Abstract
The importance of stem cell growth and its fate is highly essential for the use of stem cells in therapy and regeneration. There are conflicting evidences regarding the actual role of stem cells when injected into a patient towards damage recovery and its lifespan inside the body. Tumor microenvironment differs from that of normal cells and may have a role in the growth of stem cells when associated with them. In cancer, the uncontrolled growth of cells remodels the extracellular matrix (ECM). The ECM alteration occurs as the mutated fibroblast cells release growth factors into the ECM which further alters the ECM directly or changes the epithelial cells and then alters the ECM. In this review we will discuss about the components and functions of ECM and how does it differ in cancer cells compared to normal cells. Abnormal dynamics of the ECM and its role in cancer progression will also be discussed.

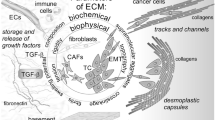
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michel, G., Tonon, T., Scornet, D., Cock, J. M., & Kloareg, B. (2010). The cell wall polysaccharide metabolism of the brown alga Ectocarpussiliculosus. Insights into the evolution of extracellular matrix polysaccharides in Eukaryotes. New Phytologist, 188(1), 82–97.
Alberts, B. (2002). Molecular biology of the cell ((4th Eds)). New York: Garland Science.
Abedin, M., & King, N. (2010). Diverse evolutionary paths to cell adhesion. Trends in Cell Biology, 20(12), 734–742.
Kumar, V., Abbas, A. K., & Aster, J. C. (2015). Robbins and cotran pathologic basis of disease. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders.
Alberts, B., Bray, D., Hopkin, K., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., Raff, M., et al. (2013). Essential cell biology. New York: Garland Science.
Brownlee, C. (2002). Role of the extracellular matrix in cell–cell signalling: paracrine paradigms. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 5(5), 396–401.
Kostakioti, M., Hadjifrangiskou, M., & &Hultgren, S. J. (2013). Bacterial biofilms: development, dispersal, and therapeutic strategies in the dawn of the postantibiotic era. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine, 3(4), a010306.
Plopper, G. (2007). ‘The extracellular matrix and cell adhesion’. In: B. Lewin, L. Cassimeris, V. Lingappa & G. Plopper (Eds.) Cells. Sudbury; pp. 645–702.
Di Lullo, G. A., Sweeney, S. M., Körkkö, J., Ala-Kokko, L., & San Antonio, J. D. (2002). Mapping the ligand-binding sites and disease-associated mutations on the most abundant protein in the human, type I collagen. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277(6), 4223–4231.
Karsenty, G., & Park, R. W. (1995). Regulation of type I collagen genes expression. International Reviews of Immunology, 12(2–4), 177–185.
Kern, B., Shen, J., Starbuck, M., & Karsenty, G. (2001). Cbfa1 contributes to the osteoblast-specific expression of type I collagen genes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276(10), 7101–7107.
Haviv, F., Bradley, M. F., Kalvin, D. M., Schneider, A. J., Davidson, D. J., Majest, S. M., McKay, L. M., Haskell, C. J., Bell, R. L., Nguyen, B., & Marsh, K. C. (2005). Thrombospondin-1 mimetic peptide inhibitors of angiogenesis and tumour growth: design, synthesis, and optimization of pharmacokinetics and biological activities. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 48(8), 2838–2846.
Hsia, H. C., & Schwarzbauer, J. E. (2005). Meet the tenascins: multifunctional and mysterious. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280(29), 26641–26644.
Carey, D. J. (1997). Syndecans: multifunctional cell-surface co-receptors. The Biochemical Journal, 327, 1–16.
Miosge, N., Holzhausen, S., Zelent, C., Sprysch, P., & Herken, R. (2001). Nidogen-1 and nidogen-2 are found in basement membranes during human embryonic development. Histochemical Journal, 33(9–10), 523–530.
Bonnans, C., Chou, J., & Werb, Z. (2014). Remodelling the extracellular matrix in development and disease. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 15(12), 786.
Gallagher, J. T., & Lyon, M. (2000). Molecular structure of heparan sulfate and interactions with growth factors and morphogens. In R. V. Iozzo (Ed.), Proteoglycans: structure, biology and molecular interactions (pp. 27–59). New York: Marcel Dekker Inc.
Iozzo, R. V. (1998). Matrix proteoglycans: from molecular design to cellular function. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 67, 609–652.
McCarthy, K. J. (2015). The basement membrane proteoglycans perlecan and agrin: Something old, something new. In Current topics in membranes (Vol. 76, pp. 255–303). Cambridge: Academic.
Baeurle, S. A., Kiselev, M. G., Makarova, E. S., & Nogovitsin, E. A. (2009). Effect of the counterion behavior on the frictional–compressive properties of chondroitin sulfate solutions. Polymer, 50(7), 1805–1813.
Lodish, H., Berk, A., Matsudaira, P., Kaiser, C. A., Krieger, M., Scott, M. P., Zipursky, S. L., & Darnell, J. Integrating Cells Into Tissues. In Molecular Cell Biology (5th ed., pp. 197–234) . New York: WH Freeman and Company.
Miller, B., Sheppard, A. M., & Pearlman, A. L. (1997). Developmental expression of keratan sulfate-like immunoreactivity distinguishes thalamic nuclei and cortical domains. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 380(4), 533–552.
Zhang, H., Uchimura, K., & Kadomatsu, K. (2006). Brain keratan sulfate and glial scar formation. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1086(1), 81–90.
Peach, R. J., Hollenbaugh, D., Stamenkovic, I., & Aruffo, A. (1993). Identification of hyaluronic acid binding sites in the extracellular domain of CD44. Journal of Cell Biology, 122(1), 257–264.
Huleihel, L., Hussey, G. S., Naranjo, J. D., Zhang, L., Dziki, J. L., Turner, N. J., et al. (2016). Matrix-bound nanovesicles within ECM bioscaffolds. Science Advances, 2(6), e1600502.
Alberts, B., Johnson, A., Lewis, J., et al. (2002). ‘Membrane transport of small molecules and the electrical properties of membranes’ in Molecular biology of the cell (4th ed., pp. 615–657). New York: Garland Science.
Plotnikov, S. V., Pasapera, A. M., Sabass, B., & Waterman, C. M. (2012). Force fluctuations within focal adhesions mediate ECM-rigidity sensing to guide directed cell migration. Cell, 151(7), 1513–1527.
Discher, D. E., Janmey, P., & Wang, Y. L. (2005). Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate. Science, 310(5751), 1139–1143.
Lo, C. M., Wang, H. B., Dembo, M., & Wang, Y. L. (2000). Cell movement is guided by the rigidity of the substrate. Biophysical Journal, 79(1), 144–152.
Hadjipanayi, E., Mudera, V., & Brown, R. A. (2009). Close dependence of fibroblast proliferation on collagen scaffold matrix stiffness. Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, 3(2), 77–84.
Engler, A. J., Sen, S., Sweeney, H. L., & Discher, D. E. (2006). Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell, 126(4), 677–689.
Wang, H. B., Dembo, M., & Wang, Y. L. (2000). Substrate flexibility regulates growth and apoptosis of normal but not transformed cells. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology, 279(5), C1345–C1350.
Allen, J. L., Cooke, M. E., & Alliston, T. (2012). ECM stiffness primes the TGFβ pathway to promote chondrocyte differentiation. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 23(18), 3731–3742.
Kanchanawong, P., Shtengel, G., Pasapera, A. M., Ramko, E. B., Davidson, M. W., Hess, H. F., & Waterman, C. M. (2010). Nanoscale architecture of integrin-based cell adhesions. Nature, 468(7323), 580.
Hynes, R. O. (2009). The extracellular matrix: not just pretty fibrils. Science, 326(5957), 1216–1219.
Lu, P., Takai, K., Weaver, V. M., & Werb, Z. (2011). Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 3(12), a005058.
Zhen, G., & Cao, X. (2014). Targeting TGFβ signaling in subchondral bone and articular cartilage homeostasis. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 35(5), 227–236.
Frantz, C., Stewart, K. M., & Weaver, V. M. (2010). The extracellular matrix at a glance. Journal of Cell Science, 123(24), 4195–4200.
Hay, E. D. (1993). Extracellular matrix alters epithelial differentiation. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 5(6), 1029–1035.
Oskarsson, T. (2013). Extracellular matrix components in breast cancer progression and metastasis. The Breast, 22, S66–S72.
Bussard, K. M., Boulanger, C. A., Booth, B. W., Bruno, R. D., & Smith, G. H. (2010). Reprogramming human cancer cells in the mouse mammary gland. Cancer Research, 70(15), 6336–6343.
Boulanger, C. A., Mack, D. L., Booth, B. W., & Smith, G. H. (2007). Interaction with the mammary microenvironment redirects spermatogenic cell fate in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104 (10), 3871–3876.
Booth, B. W., Mack, D. L., Androutsellis-Theotokis, A., McKay, R. D., Boulanger, C. A., & Smith, G. H. (2008). The mammary microenvironment alters the differentiation repertoire of neural stem cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(39), 14891–14896.
Krause, S., Maffini, M. V., Soto, A. M., & Sonnenschein, C. (2010). The microenvironment determines the breast cancer cells’ phenotype: organization of MCF7 cells in 3D cultures. BMC Cancer, 10(1), 263.
Naba, A., Clauser, K. R., Lamar, J. M., Carr, S. A., & Hynes, R. O. (2014). Extracellular matrix signatures of human mammary carcinoma identify novel metastasis promoters. eLife, 3, e01308. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.01308.
Nelson, C. M., & Bissell, M. J. (2006). Of extracellular matrix, scaffolds, and signaling: tissue architecture regulates development, homeostasis, and cancer. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 22, 287–309.
Gaudet, A. D., & Popovich, P. G. (2014). Extracellular matrix regulation of inflammation in the healthy and injured spinal cord. Experimental Neurology, 258, 24–34.
Bianchi, M. E. (2007). DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: all we need to know about danger. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 81(1), 1–5.
Erridge, C. (2010). Endogenous ligands of TLR2 and TLR4: agonists or assistants? Journal of Leukocyte Biology, 87(6), 989–999.
Kigerl, K. A., de RiveroVaccari, J. P., Dietrich, W. D., Popovich, P. G., & Keane, R. W. (2014). Pattern recognition receptors and central nervous system repair. Experimental Neurology, 258, 5–16.
Conklin, M. W., Eickhoff, J. C., Riching, K. M., Pehlke, C. A., Eliceiri, K. W., Provenzano, P. P., et al. (2011). Aligned collagen is a prognostic signature for survival in human breast carcinoma. The American Journal of Pathology, 178(3), 1221–1232.
Egeblad, M., Rasch, M. G., & Weaver, V. M. (2010). Dynamic interplay between the collagen scaffold and tumor evolution. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 22(5), 697–706.
Levental, K. R., Yu, H., Kass, L., Lakins, J. N., Egeblad, M., Erler, J. T., Fong, S. F., Csiszar, K., Giaccia, A., Weninger, W., & Yamauchi, M. (2009). Matrix crosslinking forces tumor progression by enhancing integrin signaling. Cell, 139(5), 891–906.
Mouw, J. K., Yui, Y., Damiano, L., Bainer, R. O., Lakins, J. N., Acerbi, I., & Hwang, E. S. (2014). Tissue mechanics modulate microRNA-dependent PTEN expression to regulate malignant progression. Nature Medicine, 20(4), 360.
Paszek, M. J., Zahir, N., Johnson, K. R., Lakins, J. N., Rozenberg, G. I., Gefen, A., et al. (2005). Tensional homeostasis and the malignant phenotype. Cancer Cell, 8(3), 241–254.
Provenzano, P. P., Inman, D. R., Eliceiri, K. W., & Keely, P. J. (2009). Matrix density-induced mechanoregulation of breast cell phenotype, signaling and gene expression through a FAK–ERK linkage. Oncogene, 28(49), 4326.
Provenzano, P. P., Eliceiri, K. W., Campbell, J. M., Inman, D. R., White, J. G., & Keely, P. J. (2006). Collagen reorganization at the tumor-stromal interface facilitates local invasion. BMC Medicine, 4(1), 38.
Ilan, N., Elkin, M., & Vlodavsky, I. (2006). Regulation, function and clinical significance of heparanase in cancer metastasis and angiogenesis. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 38(12), 2018–2039.
Kessenbrock, K., Plaks, V., & Werb, Z. (2010). Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell, 141(1), 52–67.
Lopez, J. I., Kang, I., You, W. K., McDonald, D. M., & Weaver, V. M. (2011). In situ force mapping of mammary gland transformation. Integrative Biology: Quantitative Biosciences from Nano to Macro, 3(9), 910–921.
Le, Q. T., Harris, J., Magliocco, A. M., Kong, C. S., Diaz, R., Shin, B., et al. (2009). Validation of lysyl oxidase as a prognostic marker for metastasis and survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: radiation therapy oncology group trial 90 – 03. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 27(26), 4281.
Barker, H. E., Chang, J., Cox, T. R., Lang, G., Bird, D., Nicolau, M., Evans, H. R., Gartland, A., & Erler, J. T. (2011). LOXL2-mediated matrix remodeling in metastasis and mammary gland involution. Cancer Research, 71(5), 1561–1572.
Hanahan, D., & Weinberg, R. A. (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell, 100(1), 57–70.
Hanahan, D., & Weinberg, R. A. (2011). Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell, 144(5), 646–674.
Feigin, M. E., & Muthuswamy, S. K. (2009). Polarity proteins regulate mammalian cell–cell junctions and cancer pathogenesis. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 21(5), 694–700.
Luo, J., Solimini, N. L., & Elledge, S. J. (2009). Principles of cancer therapy: oncogene and non-oncogene addiction. Cell, 136(5), 823–837.
Wozniak, M. A., Desai, R., Solski, P. A., Der, C. J., & Keely, P. J. (2003). ROCK-generated contractility regulates breast epithelial cell differentiation in response to the physical properties of a three-dimensional collagen matrix. Journal of Cell Biology, 163(3), 583–595.
Mott, J. D., & Werb, Z. (2004). Regulation of matrix biology by matrix metalloproteinases. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 16(5), 558–564.
Rozario, T., & DeSimone, D. W. (2010). The extracellular matrix in development and morphogenesis: a dynamic view. Development Biology, 341(1), 126–140.
Dalby, M. J., Gadegaard, N., & Oreffo, R. O. (2014). Harnessing nanotopography and integrin–matrix interactions to influence stem cell fate. Nature Materials, 13(6), 558.
Dalby, M. J., Gadegaard, N., Tare, R., Andar, A., Riehle, M. O., Herzyk, P., Wilkinson, C. D., & Oreffo, R. O. (2007). The control of human mesenchymal cell differentiation using nanoscale symmetry and disorder. Nature Materials, 6(12), 997.
McMurray, R. J., Gadegaard, N., Tsimbouri, P. M., Burgess, K. V., McNamara, L. E., Tare, R., Murawski, K., Kingham, E., Oreffo, R., & Dalby, M. J. (2011). Nanoscale surfaces for the long-term maintenance of mesenchymal stem cell phenotype and multipotency. Nature Materials, 10(8), 637.
Kingham, E., White, K., Gadegaard, N., Dalby, M. J., & Oreffo, R. O. (2013). Nanotopographical cues augment mesenchymal differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 9(12), 2140–2151.
Cavo, M., Fato, M., Peñuela, L., Beltrame, F., Raiteri, R., & Scaglione, S. (2016). Microenvironment complexity and matrix stiffness regulate breast cancer cell activity in a 3D in vitro model. Scientific Reports, 6, 35367.
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to Chettinad Academy of Research and Education for the infrastructural support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Girigoswami, K., Saini, D. & Girigoswami, A. Extracellular Matrix Remodeling and Development of Cancer. Stem Cell Rev and Rep 17, 739–747 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-020-10070-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-020-10070-1