Abstract
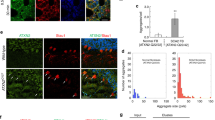
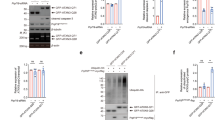
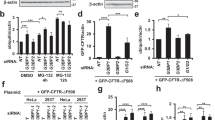
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 (SCA7) is one of nine neurodegenerative disorders caused by expanded polyglutamine domains. These so-called polyglutamine (polyQ) diseases are all characterized by aggregation. Reducing the level of aggregating polyQ proteins via pharmacological activation of autophagy has been suggested as a therapeutic approach. However, recently, evidence implicating autophagic dysfunction in these disorders has also been reported. In this study, we show that the SCA7 polyglutamine protein ataxin-7 (ATXN7) reduces the autophagic activity via a previously unreported mechanism involving p53-mediated disruption of two key proteins involved in autophagy initiation. We show that in mutant ATXN7 cells, an increased p53–FIP200 interaction and co-aggregation of p53–FIP200 into ATXN7 aggregates result in decreased soluble FIP200 levels and subsequent destabilization of ULK1. Together, this leads to a decreased capacity for autophagy induction via the ULK1–FIP200–Atg13–Atg101 complex. We also show that treatment with a p53 inhibitor, or a blocker of ATXN7 aggregation, can restore the soluble levels of FIP200 and ULK1, as well as increase the autophagic activity and reduce ATXN7 toxicity. Understanding the mechanism behind polyQ-mediated inhibition of autophagy is of importance if therapeutic approaches based on autophagy stimulation should be developed for these disorders.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Atg:
-
Autophagy-related gene
- ATXN7:
-
Ataxin-7
- BafA:
-
Bafilomycin A1
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescence protein
- HD:
-
Hungtinton’s disease
- kDa:
-
Kilodalton
- PolyQ:
-
Polyglutamine
- Q:
-
Glutamine
- QBP1:
-
Polyglutamine binding peptide 1
- SCA7:
-
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 7
References
Ajayi A, Yu X, Lindberg S, Langel U, Strom AL (2012) Expanded ataxin-7 cause toxicity by inducing ROS production from NADPH oxidase complexes in a stable inducible spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 (SCA7) model. BMC Neurosci 13:86
Bae BI, Xu H, Igarashi S, Fujimuro M, Agrawal N, Taya Y, Hayward SD, Moran TH, Montell C, Ross CA, Snyder SH, Sawa A (2005) p53 mediates cellular dysfunction and behavioral abnormalities in Huntington's disease. Neuron 47:29–41
Chen Y, Klionsky DJ (2011) The regulation of autophagy—unanswered questions. J Cell Sci 124:161–170
Cheung ZH, Ip NY (2011) Autophagy deregulation in neurodegenerative diseases—recent advances and future perspectives. J Neurochem 118:317–325
Chou AH, Lin AC, Hong KY, Hu SH, Chen YL, Chen JY, Wang HL (2011) p53 activation mediates polyglutamine-expanded ataxin-3 upregulation of Bax expression in cerebellar and pontine nuclei neurons. Neurochem Int 58:145–152
Garden GA, Libby RT, Fu YH, Kinoshita Y, Huang J, Possin DE, Smith AC, Martinez RA, Fine GC, Grote SK, Ware CB, Einum DD, Morrison RS, Ptacek LJ, Sopher BL, La Spada AR (2002) Polyglutamine-expanded ataxin-7 promotes non-cell-autonomous Purkinje cell degeneration and displays proteolytic cleavage in ataxic transgenic mice. J Neurosci 22:4897–4905
Grison A, Mantovani F, Comel A, Agostoni E, Gustincich S, Persichetti F, Del Sal G (2011) Ser46 phosphorylation and prolyl-isomerase Pin1-mediated isomerization of p53 are key events in p53-dependent apoptosis induced by mutant huntingtin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:17979–17984
Hara T, Nakamura K, Matsui M, Yamamoto A, Nakahara Y, Suzuki-Migishima R, Yokoyama M, Mishima K, Saito I, Okano H, Mizushima N (2006) Suppression of basal autophagy in neural cells causes neurodegenerative disease in mice. Nature 441:885–889
Hara T, Takamura A, Kishi C, Iemura S, Natsume T, Guan JL, Mizushima N (2008) FIP200, a ULK-interacting protein, is required for autophagosome formation in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol 181:497–510
He C, Klionsky DJ (2009) Regulation mechanisms and signaling pathways of autophagy. Annu Rev Genet 43:67–93
Helmlinger D, Hardy S, Sasorith S, Klein F, Robert F, Weber C, Miguet L, Potier N, Van-Dorsselaer A, Wurtz JM, Mandel JL, Tora L, Devys D (2004) Ataxin-7 is a subunit of GCN5 histone acetyltransferase-containing complexes. Hum Mol Genet 13:1257–1265
Heng MY, Duong DK, Albin RL, Tallaksen-Greene SJ, Hunter JM, Lesort MJ, Osmand A, Paulson HL, Detloff PJ (2010) Early autophagic response in a novel knock-in model of Huntington disease. Hum Mol Genet 19:3702–3720
Illuzzi JL, Vickers CA, Kmiec EB (2011) Modifications of p53 and the DNA damage response in cells expressing mutant form of the protein huntingtin. J Mol Neurosci 45:256–268
Jonasson J, Strom AL, Hart P, Brannstrom T, Forsgren L, Holmberg M (2002) Expression of ataxin-7 in CNS and non-CNS tissue of normal and SCA7 individuals. Acta Neuropathol 104:29–37
Katsuno M, Banno H, Suzuki K, Takeuchi Y, Kawashima M, Tanaka F, Adachi H, Sobue G (2008) Molecular genetics and biomarkers of polyglutamine diseases. Curr Mol Med 8:221–234
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H, Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M, Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, Ahn HJ, Ait-Mohamed O, Ait-Si-Ali S, Akematsu T, Akira S, Al-Younes HM, Al-Zeer MA, Albert ML, Albin RL, Alegre-Abarrategui J, Aleo MF, Alirezaei M, Almasan A, Almonte-Becerril M, Amano A, Amaravadi R, Amarnath S, Amer AO, Andrieu-Abadie N, Anantharam V, Ann DK, Anoopkumar-Dukie S, Aoki H, Apostolova N, Arancia G, Aris JP, Asanuma K, Asare NY, Ashida H, Askanas V, Askew DS, Auberger P, Baba M, Backues SK, Baehrecke EH, Bahr BA, Bai XY, Bailly Y, Baiocchi R, Baldini G, Balduini W, Ballabio A, Bamber BA, Bampton ET, Banhegyi G, Bartholomew CR, Bassham DC, Bast RC Jr, Batoko H, Bay BH, Beau I, Bechet DM, Begley TJ, Behl C, Behrends C, Bekri S, Bellaire B, Bendall LJ, Benetti L, Berliocchi L, Bernardi H, Bernassola F, Besteiro S, Bhatia-Kissova I, Bi X, Biard-Piechaczyk M, Blum JS, Boise LH, Bonaldo P, Boone DL, Bornhauser BC, Bortoluci KR, Bossis I, Bost F, Bourquin JP, Boya P, Boyer-Guittaut M, Bozhkov PV, Brady NR, Brancolini C, Brech A, Brenman JE, Brennand A, Bresnick EH, Brest P, Bridges D, Bristol ML, Brookes PS, Brown EJ, Brumell JH et al (2012) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy 8:445–544
Komatsu M, Wang QJ, Holstein GR, Friedrich VL Jr, Iwata J, Kominami E, Chait BT, Tanaka K, Yue Z (2007) Essential role for autophagy protein Atg7 in the maintenance of axonal homeostasis and the prevention of axonal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:14489–14494
Konigsmark BW, Weiner LP (1970) The olivopontocerebellar atrophies: a review. Medicine (Baltimore) 49:227–241
Li X, Li H, Li XJ (2008) Intracellular degradation of misfolded proteins in polyglutamine neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Rev 59:245–252
Liang CC, Wang C, Peng X, Gan B, Guan JL (2010) Neural-specific deletion of FIP200 leads to cerebellar degeneration caused by increased neuronal death and axon degeneration. J Biol Chem 285:3499–3509
Lindenberg KS, Yvert G, Muller K, Landwehrmeyer GB (2000) Expression analysis of ataxin-7 mRNA and protein in human brain: evidence for a widespread distribution and focal protein accumulation. Brain Pathol 10:385–394
Maiuri MC, Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Kepp O, Malik SA, Kroemer G (2010) Autophagy regulation by p53. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:181–185
Martin JJ, Van Regemorter N, Krols L, Brucher JM, de Barsy T, Szliwowski H, Evrard P, Ceuterick C, Tassignon MJ, Smet-Dieleman H et al (1994) On an autosomal dominant form of retinal-cerebellar degeneration: an autopsy study of five patients in one family. Acta Neuropathol 88:277–286
Martinez-Vicente M, Talloczy Z, Wong E, Tang G, Koga H, Kaushik S, de Vries R, Arias E, Harris S, Sulzer D, Cuervo AM (2010) Cargo recognition failure is responsible for inefficient autophagy in Huntington's disease. Nat Neurosci 13:567–576
Metzger S, Saukko M, Van Che H, Tong L, Puder Y, Riess O, Nguyen HP (2010) Age at onset in Huntington's disease is modified by the autophagy pathway: implication of the V471A polymorphism in Atg7. Hum Genet 128:453–459
Mizushima N (2010) The role of the Atg1/ULK1 complex in autophagy regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 22:132–139
Morselli E, Shen S, Ruckenstuhl C, Bauer MA, Marino G, Galluzzi L, Criollo A, Michaud M, Maiuri MC, Chano T, Madeo F, Kroemer G (2011) p53 inhibits autophagy by interacting with the human ortholog of yeast Atg17, RB1CC1/FIP200. Cell Cycle 10:2763–2769
Morselli E, Tasdemir E, Maiuri MC, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Criollo A, Vicencio JM, Soussi T, Kroemer G (2008) Mutant p53 protein localized in the cytoplasm inhibits autophagy. Cell Cycle 7:3056–3061
Nagai Y, Fujikake N, Ohno K, Higashiyama H, Popiel HA, Rahadian J, Yamaguchi M, Strittmatter WJ, Burke JR, Toda T (2003) Prevention of polyglutamine oligomerization and neurodegeneration by the peptide inhibitor QBP1 in Drosophila. Hum Mol Genet 12:1253–1259
Nagai Y, Tucker T, Ren H, Kenan DJ, Henderson BS, Keene JD, Strittmatter WJ, Burke JR (2000) Inhibition of polyglutamine protein aggregation and cell death by novel peptides identified by phage display screening. J Biol Chem 275:10437–10442
Nakamura S, Roth JA, Mukhopadhyay T (2000) Multiple lysine mutations in the C-terminal domain of p53 interfere with MDM2-dependent protein degradation and ubiquitination. Mol Cell Biol 20:9391–9398
Nakamura Y, Tagawa K, Oka T, Sasabe T, Ito H, Shiwaku H, La Spada AR, Okazawa H (2012) Ataxin-7 associates with microtubules and stabilizes the cytoskeletal network. Hum Mol Genet 21:1099–1110
Palhan VB, Chen S, Peng GH, Tjernberg A, Gamper AM, Fan Y, Chait BT, La Spada AR, Roeder RG (2005) Polyglutamine-expanded ataxin-7 inhibits STAGA histone acetyltransferase activity to produce retinal degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:8472–8477
Qin Q, Inatome R, Hotta A, Kojima M, Yamamura H, Hirai H, Yoshizawa T, Tanaka H, Fukami K, Yanagi S (2006) A novel GTPase, CRAG, mediates promyelocytic leukemia protein-associated nuclear body formation and degradation of expanded polyglutamine protein. J Cell Biol 172:497–504
Ravikumar B, Duden R, Rubinsztein DC (2002) Aggregate-prone proteins with polyglutamine and polyalanine expansions are degraded by autophagy. Hum Mol Genet 11:1107–1117
Ravikumar B, Vacher C, Berger Z, Davies JE, Luo S, Oroz LG, Scaravilli F, Easton DF, Duden R, O'Kane CJ, Rubinsztein DC (2004) Inhibition of mTOR induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease. Nat Genet 36:585–595
Shahbazian MD, Orr HT, Zoghbi HY (2001) Reduction of Purkinje cell pathology in SCA1 transgenic mice by p53 deletion. Neurobiol Dis 8:974–981
Steffan JS, Kazantsev A, Spasic-Boskovic O, Greenwald M, Zhu YZ, Gohler H, Wanker EE, Bates GP, Housman DE, Thompson LM (2000) The Huntington's disease protein interacts with p53 and CREB-binding protein and represses transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:6763–6768
Strom AL, Forsgren L, Holmberg M (2005) A role for both wild-type and expanded ataxin-7 in transcriptional regulation. Neurobiol Dis 20:646–655
Tanaka M, Machida Y, Niu S, Ikeda T, Jana NR, Doi H, Kurosawa M, Nekooki M, Nukina N (2004) Trehalose alleviates polyglutamine-mediated pathology in a mouse model of Huntington disease. Nat Med 10:148–154
Tasdemir E, Maiuri MC, Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Djavaheri-Mergny M, D'Amelio M, Criollo A, Morselli E, Zhu C, Harper F, Nannmark U, Samara C, Pinton P, Vicencio JM, Carnuccio R, Moll UM, Madeo F, Paterlini-Brechot P, Rizzuto R, Szabadkai G, Pierron G, Blomgren K, Tavernarakis N, Codogno P, Cecconi F, Kroemer G (2008) Regulation of autophagy by cytoplasmic p53. Nat Cell Biol 10:676–687
Tsoi H, Lau TC, Tsang SY, Lau KF, Chan HY (2012) CAG expansion induces nucleolar stress in polyglutamine diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:13428–13433
Wang HL, Chou AH, Lin AC, Chen SY, Weng YH, Yeh TH (2010) Polyglutamine-expanded ataxin-7 upregulates Bax expression by activating p53 in cerebellar and inferior olivary neurons. Exp Neurol 224:486–494
Wang T, Lao U, Edgar BA (2009) TOR-mediated autophagy regulates cell death in Drosophila neurodegenerative disease. J Cell Biol 186:703–711
Wong E, Cuervo AM (2010) Autophagy gone awry in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Neurosci 13:805–811
Young JE, Gouw L, Propp S, Sopher BL, Taylor J, Lin A, Hermel E, Logvinova A, Chen SF, Chen S, Bredesen DE, Truant R, Ptacek LJ, La Spada AR, Ellerby LM (2007) Proteolytic cleavage of ataxin-7 by caspase-7 modulates cellular toxicity and transcriptional dysregulation. J Biol Chem 282:30150–30160
Young JE, Martinez RA, La Spada AR (2009) Nutrient deprivation induces neuronal autophagy and implicates reduced insulin signaling in neuroprotective autophagy activation. J Biol Chem 284:2363–2373
Yu X, Ajayi A, Boga NR, Strom AL (2012) Differential degradation of full-length and cleaved ataxin-7 fragments in a novel stable inducible SCA7 model. J Mol Neurosci 47:219–233
Yvert G, Lindenberg KS, Devys D, Helmlinger D, Landwehrmeyer GB, Mandel JL (2001) SCA7 mouse models show selective stabilization of mutant ataxin-7 and similar cellular responses in different neuronal cell types. Hum Mol Genet 10:1679–1692
Zander C, Takahashi J, El Hachimi KH, Fujigasaki H, Albanese V, Lebre AS, Stevanin G, Duyckaerts C, Brice A (2001) Similarities between spinocerebellar ataxia type 7 (SCA7) cell models and human brain: proteins recruited in inclusions and activation of caspase-3. Hum Mol Genet 10:2569–2579
Acknowledgments
We thank Jessica Lundqvist and Christina Svensson for their help with RNA and RT-PCR analyses and Dr. Monica Holmberg, Umeå University, for ATXN7 constructs and antibodies. This work was supported by the Swedish Research Council (90274201), Harald Jeanssons stiftelse, Harald och Greta Jeanssons stiftelse, Magn Bergvalls stiftelse, O.E. och Edla Johanssons vetenskapliga stiftelse, Åhlen stiftelsen, Goljes stiftelse, and The Swedish Association of Persons with Neurological Disabilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 1081 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Muñoz-Alarcón, A., Ajayi, A. et al. Inhibition of Autophagy via p53-Mediated Disruption of ULK1 in a SCA7 Polyglutamine Disease Model. J Mol Neurosci 50, 586–599 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0012-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0012-x