Abstract
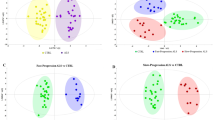
Neurosyphilis is a chronic central nervous system infectious disease caused by Treponema pallidum. Our aim was to study the metabolic profiling in the cerebrospinal fluid of neurosyphilis patients and identify specific potential biomarkers. Fifteen cerebrospinal fluid samples from neurosyphilis patients and 14 non-neurosyphilis samples were analyzed by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometer (LC–MS). The LC–MS data were preprocessed by supervised pattern recognition to obtain diagnostic models. Both orthogonal projections to a latent structures discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) and a t test were used to obtain specific metabolites for neurosyphilis. LC–MS data showed that the metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from neurosyphilis are different from the non-neurosyphilis group. The OPLS-DA model parameters R2Y and Q2Y are both more than 0.7 and indicated a satisfactory diagnostic performance. Bilirubin, l-histidine, prostaglandin E2, alpha-kamlolenic acid, and butyryl-l-carnitine and palmitoyl-l-carnitine were identified as novel potential biomarkers for neurosyphilis. The metabolic study of CSF may provide a new way to explore the pathogenesis of neurosyphilis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during this study are available in the data repository: https://github.com/xuying11/data.git
References
Bjerrum JT (2015) Metabonomics: methods and protocols: preface. Methods Mol Biol:1277:v
Castro R, Prieto ES, FDM P (2008) Nontreponemal tests in the diagnosis of neurosyphilis: an evaluation of the venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) and the rapid plasma Reagin (RPR) tests. J Clin Lab Anal 22:257–261. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.20254
Chong WPK, Thng SH, Hiu AP, Lee DY, ECY C, Ho YS (2012) LC-MS-based metabolic characterization of high monoclonal antibody-producing Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:3103–3111. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24580
de Voux A, Kidd S (2015) Torrone EA (2018) reported cases of Neurosyphilis among early syphilis cases-United States, 2009 to. Sex Transm Dis 45:39–41. https://doi.org/10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000687
Elias J, Deconing JP, Vorster SA, Joubert HF (1989) The rapid and sensitive diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis by the detection of Tuberculostearic acid in cerebrospinal-fluid using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry with selective ion monitoring. Clin Biochem 22:463–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-9120(89)80099-2
Friedrich F, Aigner M, Fearns N, Friedrich ME, Frey R (2014) Geusau A, Psychosis in neurosyphilis -- clinical aspects and implications psychopathology. 47:3–9. https://doi.org/10.1159/000350059
Gazzin S, Strazielle N, Tiribelli C, Ghersi-Egea JF (2012) Transport and metabolism at blood-brain interfaces and in neural cells: relevance to bilirubininduced encephalopathy Front Pharmacol 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2012.00089
Guarner J, Jost H, Pillay A, Sun Y, Cox D, Notenboom R, Workowski K (2015) Evaluation of treponemal serum tests performed on cerebrospinal fluid for diagnosis of neurosyphilis. Am J Clin Pathol 143:479–484. https://doi.org/10.1309/AJCPWSL3G8RXMCQR
Hicks LC, Ralphs SJ, Williams HR (2015) Metabonomics and diagnostics. Methods Mol Biol 1277:233–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2377-9_16
Ho EL, Tantalo LC, Jones T, Sahi SK, Marra CM (2015) Point-of-care treponemal tests for neurosyphilis diagnosis. Sex Transm Dis 42:48–52. https://doi.org/10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000222
Hosotani R, Inoue W, Takemiya T, Yamagata K, Kobayashi S, Matsumura K (2015) Prostaglandin transporter in the rat brain: its localization and induction by lipopolysaccharide. Temperature (Austin) 2:425–434. https://doi.org/10.1080/23328940.2015.1062953
Kinikar A et al (2017) Maternal syphilis: an independent risk factor for mother to infant human immunodeficiency virus transmission. Sex Transm Dis 44:371–375. https://doi.org/10.1097/OLQ.0000000000000622
Lee JH, Lim CS, Lee MG, Kim HS (2015) Evaluation of a rapid Immunochromatographic Treponemal antibody test comparing the Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay. J Clin Lab Anal 29:383–386. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.21783
Mao C, Gao J, Jin L, Peng B, Guo Y (2018) Postmortem histopathologic analysis of Neurosyphilis: a report of 3 cases with Clinicopathologic correlations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnen/nly004
Marra CM et al (2013) Neurocognitive impairment in HIV-infected individuals with previous syphilis. Int J STD AIDS 24:351–355. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956462412472827
Marra CM, Maxwell CL, Dunaway SB, Sahi SK, Tantalo LC (2017) Cerebrospinal fluid Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay for Neurosyphilis Diagnosis. J Clin Microbiol 55:1865–1870. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00310-17
Morshed MG, Singh AE (2015) Recent trends in the serologic diagnosis of syphilis. Clin Vaccine Immunol 22:137–147. https://doi.org/10.1128/CVI.00681-14
Musharraf SG, Siddiqui AJ, Shamsi T, Choudhary MI, Rahman AU (2016) Serum metabonomics of acute leukemia using nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy Scientific Reports 6 Artn 30693 doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/Srep30693
Pamphlet STD surveillance case definitions
Pecenak J, Janik P, Vaseckova B, Trebulova K (2015) Electroconvulsive therapy treatment in a patient with Neurosyphilis and psychotic disorder: case report and literature review. J ECT 31:268–270. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCT.0000000000000217
Pyne-Geithman GJ et al (2005) Bilirubin production and oxidation in CSF of patients with cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:1070–1077. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600101
Shan L, Bao AM, Swaab DF (2017) Changes in histidine decarboxylase, histamine N-methyltransferase and histamine receptors in neuropsychiatric disorders. Handb Exp Pharmacol 241:259–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/164_2016_125
Shan L, Swaab DF, Bao AM (2013) Neuronal histaminergic system in aging and age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Exp Gerontol 48:603–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2012.08.002
Singh SM, Sharma R, Batra N, Sethi S (2017) Neurosyphilis: an underdiagnosed entity. Asian J Psychiatr 30:47–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajp.2017.07.015
Smith MA, Zhang H, Forseille L, Purves RW (2013) Characterization of novel triacylglycerol estolides from the seed oil of Mallotus philippensis and Trewia nudiflora. Lipids 48:75–85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-012-3721-y
Strand E et al (2017) Serum Acylcarnitines and risk of cardiovascular death and acute myocardial infarction in patients with stable angina pectoris. J Am Heart Assoc:6. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.116.003620
Sun R, Lai DH, Ren RX, Lian S, Zhang HP (2013) Treponema pallidum-specific antibody expression for the diagnosis of different stages of syphilis. Chin Med J 126:206–210
Tachikawa M, Ozeki G, Higuchi T, Akanuma S, Tsuji K, Hosoya K (2012) Role of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier transporter as a cerebral clearance system for prostaglandin E(2) produced in the brain. J Neurochem 123:750–760. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12018
Taylor MM, Kamb M, Wu D, Hawkes S (2017) Syphilis screening and treatment: integration with HIV services. Bull World Health Organ 95:610–610A. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.17.200923
Vanhaecke C et al (2016) Clinical and biological characteristics of 40 patients with Neurosyphilis and evaluation of Treponema pallidum nested polymerase chain reaction in cerebrospinal fluid samples. Clin Infect Dis 63:1180–1186. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciw499
Wang C, Wu K, Yu Q, Zhang S, Gao Z, Liu Y et al (2016) Cxcl13, cxcl10 and cxcl8 as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of neurosyphilis patients. Sci Rep 6:33569. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep33569
Worley B, Powers R (2016) PCA as a Practical Indicator of OPLS-DA Model Reliability. Curr Metabolomics 4:97–103. https://doi.org/10.2174/2213235x04666160613122429
Yan YX, Wang J, Qu B, Zhang Y, Wei YN, Liu HL, Wu CL (2017) CXCL13 and TH1/Th2 cytokines in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid of neurosyphilis patients Medicine 96 doi:Artn E8850 https://doi.org/10.1097/Md.0000000000008850
Yang Q, Lin SS, Yang JT, Tang LJ, Yu RQ (2017) Detection of inborn errors of metabolism utilizing GC-MS urinary metabolomics coupled with a modified orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis. Talanta 165:545–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.01.018
Ying J, Xiaohong C, Xiaomeng M, Yu Y, Fuhua P, Xueqiang H (2010) The usefulness of toluidine red unheated serum test (TRUST) in the diagnosis of HIV-negative neurosyphilis. Eur J Neurol 17:571–571
Zeng YL, Lin YQ, Zhang NN, Zou CN, Zhang HL, Peng F et al (2016) Cxcl13 chemokine as a promising biomarker to diagnose neurosyphilis in hiv-negative patients. Springerplus 5(1):743. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-016-2462-4
Funding
This work was economically supported by Shenzhen Science Plan (Nos. JCYJ20160307114925241, JCYJ20150330102720122, JCYJ20140415093052190, and cxzz201418182638764), National Natural Science Foundation of China—Shenzhen Joint Fund Project (Nos. U1713220), and Shenzhen Science and Technology Project (Nos. JCYJ20170302152605463 and JCYJ20170306123423907).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Suwen Qi, Ying Xu, Ruitian Luo, Si Huang, Tao Nie, and Quejian Zhang are responsible for the study design. The writing depends on Pu Li, Zhifeng Huang, and Qiaoliang Li.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Disclaimer
The manuscript has been seen and approved by all authors; it is neither under active consideration for publication, has not been accepted for publication, nor has it been published.
Ethical Approval
We have read and complied with the policy of the journal on ethical consent and the standards of animal care, as stated in the Guide to Authors. The approval was not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, S., Xu, Y., Luo, R. et al. Novel Biochemical Insights in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Neurosyphilis Based on a Metabonomics Study. J Mol Neurosci 69, 39–48 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01320-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01320-0