrf2 suppresses macrophage inflammatory response by blocking proinflammatory cytokine transcription. Nat Commun 7:11624. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11624
Li Q, Niu C, Zhang X, Dong M (2017) Gastrodin and isorhynchophylline synergistically inhibit MPP+-induced oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells by targeting ERK1/2 and GSK-3β pathways: involvement of Nrf2 nuclear translocation. ACS Chem Neurosci 9:482–493. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00247
Liang WZ, Jan CR, Hsu SS (2017) Cytotoxic effects of gastrodin extracted from the rhizome of Gastrodia elata Blume in glioblastoma cells, but not in normal astrocytes, via the induction of oxidative stress-associated apoptosis that involved cell cycle arrest and p53 activation. Food Chem Toxicol 107:280–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.07.013
Liu B, Li F, Shi J, Yang D, Deng Y, Gong Q (2016) Gastrodin ameliorates subacute phase cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Mol Med Rep 14:4144–4152. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5785
Ljubisavljevic S (2016) Oxidative stress and neurobiology of demyelination. Mol Neurobiol 53:744–758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9041-x
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Muriach M, Flores-Bellver M, Romero FJ, Barcia JM (2014) Diabetes and the brain: oxidative stress, inflammation, and autophagy. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2014:102158. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/102158
Nguyen T, Sherratt PJ, Pickett CB (2003) Regulatory mechanisms controlling gene expression mediated by the antioxidant response element. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:233–260
Niranjan R (2014) The role of inflammatory and oxidative stress mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease: focus on astrocytes. Mol Neurobiol 49:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8483-x
Nopparat C, Chantadul V, Permpoonputtana K, Govitrapong P (2017) The anti-inflammatory effect of melatonin in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells exposed to sublethal dose of hydrogen peroxide. Mech Ageing Dev 164:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2017.04.001
Peng Z, Wang H, Zhang R, Chen Y, Xue F, Nie H, Chen Y, Wu D, Wang Y, Wang H, Tan Q (2013) Gastrodin ameliorates anxiety-like behaviors and inhibits IL-1beta level and p38 MAPK phosphorylation of hippocampus in the rat model of posttraumatic stress disorder. Physiol Res 62:537–545
Quesada A, Ogi J, Schultz J, Handforth A (2011) C-terminal mechano-growth factor induces heme oxygenase-1-mediated neuroprotection of SH-SY5Y cells via the protein kinase Cϵ/Nrf2 pathway. J Neurosci Res 89:394–405. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.22543
Rao NA, Romero JL, Sevanian A, Fernandez MA, Wong C, Ward PA, Marak GE Jr (1988) Anti-inflammatory effect of glutathione peroxidase on experimental lens-induced uveitis. Ophthalmic Res 20:213–219
Rojo AI, Innamorato NG, Martín-Moreno AM, De Ceballos ML, Yamamoto M, Cuadrado A (2010) Nrf2 regulates microglial dynamics and neuroinflammation in experimental Parkinson's disease. Glia 58:588–598. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.20947
Taki-Nakano N, Ohzeki H, Kotera J, Ohta H (2014) Cytoprotective effects of 12-oxo phytodienoic acid, a plant-derived oxylipin jasmonate, on oxidative stress-induced toxicity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840:3413–3422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.09.003
van der Vliet A, Janssen-Heininger YM (2014) Hydrogen peroxide as a damage signal in tissue injury and inflammation: murderer, mediator, or messenger? J Cell Biochem 115:427–435. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24683
Wang J, Liu H, Zhang X, Li X, Geng L, Zhang H, Zhang Q (2017) Sulfated hetero-polysaccharides protect SH-SY5Y cells from H2O2-induced apoptosis by affecting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Mar Drugs 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15040110
Wardyn JD, Ponsford AH, Sanderson CM (2015) Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways. Biochem Soc Trans 43:621–626. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20150014
Xiao MM, Zhang YQ, Wang WT, Han WJ, Lin Z, Xie RG, Cao Z, Lu N, Hu SJ, Wu SX, Dong H, Luo C (2016) Gastrodin protects against chronic inflammatory pain by inhibiting spinal synaptic potentiation. Sci Rep 6:37251. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37251
Xue B, Wu Y, Yin Z, Zhang H, Sun S, Yi T, Luo L (2005) Regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by glutathione S-transferase P1 in RAW264.7 cells. FEBS Lett 579:4081–4087
Yang XD, Zhu J, Yang R, Liu JP, Li L, Zhang HB (2007) Phenolic constituents from the rhizomes of Gastrodia elata. Nat Prod Res 21:180–186
Funding
This work was supported by CNPq and FOPESQ/UFF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Figure S1.
The effect of GAS on the viability of H2O2-treated SH-SY5Y cells. The cells were exposed to GAS at 1-25 μM for 30 min prior a challenge with H2O2 at 300 μM for further 24 h. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM of three or five independent experiments each done in triplicate. One-way ANOVA followed by the post hoc Tukey’s test, *p < 0.05 different from the control group; # different from H2O2-treated group. (PDF 100 kb)
Figure S2.
The effect of GAS on the levels of p65 in the nucleus of H2O2-treated SH-SY5Y cells. The cells were exposed to GAS at 25 μM for 30 min prior a challenge with H2O2 at 300 μM for further 24 h. SN50 at 0.5 μM was administrated to the cells for 1 h before exposure to GAS. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM of three or five independent experiments each done in triplicate. One-way ANOVA followed by the post hoc Tukey’s test, *p < 0.05 different from the control group; # different from H2O2-treated group. (PDF 95.9 kb)
Figure S3.
The effect of SN50 on the activity of NF-κB in H2O2-treated SH-SY5Y cells. The cells were exposed to SN50 at 0.5 μM for 1 h before a challenge with H2O2 at 300 μM for further 24 h. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM of three or five independent experiments each done in triplicate. One-way ANOVA followed by the post hoc Tukey’s test, *p < 0.05 different from the control group; # different from H2O2-treated group. (PDF 98.3 kb)
Figure S4.
The effects of silencing with siRNA (for 48 h) on the activity of Nrf2 in SH-SY5Y cells treated with GAS at 25 μM for 12 h. Data are exhibited as the mean ± SEM of three or five independent experiments each done in triplicate. One-way ANOVA followed by the post hoc Tukey’s test, * p < 0.05 vs the control group; ** p < 0.05 vs GAS-treated cells transfected with negative control (NC) siRNA. (PDF 82.5 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, M.R., Brasil, F.B. & Fürstenau, C.R. Nrf2 Mediates the Anti-apoptotic and Anti-inflammatory Effects Induced by Gastrodin in Hydrogen Peroxide–Treated SH-SY5Y Cells. J Mol Neurosci 69, 115–122 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01339-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01339-3