Abstract
Purpose
Radioactive-iodine (RAI)-resistant differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) patients benefit from multi-kinase inhibitors (MKIs), such as lenvatinib. Incidence of treatment-related (TR) late toxicities has been not yet described.
Methods
From January 2015 to June 2019 we retrospectively reviewed clinical records of patients with RAI-resistant DTC treated with lenvatinib at Istituto Nazionale dei Tumori (Milan, Italy). New side effect of any grade, appeared after 12 months of lenvatinib, was defined as late adverse event (AE). Descriptive analyses were performed. Survival curves were estimated with Kaplan–Meier method and compared with log-rank test.
Results
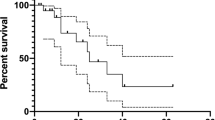
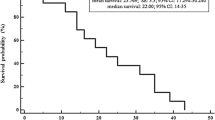
Thirty-seven patients were included, 65% had ≥65 years and 68% were female. Thirty patients received lenvatinib for >12 months. Lenvatinib was started at ≤20 mg/daily in 59% of patients, 64% were ≥65 years. The frequency of late AEs was 80% and cardiovascular toxicity was the most common (57%). There was no difference in the incidence of late AEs between younger/older population (77% and 82%, respectively). Median lenvatinib treatment duration (TD) was 39.96 months (95% CI 21.64-NR): 39.96 months for patients <65 years (95% CI: 13.25-NR) and 37.53 months for those ≥65 years, respectively (95% CI: 15.85-NR). Median overall survival (OS) was 39.96 months (95% CI: 21.84-NR), no statistically differences in OS was observed between younger (<65 years) and older patients (≥65 years) (HR 1.013; 95% CI 0.963–1.065; p = 0.62).
Conclusion
Late toxicity burden of lenvatinib is not negligible. Cardiovascular toxicity remains the principal side effect even after a prolonged lenvatinib exposition.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Electronic dataset.
References
N. Howlader, A. M. Noone, M. Krapcho, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2013. (National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, 2016) http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2013
M. Schlumberger, M. Tahara, L.J. Wirth et al. Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodine-refractory thyroid cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 372(7), 621–630 (2015)
M.S. Brose, C.M. Nutting, B. Jarzab et al. Sorafenib in radioactive iodine-refractory, locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer: a randomized, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet 384(9940), 319–328 (2014)
R.I. Haddad, M. Schlumberger, L.J. Wirth et al. Incidence and timing of common adverse events in Lenvatinib-treated patients from the SELECT trial and their association with survival outcomes. Endocrine 56(1), 121–128 (2017)
A. Berdelou, I. Borget, Y. Godbert, et al. Lenvatinib for the Treatment of Radioiodine-Refractory Thyroid Cancer in Real-Life Practice. Thyroid; https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2017.0205 (2017)
A. Nervo, M. Gallo, M.T. Samà et al. Lenvatinib in Advanced Radioiodine-refractory Thyroid Cancer: a Snapshot of Real-life Clinical Practice. Anticancer Res. 38(3), 1643–1649 (2018)
L.D. Locati, A. Piovesan, C. Durante et al. Real-world efficacy and safety of lenvatinib: data from a compassionate use in the treatment of radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer patients in Italy. Eur. J. Cancer 118, 35–40 (2019)
F. Jerkovich, I. Califano, F. Bueno et al. Real-life use of lenvatinib in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: experience from Argentina. Endocrine 69(1), 142–148 (2020)
E.V. Borodavina, P. Isaev, A. Shurinov, V. Krylov, Efficacy and tolerability of lenvatinib in patients with radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid Cancer: results a multicentre observational study Russian Federation. Head Neck Tumours 10, 65–72 (2020)
AAVV, AIOM guidelines on thyroid cancer, https://www.aiom.it (2017)
B.R. Haugen, E.K. Alexander, K.C. Bible et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: the American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 26(1), 1–133 (2016)
S. Filetti, C. Durante, D. Hartl et al. ESMO Guidelines Committee. Thyroid cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 30(12), 1856–1883 (2019)
M.E. Cabanillas, D.G. McFadden, C. Durante, Thyroid Cancer Lancet 388(10061), 2783–2795 (2016)
L.J. Wirth, M. Tahara, B. Robinson et al. Treatment-emergent hypertension and efficacy in the phase 3 Study of (E7080) lenvatinib in differentiated cancer of the thyroid (SELECT). Cancer 124(11), 2365–2372 (2018)
J.F. Piccirillo, Importance of comorbidity in head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope 110(4), 593–602 (2000)
M. Schlumberger, M. Brose, R. Elisei et al. Definition and management of radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2(5), 356–358 (2014)
M. Tahara, M.S. Brose, L.J. Wirth et al. Impact of dose interruption on the efficacy of lenvatinib in a phase 3 study in patients with radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 106, 61–68 (2019)
L. Paschke, T. Lincke, K. Mühlberg, T.H. Lindner, R. Paschke, Myocardial Infarction after Long-Term Treatment with a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) with Anti-VEGF Receptor Activity. Case Rep. Endocrinol. 2019, 7927450 (2019)
A. Ravaud, C. de la Fouchardière, P. Caron et al. A multicenter phase II study of sunitinib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic differentiated, anaplastic or medullary thyroid carcinomas: mature data from the THYSU study. Eur. J. Cancer 76, 110–117 (2017)
G. Curigliano, D. Lenihan, M. Fradley et al. ESMO Guidelines Committee. Management of cardiac disease in cancer patients throughout oncological treatment: ESMO consensus recommendations. Ann. Oncol. 31(2), 171–190 (2020)
S. Cavalieri, L. Cosmai, A. Genderini et al. Lenvatinib-induced renal failure: two first-time case reports and review of literature. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 14(4), 379–385 (2018)
C. Resteghini, S. Cavalieri, D. Galbiati et al. Management of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) side effects in differentiated and medullary thyroid cancer patients. Best. Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 31(3), 349–361 (2017)
M. Sanda, H. Tamai, H. Deguchi et al. Acalculous cholecystitis in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma on sorafenib. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2011, 201529 (2011)
Y. Aihara, H. Yoshiji, M. Yamazaki et al. A case of severe acalculous cholecystitis associated with sorafenib treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 4(5), 115–118 (2012)
J. Song, S.B. Kim, K.H. Kim, T.N. Kim, K.H. Lee, A case report of motesanib-induced biliary sludge formation causing obstructive cholangitis with acute pancreatitis treated by endoscopic sphincterotomy. Med. (Baltim.) 95(37), e4645 (2016)
K. Ishigaki, T. Hamada, Y. Nakai et al. Lenvatinib-induced acute acalculous cholecystitis in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 13(4), 568–571 (2020)
A. Nervo, A. Ragni, M. Gallo et al. Symptomatic Biliary Disorders During Lenvatinib Treatment for Thyroid Cancer: an Underestimated Problem. Thyroid 30(2), 229–236 (2020)
C. Colombo, S. De Leo, M. Di Stefano, G. Vannucchi, L. Persani, L. Fugazzola, Primary Adrenal Insufficiency During Lenvatinib or Vandetanib and Improvement of Fatigue After Cortisone Acetate Therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 104(3), 779–784 (2019)
J.D. Cox, J. Stetz, T.F. Pajak, Toxicity criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC). Int J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 31(5), 1341–1346 (1995)
J.A. Langendijk, P. Doornaert, Verdonck-de Leeuw IM, Leemans CR, Aaronson NK, Slotman BJ. Impact of late treatment-related toxicity on quality of life among patients with head and neck cancer treated with radiotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 26(22), 3770–3776 (2008)
G. Thanarajasingam, P.J. Atherton, P.J. Novotny, C.L. Loprinzi, J.A. Sloan, A. Grothey, Longitudinal adverse event assessment in oncology clinical trials: the Toxicity over Time (ToxT) analysis of Alliance trials NCCTG N9741 and 979254. Lancet Oncol. 17(5), 663e70 (2016)
A. Hochhaus, S.G. O’Brien, F. Guilhot et al. Six-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for the first line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 23, 1054–1061 (2009)
C. Giani, L. Valerio, A. Bongiovanni et al. Safety and Quality-of-Life Data from an Italian Expanded Access Program of Lenvatinib for Treatment of Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 31(2), 224–232 (2021)
T.H. Brümmendorf, J.E. Cortes, C.A. de Souza et al. Bosutinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronicmyeloid leukaemia: results from the 24-month follow-up of the BELA trial. Br. J. Haematol. 168, 69–81 (2014)
E. Jabbour, H.M. Kantarjian, G. Saglio et al. Early response with dasatinib or imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia: 3-year followup from a randomized phase 3 trial (DASISION). Blood 123, 494–500 (2014)
R.A. Larson, A. Hochhaus, T.P. Hughes et al. Nilotinib vs. imatinib in patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase: ENESTnd 3-year follow-up. Leukemia 26, 2197–2203 (2012)
M.S. Marcolino, E. Boersma, N.C.D. Clementino et al. Imatinib treatment duration is related to decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate in chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Ann. Oncol. 22, 2073–2079 (2011)
M.S. Brose, F.P. Worden, K.L. Newbold, M. Guo, A. Hurria, Effect of Age on the Efficacy and Safety of Lenvatinib in Radioiodine-Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer in the Phase III SELECT Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 35(23), 2692–2699 (2017)
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors revised the paper; F.P., S.C. and L.D.L. wrote the first paper draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
L.D.L. reports grant and other financial relationship with Eisai, Ipsen, Merck Serono, MSD, BMS, Lilly. No competing interests could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Ethical approval
Approved with the code INT 135/20.
Informed consent
All the patients signed up a written informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Platini, F., Cavalieri, S., Alfieri, S. et al. Late toxicities burden in patients with radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer treated with lenvatinib. Endocrine 73, 641–647 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02702-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-021-02702-4