Abstract
Aim
To evaluate the prognostic role of the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) in patients with operable gastric cancer.
Methods
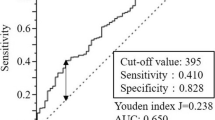
We assessed 354 patients with operable gastric cancer from tertiary centers in Turkey. SII was calculated by following formula: [neutrophil (cells × 109/L) × platelet (cells × 109/L)]/lymphocyte (cells × 109/L). The best cut-off value for SII was determined by using “receiver operating characteristics (ROC)” analysis. We used log-rank and Cox-regression analysis for survival analyses.
Results
One hundred twenty patients were in the late recurrence group (recurrences have developed 36 months after the surgery). SII was not a prognostic factor in the early recurrence group. However, relapse-free survival (RFS) was longer in SII-low patients than SII-high patients in the late recurrence group. In multivariable analysis, SII was the only independent prognostic factor for RFS in the late recurrence group (hazard ratio (HR): 5.42, 95% CI: 1.18–24.82, p = 0.03).
Conclusion
SII was an independent prognostic factor for RFS in GC patients with late recurrence. Late recurrence risk was higher in SII-high patients than SII-low patients. Inflammation contributes to tumor progression, invasion, and metastasis. Prolonged exposure to chronic inflammation could explain the results of this study.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu J, Shen L, Shui Y, et al. Patterns of recurrence after curative D2 resection for gastric cancer: Implications for postoperative radiotherapy. Cancer Med. 2020;9:4724–35.
Wu CW, Lo SS, Shen KH, et al. Incidence and factors associated with recurrence patterns after intended curative surgery for gastric cancer. World J Surg. 2003;27:153–8.
Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science. 2011;331:1565–70.
Gonzalez H, Hagerling C, Werb Z. Roles of the immune system in cancer: from tumor initiation to metastatic progression. Genes Dev. 2018;32:1267–84.
Greten FR, Grivennikov SI. Inflammation and cancer: triggers, mechanisms, and consequences. Immunity. 2019;51:27–41.
Rosales C. Neutrophil: a cell with many roles in inflammation or several cell types? Front Physiol. 2018;9:113.
Thomas MR, Storey RF. The role of platelets in inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 2015;114:449–58.
Vicente Conesa MA, Garcia-Martinez E, Gonzalez Billalabeitia E, et al. Predictive value of peripheral blood lymphocyte count in breast cancer patients treated with primary chemotherapy. Breast. 2012;21:468–74.
Liu J, Li S, Zhang S, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio can predict clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019;33:e22964.
Gao Y, Guo W, Cai S, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) is useful to predict survival outcomes in patients with surgically resected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer. 2019;10:3188–96.
Unger JM, Hershman DL, Fleury ME, Vaidya R. Association of patient comorbid conditions with cancer clinical trial participation. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5:326–33.
Kang WM, Meng QB, Yu JC, Ma ZQ, Li ZT. Factors associated with early recurrence after curative surgery for gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:5934–40.
Park JM, Ryu WS, Kim JH, et al. Prognostic factors for advanced gastric cancer: stage-stratified analysis of patients who underwent curative resection. Cancer Res Treat. 2006;38:13–8.
Habu H, Takeshita K, Sunagawa M, Endo M. Prognostic factors of early gastric cancer–results of long-term follow-up and analysis of recurrent cases. Jpn J Surg. 1987;17:248–55.
Wang Q, Zhu D. The prognostic value of systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) in patients after radical operation for carcinoma of stomach in gastric cancer. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019;10:965–78.
Chen L, Yan Y, Zhu L, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index as a useful prognostic indicator predicts survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer Manag Res. 2017;9:849–67.
Kim JP, Lee JH, Kim SJ, Yu HJ, Yang HK. Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognostic factors in 10 783 patients with gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 1998;1:125–33.
Chang SC, Liu KH, Hung CY, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy improves survival in stage III gastric cancer after D2 surgery. J Cancer. 2018;9:81–91.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–44.
Wu L, Saxena S, Awaji M, Singh RK. Tumor-associated neutrophils in cancer: going pro. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11.
Pilatova K, Zdrazilova-Dubska L, Klement GL. The role of platelets in tumour growth. Klin Onkol. 2012;25 Suppl 2:2S50–57.
Huong PT, Nguyen LT, Nguyen XB, Lee SK, Bach DH. The role of platelets in the tumor-microenvironment and the drug resistance of cancer cells. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11.
Aggarwal BB, Vijayalekshmi RV, Sung B. Targeting inflammatory pathways for prevention and therapy of cancer: short-term friend, long-term foe. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:425–30.
Hirahara N, Tajima Y, Matsubara T, et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts overall survival in patients with gastric cancer: a propensity score-matched analysis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yekedüz, E., Dogan, İ., Kaya, D.M. et al. Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index as a Prognostic Marker of Late Recurrence in Operable Gastric Cancer: a Dual-Center Study. J Gastrointest Canc 53, 870–879 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-021-00769-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-021-00769-w