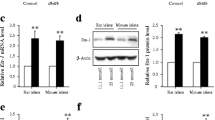
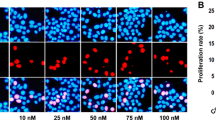
Abstract
Increased cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression is associated with pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. We previously demonstrated that the transcription factor Ets-1 significantly up-regulated COX-2 gene promoter activity. In this report, we used the pancreatic β-cell line INS-1 and isolated rat islets to investigate whether Ets-1 could induce β-cell dysfunction through up-regulating COX-2 gene expression. We investigated the effects of ETS-1 overexpression and the effects of ETS-1 RNA interference on endogenous COX-2 expression in INS-1 cells. We used site-directed mutagenesis and a dual luciferase reporter assay to study putative Ets-1 binding sites in the COX-2 promoter. The effect of ETS-1 1 overexpression on the insulin secretion function of INS-1 cells and rat islets and the potential reversal of these effects by a COX-2 inhibitor were determined in a glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) assay. ETS-1 overexpression significantly induces endogenous COX-2 expression, but ETS-1 RNA interference has no effect on basal COX-2 expression in INS-1 cells. Ets-1 protein significantly increases COX-2 promoter activity through the binding site located in the −195/−186 region of the COX-2 promoter. ETS-1 overexpression significantly inhibited the GSIS function of INS-1 cells and islet cells and COX-2 inhibitor treatment partly reversed this effect. These findings indicated that ETS-1 overexpression induces β-cell dysfunction partly through up-regulation of COX-2 gene expression. Moreover, Ets-1, the transcriptional regulator of COX-2 expression, may be a potential target for the prevention of β-cell dysfunction mediated by COX-2.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.A. Rouzer, L.J. Marnett, Cyclooxygenases: structural and functional insights. J. Lipid Res. 50, S29–S34 (2009)
P. Hegde, M.S. Maddur, A. Friboulet, J. Bayry, S.V. Kaveri, Viscum album exerts anti-inflammatory effect by selectively inhibiting cytokine-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2. PLoS ONE 6, e26312 (2011)
O.O. Ogunwobi, T. Wang, L. Zhang, C. Liu, COX-2 and Akt mediate multiple growth factor-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 27, 566–578 (2012)
M.A. Panaro, M. Pricci, F. Meziani, T. Ragot, R. Andriantsitohaina, V. Mitolo, A. Tesse, Cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostacyclin protective role on endotoxin-induced mouse cardiomyocyte mortality. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 11, 347–356 (2011)
E. Tahanian, L.A. Sanchez, T.C. Shiao, R. Roy, B. Annabi, Flavonoids targeting of IκB phosphorylation abrogates carcinogen-induced MMP-9 and COX-2 expression in human brain endothelial cells. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 5, 299–309 (2011)
L.S. Simon, Role and regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 during inflammation. Am. J. Med. 106, 37S–42S (1999)
M. Tsujii, S. Kawano, R.N. DuBois, Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human colon cancer cells increases metastatic potential. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94, 3336–3340 (1997)
O.C. Trifan, T. Hla, Cyclooxygenase-2 modulates cellular growth and promotes tumorigenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 7, 207–222 (2003)
M.L. Sheu, F.M. Ho, R.S. Yang, K.F. Chao, W.W. Lin, S.Y. Lin-Shiau, S.H. Liu, High glucose induces human endothelial cell apoptosis through a phosphoinositide 3-kinase–regulated cyclooxygenase-2 pathway. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 25, 539–545 (2005)
T. Kuwano, S. Nakao, H. Yamamoto, M. Tsuneyoshi, T. Yamamoto, M. Kuwano, M. Ono, Cyclooxygenase 2 is a key enzyme for inflammatory cytokine-induced angiogenesis. FASEB J. 18, 300–310 (2004)
R.P. Robertson, Dominance of cyclooxygenase-2 in the regulation of pancreatic islet prostaglandin synthesis. Diabetes 47, 1379–1383 (1998)
P.O. Tran, C.E. Gleason, V. Poitout, R.P. Robertson, Prostaglandin E (2) mediates inhibition of insulin secretion by interleukin-1beta. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 31245–31248 (1999)
P.O. Tran, C.E. Gleason, R.P. Robertson, Inhibition of interleukin-1β-induced COX-2 and EP3 gene expression by sodium salicylate enhances pancreatic islet β-cell function. Diabetes 51, 1772–1778 (2002)
R. Tazawa, X.M. Xu, K.K. Wu, L.H. Wang, Characterization of the genomic structure, chromosomal location and promoter of human prostaglandin H synthase-2 gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 203, 190–199 (1994)
K. Kirtikara, R. Raghow, S.J. Laulederkind, S. Goorha, T. Kanekura, L.R. Ballou, Transcriptional regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in the human microvascular endothelial cell line, HMEC-1: control by the combinatorial actions of AP2, NF-IL-6 and CRE elements. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 203, 41–51 (2000)
L.J. Crofford, B. Tan, C.J. McCarthy, T. Hla, Involvement of nuclear factor kappa B in the regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by interleukin-1 in rheumatoid synoviocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 40, 226–236 (1997)
J.R. Mestre, D.E. Rivadeneira, P.J. Mackrell, M. Duff, P.P. Stapleton, V. Mack-Strong, S. Maddali, G.P. Smyth, T. Tanabe, J.M. Daly, Overlapping CRE and E-box promoter elements can independently regulate COX-2 gene transcription in macrophages. FEBS Lett. 496, 147–151 (2001)
H.W. Koon, D. Zhao, Y. Zhan, S.H. Rhee, M.P. Moyer, C. Pothoulakis, Substance P stimulates cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 expression through JAK-STAT activation in human colonic epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 176, 5050–5059 (2006)
K. Schroer, Y. Zhu, M.A. Saunders, W.G. Deng, X.M. Xu, J. Meyer-Kirchrath, K.K. Wu, Obligatory role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element in cyclooxygenase-2 promoter induction and feedback regulation by inflammatory mediators. Circulation 105, 2760–2765 (2002)
M.A. Saunders, L. Sansores-Garcia, D.W. Gilroy, K.K. Wu, Selective suppression of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta binding and cyclooxygenase-2 promoter activity by sodium salicylate in quiescent human fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 18897–18904 (2001)
Y. Zhu, M.A. Saunders, H. Yeh, W.G. Deng, K.K. Wu, Dynamic regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 promoter activity by isoforms of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 6923–6928 (2002)
X. Zhang, J. Zhang, X. Yang, X. Han, Several transcription factors regulate COX-2 gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 34, 199–206 (2007)
B. Wasylyk, S.L. Hahn, A. Giovane, The Ets family of transcription factors. Eur. J. Biochem. 211, 7–18 (1993)
V.I. Sementchenko, D.K. Watson, Ets target genes: past, present, and future. Oncogene 19(55), 6533–6548 (2000)
D.K. Watson, A. Seth, Ets gene family, in Oncogene Reviews, ed. by J. Jenkins, E.P. Reddy (Nature Publishing Group, London, 2000), pp. 6393–6548
D.K. Watson, R. Li, V.I. Sementchenko, G. Mavrothalassitis, A. Seth, The ETS genes, in Encyclopedia of Cancer, ed. by J.R. Bertino (Academic Press, San Diego, 2001), pp. 189–196
J. Dittmer, The biology of the Ets1 proto-oncogene. Mol. Cancer 2, 29 (2003)
T. Oikawa, T. Yamada, Molecular biology of the Ets family of transcription factors. Gene 303, 11–34 (2003)
J.S. Yordy, R.C. Muise-Helmericks, Signal transduction and the Ets family of transcriptio factors. Oncogene 19, 6503–6513 (2000)
S. Sung, Y. Park, J.R. Jo, N.K. Jung, D.K. Song, J. Bae, D.Y. Keum, J.B. Kim, G.Y. Park, B.C. Jang, J.W. Park, Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 in NCI-H292 human alveolar epithelial carcinoma cells: roles of p38 MAPK, ERK-1/2, and PI3K/PKB signaling proteins. J. Cell. Biochem. 112, 3015–3024 (2011)
K. Bansal, S. Holla, S. Verma-Kumar, P. Sharma, K.N. Balaji, ESAT-6 induced COX-2 expression involves coordinated interplay between PI3K and MAPK signaling. Mol. Immunol. 49, 655–663 (2012)
X.F. Zhang, W. Yong, J.H. Lv, Y.X. Zhu, J.J. Zhang, F. Chen, R.H. Zhang, T. Yang, Y.J. Sun, X. Han, Inhibition of forkhead box O1 protects pancreatic β-cells against dexamethasone-induced dysfunction. Endocrinology 150, 4065–4073 (2009)
K.J. Livak, T.D. Schmittgen, Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402–408 (2001)
T. Tabatabaie, A.M. Waldon, J.M. Jacob, R.A. Floyd, Y. Kotake, COX-2 inhibition prevents insulin-dependent diabetes in low-dose streptozotocin-treated mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 273, 699–704 (2000)
S.J. Persaud, C.J. Burns, V.D. Belin, P.M. Jones, Glucose-induced regulation of COX-2 expression in human islets of Langerhans. Diabetes 53, S190–S192 (2004)
T. Tanabe, N. Tohnai, Cyclooxygenase isozymes and their gene structures and expression. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 68–69, 95–114 (2002)
S.J. Yeo, D. Gravis, J.G. Yoon, A.K. Yi, Myeloid differentiation factor 88-dependent transcriptional regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by CpG DNA: role of NF-kappaB and p38. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 22563–22573 (2003)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81001079, 81101802), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Y2110310), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2011845), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD, JX10231801).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiong-Fei Zhang and Yi Zhu have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, XF., Zhu, Y., Liang, WB. et al. Transcription factor Ets-1 inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion of pancreatic β-cells partly through up-regulation of COX-2 gene expression. Endocrine 46, 470–476 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-0114-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-013-0114-9