Abstract
Background
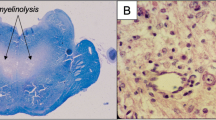
Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis (CPEPM) is a rare but potentially fatal complication after orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT). The aim of this study was to identify risk factors for development of CPEPM after OLT and to assess patient outcome.
Methods
We reviewed the clinical data of 1,378 patients who underwent OLT between 1987 and 2009 in Geneva, Switzerland and Edmonton, Canada. Nineteen patients (1.4 %) developed CPEPM. We compared their characteristics with control patients, matched by age, gender, date of OLT, and MELD score.
Results
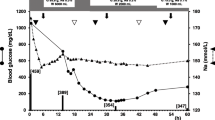
The 19 patients with CPEPM (7F, mean age 52.1 ± 2 years) had a mean MELD score of 26 ± 2.2. Before OLT, patients who develop CPEPM presented more frequently low (<130 mmol/l; p < 0.04) and very low (<125 mmol/l; p < 0.009) sodium than controls. In patients developing CPEPM, the number of platelet units and fresh frozen plasma transfused during surgery was higher (p = 0.05 and 0.047), hemorrhagic complications were more frequent after OLT (p = 0.049), and variations of sodium before and after OLT were higher (p = 0.023). The association of >2 of these conditions were strongly associated with CPEPM (p = 0.00015). Mortality at 1 year of patients developing CPEPM was higher (63 vs. 13 %, p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
High MELD score patients undergoing OLT, receiving massive perfusions of Na-rich products, experiencing surgery-related hemorrhagic complication and important fluctuations of Na are at risk of developing CPEPM. Therefore careful monitoring of natremia in the perioperative period and use of water-free perfusion in case of massive blood-products transfusion are critical points of this patient management.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Adams RD, Victor M, Mancall EL. Central pontine myelinolysis: a hitherto undescribed disease occurring in alcoholic and malnourished patients. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1959;81(2):154–72.
Wright DG, Laureno R, Victor M. Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Brain. 1979;102:361–85.
Pfister HW, Einhaupl KM, Brandt T. Mild central pontine myelinolysis: a frequently undetected syndrome. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci. 1985;235(3):134–9.
Kato T, Hattori H, Nagato M, et al. Subclinical central pontine myelinolysis following liver transplantation. Brain Dev. 2002;24(3):179–82.
Winnock S, Janvier G, Parmentier F, et al. Pontine myelinolysis following liver transplantation: a report of two cases. Transpl Int. 1993;6:26–8.
Fryer JP, Fortier M, Metrakos P, et al. Central Pontine Myelinolysis and Cyclosporine neurotoxicity following liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1996;61:658–61.
Bonham CA, Dominguez EA, Fukui MB, et al. Central nervous system lesions in liver transplant recipients: prospective assessment of indications for biopsy and implications for management. Transplantation. 1998;66(12):1596–604.
Bronster DJ, Emre S, Boccagni P, Sheiner PA, Schwartz ME, Miller CM. Central nervous system complications in liver transplant recipients-incidence, timing, and long-term follow-up. Clin Transplant. 2002;14:1–7.
Yu J, Shu-Sen Z, Ting-Bo L, Yan S, Wei-Lin W, Qing-Hong K. Possible causes of central pontine myelinolysis after liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10(17):2540–3.
Kim BS, Lee SG, Hwang S, et al. Neurologic complications in adult living donor liver transplant recipients. Clin Transplant. 2007;21:544–7.
Lee EM, Kang JK, Yun SC, et al. Risk factors for central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis following orthotopic liver transplantation. Eur Neurol. 2009;62(6):362–8.
Yun BC, Kim WR, Benson JT, et al. Impact of pretransplant hyponatremia on outcome following liver transplantation. Hepatology. 2009;49(5):1610–5.
Wszolek ZK, McComb RD, Pfeiffer RF, et al. Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis following liver transplantation. Relationship to serum sodium. Transplantation. 1989;48(6):1006–12.
Estol CJ, Faris AA, Martinez AJ, Ahdab-Barmada M. Central pontine myelinolysis after liver transplantation. Neurology. 1989;39:493–8.
Boon AP, Adams DH, Buckels JA, McMaster P. Neuropathological findings in autopsies after liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1991;23:1471–2.
Ferreiro JA, Robert MA, Townsend J, Vinters HV. Neuropathologic findings after liver transplantation. Acta Neuropathol. 1992;84(1):1–14.
Singh N, Yu VL, Gayowski T. Central nervous system lesions in adult liver transplant recipients: review with implications for management. Medicine. 1994;73:110–8.
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Rojiani AM, Filley CM. Central and extrapontine myelinolysis: then and now. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2006;65:1–11.
Lampl C, Yazdi K. Central pontine myelinolysis. Eur Neurol. 2002;47(1):3–10.
Cuervas-Mons V, Martinez AJ, Dekker A, Starzl TE, Thiel DH. Adult liver transplantation: an analysis of the early causes of death in 40 consecutive cases. Hepatology. 1986;6:495–501.
Adams DH, Gunson B, Honigsberger L, et al. Neurological complications following liver transplantation. Lancet. 1987;1:949–51.
Miller GM, Baker HL, Okazaki H, Whisnant JP. Central pontine myelinolysis and its imitators: MR findings. Radiology. 1988;168:795–802.
Reyes J, Gayowski T, Fung J, Todo S, Alessiani M, Starzl TE. Expressive dysphasia possibly related to FK 506 in two liver transplant recipients. Transplantation. 1990;50:1043–5.
Bird GL, Meadows J, Goka J, Polson R, Williams R. Cyclosporin-associated akinetic mutism and extrapyramidal syndrome after liver transplantation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990;53:1068–71.
Boon AP, Carey MP, Adams DH, Buckels J, McMaster P. Central pontine myelinolysis in liver transplantation. J Clin Pathol. 1991;44:909–14.
Burkhalter EL, Starzl TE, Van Thiel DH. Severe neurological complications following orthotopic liver transplantation in patients receiving FK 506 and Prednisone. J Hepatol. 1994;21:572–7.
Kabeer MH, Filo RS, Milgrom ML, et al. Central pontine myelinolysis following orthotopic liver transplant: association with cyclosporin toxicity. Postgrad Med J. 1995;71(834):239–41.
Menger H, Jorg J. Outcome of central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis (n = 44). J Neurol. 1999;246:700–5.
Murdoch M, Chang M, McVicar J. Central pontine myelinolysis after liver transplantation: a case report. Transpl Int. 1995;8(5):399–402.
Rodriguez J, Benito-Leon J, Molina JA, Ramos A, Bermeo F. Central Pontine myelinolysis associated with cyclosporine in liver transplantation. Neurologia. 1998;13:437–40.
Buis CI, Wijdicks EFM. Serial magnetic resonance imaging of central pontine myelinolysis. Liver Transplant. 2002;8:643–7.
Guo Y, Hu JH, Lin W, Zheng KH. Central pontine myelinolysis after liver transplantation: MR diffusion, spectroscopy and perfusion findings. Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24:1395–8.
Senzolo M, Ferronato C, Burra P. Neurologic complications after solid organ transplantation. Transpl Int. 2009;22(3):269–78.
Bechstein WO. Neurotoxicity of calcineurin inhibitors: impact and clinical management. Transpl Int. 2000;13(5):313–26.
Howard SA, Barletta JA, Klufas RA, Saad A, De Girolami U. Best cases from the AFIP: osmotic demyelination syndrome. Radiographics. 2009;29:933–8.
Chu K, Kang DW, Ko SB, Kim M. Diffusion-weighted MR findings of central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Acta Neurol Scand. 2001;104:385–8.
Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 2001;33:464–70.
Ashrafian H, Davey D. A review of the causes of central pontine myelinolysis: yet another apoptotic illness? Eur J Neurol. 2001;8:103–9.
Thurston JH, Hauhart RE, Nelson JS. Adaptive increases in amino acids (taurine in particular), creatine, and electrolytes prevent cerebral edema in chronically hyponatremic mice; rapid correction (experimental model of central pontine myelinolysis) causes dehydration and shrinkage of brain. Metab Brain Dis. 1987;2:223–41.
Brown WD. Osmotic demyelination disorders: central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Curr Opin Neurol. 2000;13:691–7.
Gines P, Guevara M. Hyponatremia in cirrhosis: pathogenesis, clinical significance, and management. Hepatology. 2008;48:1002–10.
Fukazawa K, Nishida S, Aguina L, Pretto E Jr. Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) associated with tacrolimus (FK506) after liver transplantation. Ann Transplant. 2011;16(3):139–42.
Acknowledgments
Christian Toso was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SCORE Grant 3232230-126233).
Conflict of interest
Isabelle Morard, Yvan Gasche, Mark Kneteman, Christian Toso, Ariane Mentha, Glenda Meeberg, Gilles Mentha, Norman Kneteman, and Emiliano Giostra declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morard, I., Gasche, Y., Kneteman, M. et al. Identifying Risk Factors for Central Pontine and Extrapontine Myelinolysis After Liver Transplantation: A Case–Control Study. Neurocrit Care 20, 287–295 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-013-9928-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-013-9928-9