Abstract
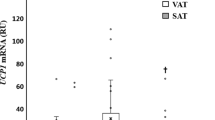
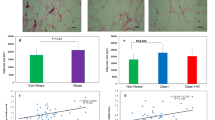
The objective of this study is to determine the property of human perirenal adipose tissue (PAT) and assess the adipose property of PAT in hypertension. Ninety-four patients, including 64 normotensive patients (T-NP) and 30 hypertensive patients (HP), who underwent renal surgery were included. Expression analysis was performed using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry in PAT and back subcutaneous adipose tissue (bSAT) depots. Compared with bSAT, PAT adipocytes were smaller, and the expressions of uncoupling protein-1 (UCP1) mRNA and protein were markedly higher, while the mRNA expressions of markers for classic beige and white adipocytes were lower in PAT. Immunohistochemistry analysis showed more multilocular UCP1-positive adipocytes in PAT than in bSAT. UCP1 expressions were lower in PAT in HP than in the T-NP or age- and body mass index-matched NP groups. Bigger unilocular adipocytes with less UCP1 staining in PAT were detected in HP than in NP group, although no such difference was observed in bSAT. PAT acts as a brown-like fat. UCP1 expression of PAT was lower in HP than in normotensive patients. UCP1 expression of PAT may serve as a protective indicator for hypertension.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.M. Friedman, A war on obesity, not the obese. Science 299, 856–858 (2003)
Y. Matsuzawa, T. Funahashi, T. Nakamura, The concept of metabolic syndrome: contribution of visceral fat accumulation and its molecular mechanism. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 18, 629–639 (2011)
N. Ouchi, J.L. Parker, J.J. Lugus, K. Walsh, Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 85–97 (2011)
M.C. Foster, S.J. Hwang, S.A. Porter, J.M. Massaro, U. Hoffmann, C.S. Fox, Fatty kidney, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease: the Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension 58, 784–790 (2011)
S. Ringholm, J. Grunnet Knudsen, L. Leick, A. Lundgaard, M. Munk Nielsen, H. Pilegaard, PGC-1alpha is required for exercise- and exercise training-induced UCP1 up-regulation in mouse white adipose tissue. PLoS One 8, e64123 (2013)
P. Bostrom, J. Wu, M.P. Jedrychowski, A. Korde, L. Ye, J.C. Lo, K.A. Rasbach, E.A. Bostrom, J.H. Choi, J.Z. Long, S. Kajimura, M.C. Zingaretti, B.F. Ving, H. Tu, S. Cinti, K. Hojlund, S.P. Gyqi, B.M. Spiegelman, A PGC1-alpha-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 481, 463–468 (2012)
P.A. Svensson, K. Lindberg, J.M. Hoffmann, M. Taube, M.J. Pereira, T. Mohsen-Kanson, A.L. Hafner, M. Rizell, J. Palming, C. Dani, M.K. Svensson, Characterization of brown adipose tissue in the human perirenal depot. Obesity 22, 1830–1837 (2014)
D. Ricquier, Respiration uncoupling and metabolism in the control of energy expenditure. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 64, 47–52 (2005)
L. Chang, L. Villacorta, R. Li, M. Hamblin, W. Xu, C. Dou, J. Zhang, J. Wu, R. Zeng, Y.E. Chen, Loss of perivascular adipose tissue on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma deletion in smooth muscle cells impairs intravascular thermoregulation and enhances atherosclerosis. Circulation 126, 1067–1078 (2012)
M. Dong, X. Yang, S. Lim, Z. Cao, J. Honek, H. Lu, C. Zhang, T. Seki, K. Hosaka, E. Wahlberg, J. Yang, L. Zhang, T. Lanne, B. Sun, X. Li, Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, Y. Cao, Cold exposure promotes atherosclerotic plaque growth and instability via UCP1-dependent lipolysis. Cell Metab. 18, 118–129 (2013)
A.V. Chobanian, G.L. Bakris, H.R. Black, W.C. Cushman, L.A. Green, JLJr Izzo, D.W. Jones, B.J. Materson, S. Oparil, JTJr Wright, E.J. Roccella, The seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 289, 2560–2572 (2003)
T. Montalcini, G. Gorgone, A. Fava, S. Romeo, C. Gazzaruso, A. Pujia, Carotid and brachial arterial enlargement in postmenopausal women with hypertension. Menopause 19, 145–149 (2012)
Z. Wu, P. Puigserver, U. Andersson, C. Zhang, G. Adelmant, V. Mootha, A. Troy, S. Cinti, B. Lowell, R.C. Scarpulla, B.M. Spiegelam, Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell 98, 115–124 (1999)
P. Seale, B. Bjork, W. Yang, S. Kajimura, S. Chin, S. Kuang, A. Scime, S. Devarakonda, H.M. Conroe, H. Erdjument-Bromage, P. Tempst, M.A. Rudnicki, D.R. Beier, B.M. Spiegelman, PRDM16 controls a brown fat/skeletal muscle switch. Nature 454, 961–967 (2008)
Z. Zhou, S. Yon Toh, Z. Chen, K. Guo, C.P. Ng, S. Ponniah, S.C. Lin, W. Hong, P. Li, Cidea-deficient mice have lean phenotype and are resistant to obesity. Nat. Genet. 35, 49–56 (2003)
A.M. Cypess, A.P. White, C. Vernochet, T.J. Schulz, R. Xue, C.A. Sass, T.L. Huang, C. Roberts-Toler, L.S. Weiner, C. Sze, A.T. Chacko, L.N. Deschamps, L.M. Herder, N. Truchan, A.L. Glasgow, A.R. Holman, A. Gavrila, P.O. Hasselgren, M.A. Mori, M. Molla, Y.H. Tseng, Anatomical localization, gene expression profiling and functional characterization of adult human neck brown fat. Nat. Med. 19, 635–639 (2013)
R. Drolet, C. Belanger, M. Fortier, C. Huot, J. Mailloux, D. Legare, A. Tchernof, Fat depot-specific impact of visceral obesity on adipocyte adiponectin release in women. Obesity 17, 424–430 (2009)
O. Osborn, J.M. Olefsky, The cellular and signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in disease. Nat. Med. 18, 363–374 (2012)
F. Forner, C. Kumar, C.A. Luber, T. Fromme, M. Klingenspor, M. Mann, Proteome differences between brown and white fat mitochondrial reveal specialized metabolic functions. Cell Metab. 10, 324–335 (2009)
S.J. Yeaman, Hormone-sensitive lipase-new roles for an old enzyme. Biochem. J. 379, 11–22 (2004)
J. Van de Voorde, B. Pauwels, C. Boydens, K. Decaluwe, Adipocytokines in relation to cardiovascular disease. Metabolism 62, 1513–1521 (2013)
K.T. Stepniakowski, T.L. Goodfriend, B.M. Egan, Fatty acids enhance vascular alpha-adrenergic sensitivity. Hypertension 25, 774–778 (1995)
J.E. Hall, A.A. da Silva, J.M. do Carmo, J. Dubinion, S. Hamza, S. Munusamy, G. Smith, D.E. Stec, Obesity-induced hypertension: role of sympathetic nervous system, leptin, and melanocortins. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 17271–17276 (2010)
D. Dicker, E. Atar, R. Kornowski, G.N. Bachar, Increased epicardial adipose tissue thickness as a predictor for hypertension: a cross-sectional observational study. J. Clin. Hypertens. 15, 893–898 (2013)
J. Wu, P. Bostrom, L.M. Sparks, L. Ye, J.H. Choi, A.H. Giang, M. Khandekar, K.A. Virtanen, P. Nuutila, G. Schaart, K. Huang, H. Tu, W.D. van Marken Lichtenbelt, J. Hoeks, S. Enerback, P. Schrauwen, B.M. Spiegelman, Beige adipocytes are a distinct type of thermogenic fat cell in mouse and human. Cell 150, 366–376 (2012)
M.E. Lidell, M.J. Betz, O. Dahlqvist Leinhard, M. Heglind, L. Elander, M. Slawik, T. Mussack, D. Nilsson, T. Romu, P. Nuutila, K.A. Virtanen, F. Beuschlein, A. Persson, M. Borga, S. Enerback, Evidence for two types of brown adipose tissue in humans. Nat. Med. 19, 631–634 (2013)
C.S. Tam, V. Lecoultre, E. Ravussin, Brown adipose tissue: mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Circulation 125, 2782–2791 (2012)
K.I. Stanford, R.J. Middelbeek, K.L. Townsend, D. An, E.B. Nygaard, K.M. Hitchcox, K.R. Markan, K. Nakano, M.F. Hirshman, Y.H. Tseng, L.J. Goodyear, Brown adipose tissue regulates glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity. J. Clin. Invest. 123, 215–223 (2013)
N. Petrovic, T.B. Walden, I.G. Shabalina, J.A. Timmons, B. Cannon, J. Nedergaard, Chronic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) activation of epididymally derived white adipocyte cultures reveals a population of thermogenically competent, UCP1-containing adipocytes molecularly distinct from classic brown adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 7153–7164 (2010)
M. Rosenwald, A. Perdikari, T. Rulicke, C. Wolfrum, Bi-directional interconversion of brite and white adipocytes. Nat. Cell Biol. 15, 659–667 (2013)
A. Gastaldelli, G. Basta, Ectopic fat and cardiovascular disease: what is the link? Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 20, 481–490 (2010)
F. Ertas, H. Kaya, H. Acet, H. Cil, A. Akyuz, Y. Islamoglu, E. Tekbas, Z. Ariturk, M. Aydin, S. Soydinc, Increased echocardiographic epicardial fat thickness is related to impaired diurnal blood pressure profiles. Blood Press. 21, 202–208 (2012)
P. Lee, M.M. Swarbrick, K.K. Ho, Brown adipose tissue in adult humans: a metabolic renaissance. Endocr. Rev. 34, 413–438 (2013)
V. Ouellet, A. Routhier-Labadie, W. Bellemare, L. Lakhal-Chaieb, E. Turcotte, A.C. Carpentier, D. Richard, Outdoor temperature, age, sex, body mass index, and diabetic status determine the prevalence, mass, and glucose-uptake activity of 18F-FDG-detected BAT in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96, 192–199 (2011)
T. Szasz, R.C. Webb, Perivascular adipose tissue: more than just structural support. Clin. Sci. 122, 1–12 (2012)
G. Iacobellis, C. Di Gioia, L. Petramala, C. Chiappetta, V. Serra, L. Zinnamosca, C. Marinelli, A. Ciardi, G. De Toma, C. Letizia, Brown fat expresses adiponectin in humans. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 126751 (2013)
C. Letizia, L. Petramala, C.R. Di Gioia, C. Chiappetta, L. Zinnamosca, C. Marinelli, G. Iannucci, A. Ciardi, G. De Toma, G. Iacobellis, Leptin and adiponectin mRNA expression from the adipose tissue surrounding the adrenal neoplasia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100, E101–E104 (2015)
Acknowledgments
X Li, J Liu, C Yin, and G Ding conceived and designed the experiments. X Li, J Liu, and G Wang performed the experiments and analyzed data. J Yu, Y Sheng, C Wang, Y Lv, S Lv, H Qi, and W Di contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. X Li and J Liu wrote the paper. This work was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81170796 and 81370950), the Program for Development of Innovative Research Team in the First Affiliated Hospital of NJMU (20113012) and also by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions to Guoxian Ding, and Grants from the National Natural Science Youth Foundation of China (30900504) to Juan Liu.
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the research committee of Nanjing Medical University. All participants gave written informed consent before taking part in the study.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xueqin Li and Juan Liu have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12020_2015_572_MOESM2_ESM.doc
Supplementary material 2 Other genes expressions in bSAT between HP and T-NP group. (A, B, C, D and E) The expressions of beige adipocyte genes, white adipocyte genes, mitochondrial function genes and adipocyte metabolism-related genes in the samples of bSAT between HP and T-NP group were measured by quantitative RT-PCR (n = 94). (DOC 510 kb)
12020_2015_572_MOESM3_ESM.doc
Supplementary material 3 UCP1 and other genes expressions in bSAT between HP and NP group. (A, B, C, D, E and F) The expressions of UCP1 and other BAT genes, beige adipocyte genes, white adipocyte genes, mitochondrial function genes and adipocyte metabolism-related genes in the samples of PAT between the HP and NP groups were measured by quantitative RT-PCR (n = 60). (DOC 630 kb)
12020_2015_572_MOESM4_ESM.doc
Supplementary material 4 ADIPOQ and LEP mRNA expressions in PAT between RCC and non-RCC group. The expressions of ADIPOQ and LEP genes in the samples of PAT between RCC and non-RCC group were measured by quantitative RT-PCR (n = 94). (DOC 74 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Liu, J., Wang, G. et al. Determination of UCP1 expression in subcutaneous and perirenal adipose tissues of patients with hypertension. Endocrine 50, 413–423 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0572-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0572-3