Abstract
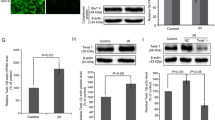
NYGGF4, also known as phosphotyrosine interaction domain containing 1(PID1), is a recently discovered gene which is involved in obesity-related insulin resistance (IR) and mitochondrial dysfunction. We aimed to further elucidate the effects and mechanisms underlying NYGGF4-induced IR by investigating the effect of overexpressing mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM), which is essential for mitochondrial DNA transcription and replication, on NYGGF4-induced IR and mitochondrial abnormalities in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Overexpression of TFAM increased the mitochondrial copy number and ATP content in both control 3T3-L1 adipocytes and NYGGF4-overexpressing adipocytes. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production was enhanced in NYGGF4-overexpressing adipocytes and reduced in TFAM-overexpressing adipocytes; co-overexpression of TFAM significantly attenuated ROS production in NYGGF4-overexpressing adipocytes. However, overexpression of TFAM did not affect the mitochondrial transmembrane potential (ΔΨm) in control 3T3-L1 adipocytes or NYGGF4-overexpressing adipocytes. In addition, co-overexpression of TFAM-enhanced insulin-stimulated glucose uptake by increasing Glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) translocation to the PM in NYGGF4-overexpressing adipocytes. Overexpression of NYGGF4 significantly inhibited tyrosine phosphorylation of Insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) and serine phosphorylation of Akt, whereas overexpression of TFAM strongly induced phosphorylation of IRS-1 and Akt in NYGGF4-overexpressing adipocytes. This study demonstrates that NYGGF4 plays a role in IR by impairing mitochondrial function, and that overexpression of TFAM can restore mitochondrial function to normal levels in NYGGF4-overexpressing adipocytes via activation of the IRS-1/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Jeffery, R. W., & Sherwood, N. E. (2008). Is the obesity epidemic exaggerated? No. British Medical Journal, 336(7638), 245.
Spiegelman, B. M., & Flier, J. S. (2001). Obesity and the regulation of energy balance. Cell, 104(4), 531–543.
Simoneau, J. A., & Kelley, D. E. (1997). Altered glycolytic and oxidative capacities of skeletal muscle contribute to insulin resistance in niddm. Journal of Applied Physiology, 83(1), 166–171.
Zhang, C. M., Chen, X. H., Wang, B., Liu, F., Chi, X., Tong, M. L., et al. (2009). Over-expression of nyggf4 inhibits glucose transport in 3t3-l1 adipocytes via attenuated phosphorylation of irs-1 and akt. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 30(1), 120–124.
Zhao, Y., Zhang, C., Chen, X., Gao, C., Ji, C., Chen, F., et al. (2010). Overexpression of nyggf4 (pid1) induces mitochondrial impairment in 3t3-l1 adipocytes. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 340(1–2), 41–48.
Petersen, K. F., Befroy, D., Dufour, S., Dziura, J., Ariyan, C., Rothman, D. L., et al. (2003). Mitochondrial dysfunction in the elderly: Possible role in insulin resistance. Science, 300(5622), 1140–1142.
Wang, B., Zhang, M., Ni, Y. H., Liu, F., Fan, H. Q., Fei, L., et al. (2006). Identification and characterization of nyggf4, a novel gene containing a phosphotyrosine-binding (ptb) domain that stimulates 3t3–l1 preadipocytes proliferation. Gene, 379, 132–140.
Qiu, J., Ni, Y. H., Gong, H. X., Fei, L., Pan, X. Q., Guo, M., et al. (2007). Identification of differentially expressed genes in omental adipose tissues of obese patients by suppression subtractive hybridization. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 352(2), 469–478.
Caratu, G., Allegra, D., Bimonte, M., Schiattarella, G. G., D’Ambrosio, C., Scaloni, A., et al. (2007). Identification of the ligands of protein interaction domains through a functional approach. Molecular and Cellular Proteomics, 6(2), 333–345.
Zhang, C. M., Zeng, X. Q., Zhang, R., Ji, C. B., Tong, M. L., Chi, X., et al. (2010). Effects of nyggf4 knockdown on insulin sensitivity and mitochondrial function in 3t3-l1 adipocytes. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes, 42(5), 433–439.
Wang, Y. M., Lin, X. F., Shi, C. M., Lu, L., Qin, Z. Y., Zhu, G. Z., et al. (2012). Alpha-lipoic acid protects 3t3-l1 adipocytes from nyggf4 (pid1) overexpression-induced insulin resistance through increasing phosphorylation of irs-1 and akt. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes, 44(3), 357–363.
Sawyer, D. E., Roman, S. D., & Aitken, R. J. (2001). Relative susceptibilities of mitochondrial and nuclear dna to damage induced by hydrogen peroxide in two mouse germ cell lines. Redox Report, 6(3), 182–184.
Abramova, N. E., Davies, K. J., & Crawford, D. R. (2000). Polynucleotide degradation during early stage response to oxidative stress is specific to mitochondria. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 28(2), 281–288.
Fridlyand, L. E., & Philipson, L. H. (2006). Reactive species and early manifestation of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 8(2), 136–145.
Lee, H. K., Song, J. H., Shin, C. S., Park, D. J., Park, K. S., Lee, K. U., et al. (1998). Decreased mitochondrial DNA content in peripheral blood precedes the development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 42(3), 161–167.
Parisi, M. A., & Clayton, D. A. (1991). Similarity of human mitochondrial transcription factor 1 to high mobility group proteins. Science, 252(5008), 965–969.
Larsson, N. G., Wang, J., Wilhelmsson, H., Oldfors, A., Rustin, P., Lewandoski, M., et al. (1998). Mitochondrial transcription factor a is necessary for mtdna maintenance and embryogenesis in mice. Nature Genetics, 18(3), 231–236.
Kang, D., Kim, S. H., & Hamasaki, N. (2007). Mitochondrial transcription factor a (tfam): Roles in maintenance of mtdna and cellular functions. Mitochondrion, 7(1–2), 39–44.
Herz, J., & Strickland, D. K. (2001). Lrp: A multifunctional scavenger and signaling receptor. Journal Of Clinical Investigation, 108(6), 779–784.
Kaaman, M., Sparks, L. M., van Harmelen, V., Smith, S. R., Sjolin, E., Dahlman, I., et al. (2007). Strong association between mitochondrial DNA copy number and lipogenesis in human white adipose tissue. Diabetologia, 50(12), 2526–2533.
Sundaresan, M., Yu, Z. X., Ferrans, V. J., Irani, K., & Finkel, T. (1995). Requirement for generation of h2o2 for platelet-derived growth factor signal transduction. Science, 270(5234), 296–299.
Woollacott, A. J., & Simpson, P. B. (2001). High throughput fluorescence assays for the measurement of mitochondrial activity in intact human neuroblastoma cells. Journal of Biomolecular Screening, 6(6), 413–420.
Ceddia, R. B., Somwar, R., Maida, A., Fang, X., Bikopoulos, G., & Sweeney, G. (2005). Globular adiponectin increases glut4 translocation and glucose uptake but reduces glycogen synthesis in rat skeletal muscle cells. Diabetologia, 48(1), 132–139.
Robin, E. D., & Wong, R. (1988). Mitochondrial DNA molecules and virtual number of mitochondria per cell in mammalian cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 136(3), 507–513.
Kang, D., & Hamasaki, N. (2002). Maintenance of mitochondrial DNA integrity: repair and degradation. Current Genetics, 41(5), 311–322.
Kang, D., & Hamasaki, N. (2005). Alterations of mitochondrial DNA in common diseases and disease states: Aging, neurodegeneration, heart failure, diabetes, and cancer. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 12(4), 429–441.
Park, S. Y., & Lee, W. (2007). The depletion of cellular mitochondrial DNA causes insulin resistance through the alteration of insulin receptor substrate-1 in rat myocytes. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 77(Suppl 1), S165–S171.
Wu, W. L., Gan, W. H., Tong, M. L., Li, X. L., Dai, J. Z., Zhang, C. M., et al. (2011). Over-expression of nyggf4 (pid1) inhibits glucose transport in skeletal myotubes by blocking the irs1/pi3k/akt insulin pathway. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism, 102(3), 374–377.
Nishio, Y., Kanazawa, A., Nagai, Y., Inagaki, H., & Kashiwagi, A. (2004). Regulation and role of the mitochondrial transcription factor in the diabetic rat heart. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1011, 78–85.
Choi, Y. S., Kim, S., & Pak, Y. K. (2001). Mitochondrial transcription factor a (mttfa) and diabetes. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 54(Suppl 2), S3–S9.
Kanazawa, A., Nishio, Y., Kashiwagi, A., Inagaki, H., Kikkawa, R., & Horiike, K. (2002). Reduced activity of mttfa decreases the transcription in mitochondria isolated from diabetic rat heart. American Journal of Physiology Endocrinology Metabolism, 282(4), E778–E785.
Noack, H., Bednarek, T., Heidler, J., Ladig, R., Holtz, J., & Szibor, M. (2006). Tfam-dependent and independent dynamics of mtdna levels in c2c12 myoblasts caused by redox stress. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1760(2), 141–150.
Bonnard, C., Durand, A., Peyrol, S., Chanseaume, E., Chauvin, M. A., Morio, B., et al. (2008). Mitochondrial dysfunction results from oxidative stress in the skeletal muscle of diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Journal Of Clinical Investigation, 118(2), 789–800.
Shadel, G. S., & Clayton, D. A. (1997). Mitochondrial DNA maintenance in vertebrates. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 66, 409–435.
Shutt, T. E., & Shadel, G. S. (2010). A compendium of human mitochondrial gene expression machinery with links to disease. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 51(5), 360–379.
Lewis, S., Thomas, S. L., Hyde, J., Castle, D., Blood, R. W., & Komesaroff, P. A. (2010). “I don’t eat a hamburger and large chips every day!” a qualitative study of the impact of public health messages about obesity on obese adults. Bmc Public Health, 10, 309.
Kanzaki, M., & Pessin, J. E. (2003). Insulin signaling: glut4 vesicles exit via the exocyst. Current Biology, 13(14), R574–R576.
Saltiel, A. R., & Pessin, J. E. (2002). Insulin signaling pathways in time and space. Trends in Cell Biology, 12(2), 65–71.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2013CB530604) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 30973231 and 81270928), the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (Grant no. 201104013), and the Talent Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant no. Hygiene-39). 2012 Graduate Student Innovation Project of Jiangsu province (Grant no. CXLX12_0559).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Chun-Mei Shi and Guang-Feng Xu contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, CM., Xu, GF., Yang, L. et al. Overexpression of TFAM Protects 3T3-L1 Adipocytes from NYGGF4 (PID1) Overexpression-Induced Insulin Resistance and Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Cell Biochem Biophys 66, 489–497 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9496-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9496-1