Abstract
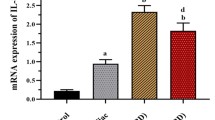
IL-39 (Interleukin-39) is a heterodimeric cytokine composed of IL-23p19 and EBI3 (Epstein-Barr virus-induced gene 3) subunits. Despite the evidence that correlates the role of IL-39 in regulating inflammation, its expression in the intestinal microenvironment of IBD (inflammatory bowel disease) patients is still unknown. Thus, this work was focused on characterizing relative mRNA (messenger RNA) IL-39 expression and intestinal synthesis in IBD patients. This study includes 37 patients diagnosed with ulcerative colitis (UC), 15 with Chron’s disease (CD), and 22 controls. Gene expression of IL-39 subunits (IL-23p19/EBI3) was measured by RT-PCR (real time polymerase chain reaction). Intestinal synthesis was evaluated by immunohistochemistry and serum levels by ELISA. Statistical analysis was done using Prism GraphPad V6. Relative mRNA IL-39 expression was increased in patients with active UC and active CD compared to the remission UC, remission CD, and control group. High levels of relative mRNA expression of IL-39 (IL-23p19 subunit) were associated with histological activity. IHQ analysis showed increased IL-39 production in mucosa, submucosa, muscular, and serosa layer of patients with active disease. IL-39 serum production was increased in patients with UC. IL-39 gene’s upregulation was found in patients with active IBD and was associated with severe histological activity in UC. This is the first report regarding the role of IL-39 in patients with IBD. The findings suggest that IL-39 might play a role as an inflammatory mediator in active IBD and could be considered a new alternative in treating this condition.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data availability will be provided upon request.
Abbreviations
- aUC:
-
Active ulcerative colitis
- aCD:
-
Active Crohn’s disease
- BAFF B:
-
Cell activation factor
- cDNA:
-
Complementary DNA
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzidine
- dNTPs:
-
Deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate
- EBI3:
-
Epstein-Barr Virus-Induced Gene 3
- GADPH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- IBD:
-
Inflammatory bowel disease
- IL-39:
-
Interleukin-39
- IL-23p19:
-
Interleukin 23 p19 subunit
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- MgCl2 :
-
Magnesium chloride
- mRNA:
-
Messenger ribonucleic acid
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- RT:
-
Reverse transcription
- RT-PCR:
-
Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Rcd:
-
Remission CD
- rUC:
-
Remission ulcerative colitis
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SEM:
-
Standard error of the mean
- STAT1/STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1–3
References
Wang X, Liu X, Zhang Y, et al. Interleukin (IL)-39 [IL-23p19/Epstein-Barr virus-induced 3 (Ebi3)] induces differentiation/expansion of neutrophils in lupus-prone mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016;186(2):144–56.
Wang X, Wei Y, Xiao H, et al. A novel IL-23p19/Ebi3 (IL-39) cytokine mediates inflammation in Lupus-like mice. Eur J Immunol. 2016;46(6):1343–50. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201546095.
Ushach I, Arrevillaga-Boni G, Heller GN, et al. Meteorin-like/meteorin-β is a novel immunoregulatory cytokine associated with inflammation. J Immunol. 2018;201(12):3669–76. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1800435.
Ushach I, Burkhardt AM, Martinez C, et al. Meteorin-like is a cytokine associated with barrier tissues and alternatively activated macrophages. Clin Immunol. 2015;156(2):119–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2014.11.00.
Bridgewood C, Alase A, Watad A, Wittmann M, Cuthbert R, McGonagle D. The IL-23p19/EBI3 heterodimeric cytokine termed IL-39 remains a theoretical cytokine in man. Inflamm Res. 2019;68(6):423–6.
Hasegawa H, Mizoguchi I, Chiba Y, Ohashi M, Xu M, Yoshimoto T. Expanding diversity in molecular structures and functions of the IL-6/IL-12 heterodimeric cytokine family. Front Immunol. 2016;4(7):479. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2016.00479.
Gholamrezayi A, Mohamadinarab M, Rahbarinejad P, et al. Characterization of the serum levels of meteorin-like in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and its association with inflammatory cytokines. Lipids Health Dis. 2020;19(1):230. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-020-01404-6.
Yamamoto-Furusho JK, Bozada-Gutiérrez KE, Sánchez-Rodríguez A, et al. Validation of a novel integral disease index for evaluating the grade of activity in Mexican patients with ulcerative colitis: a prospective cohort study. Validación de un nuevo índice integral de enfermedad para evaluar el grado de actividad en pacientes mexicanos con colitis ulcerosa: un estudio de cohorte prospectivo. Rev Gastroenterol Mex (Engl Ed). 2019;84(3):317–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rgmx.2018.07.006.
Mosli MH, Parker CE, Nelson SA, et al. Histologic scoring indices for evaluation of disease activity in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017;5(5):CD011256.
Harvey RF, Bradshaw JM. A simple index of Crohn’s-disease activity. Lancet. 1980;1(8167):514. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92767-1.
Fonseca-Camarillo G, Furuzawa-Carballeda J, Priego-Ranero ÁA, et al. AKAP12/Gravin is over-expressed in patients with ulcerative colitis. Immunol Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-021-09214-3.
Fonseca-Camarillo G, Furuzawa-Carballeda J, Priego-Ranero ÁA, Martínez-Benítez B, Barreto-Zúñiga R, Yamamoto-Furusho JK. Expression of TOB/BTG family members in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Immunol. 2021;93(4):e13004. https://doi.org/10.1111/sji.13004.
Fonseca-Camarillo G, Furuzawa-Carballeda J, Razo-López N, Barreto-Zúñiga R, Martínez-Benítez B, Yamamoto-Furusho JK. Intestinal production of secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) in patients with ulcerative colitis. Immunobiology. 2021;226(3):152095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imbio.2021.152095.
Furuzawa-Carballeda J, Uribe-Uribe NO, Arreola-Guerra JM, et al. Tissue talks: immunophenotype of cells infiltrating the graft explains histological findings and the benefits of belatacept at 10 years. Clin Exp Immunol. 2019;197(2):250–61. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.13296.
Fonseca-Camarillo G, Furuzawa-Carballeda J, Martínez-Benitez B, Barreto-Zuñiga R, Yamamoto-Furusho JK. Increased expression of extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (EMMPRIN) and MMP10, MMP23 in inflammatory bowel disease: Cross-sectional study. Scand J Immunol. 2021;93(1):e12962. https://doi.org/10.1111/sji.12962.
Lu Z, Xu K, Wang X, Li Y, Li M. Interleukin 39: a new member of interleukin 12 family. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2020;45(2):214–7. https://doi.org/10.5114/ceji.2020.97911.
Luo Y, Liu F, Liu H, et al. Elevated serum IL-39 in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction was related with left ventricular systolic dysfunction. Biomark Med. 2017;11(6):419–26. https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm-2016-0361.
Ecoeur F, Weiss J, Schleeger S, Guntermann C. Lack of evidence for expression and function of IL-39 in human immune cells. PLoS ONE. 2020;15(12):e0242329. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0242329.
Weng L, Huang G, Gong L, et al. Low levels of serum IL-39 are associated with autoimmune thyroid disease. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022;36(4):e24284. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.24284.
Papp KA, Blauvelt A, Bukhalo M, Gooderham M, Krueger JG, Lacour J-P, et al. Risankizumab versus ustekinumab for moderate to-severe plaque psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 2017;376(16):1551–60. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1607017.
Al-Janabi A, Jabbar-Lopez ZK, Griffiths CEM, Yiu ZZN. Risankizumab vs. ustekinumab for plaque psoriasis: a critical appraisal. Br J Dermatol. 2019;180(6):1348–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.17624.
Wetzel A, Scholtka B, Gerecke C, Kleuser B. Epigenetic histone modulation contributes to improvements in inflammatory bowel disease via EBI3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(23):5017–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-020-03451-9.
Guo Yifei, et al. Immunoregulatory functions of the IL-12 family of cytokines in antiviral systems. Viruses. 2019;11(9):772.22. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11090772.
Funding
This work was supported by funds from the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Clinic at the National Institute of Medical Sciences and Nutrition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GFC participated during the sample processing, performed RT-qPCR analysis for IL-39 transcript level quantification, performed IHQ analysis for protein expression, and data analysis, and prepared the manuscript, critical reviewing, and bibliographic analysis.
JFC participated during IHQ analysis for protein expression, data analysis, prepared the manuscript, critical reviewing, and bibliographic analysis.
BMB and RBZ participate during the sample acquisition.
JKYF provided the research idea and financial resources as well as assessed clinical, endoscopic and histological findings, data analysis, prepared and coordinated the manuscript editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fonseca-Camarillo, G., Furuzawa-Carballeda, J., Barreto-Zúñiga, R. et al. Increased synthesis and intestinal expression of IL-39 in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Immunol Res 72, 284–292 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-023-09432-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-023-09432-x