Abstract
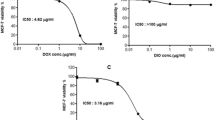
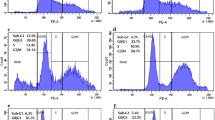
Morphine (MOR) is a strong analgesic that is often used in treatment of severe pains during cancer treatment, and thus might be concomitantly used with anticancer drugs as cisplatin (CP). The aim of the current study was to investigate the mechanisms by which MOR can affect CP-induced cardiotoxicity and to explore effects of MOR on the cytotoxic efficacy of CP. MOR (10 mg/kg/day i.p.) was administered to rats for 10 days, with or without 7.5 mg/kg CP single i.p. dose at day 5 of the experiment. In addition, MOR and/or CP were administered to MCF-7 cells to test their cytotoxicity. Compared to control, CP caused cardiotoxic effects manifested by significant increase in serum enzymatic markers; creatine kinase-MB and lactate dehydrogenase, with histopathological cardiac damage. In addition, CP caused cardiac oxidative stress, manifested by significant increased tissue lipid peroxidation product; malondialdehyde and nitric oxide, with significant decrease in tissue antioxidants as reduced glutathione, superoxide dismutase and catalase compared to control. Furthermore, CP significantly increased tissue proinflammatory cytokines; TNF-α and IL-6, as well as upregulated the apoptotic marker; caspase 3 compared to control. MOR/CP combination significantly deteriorated all tested parameters compared to CP alone. In MCF-7 breast cancer cells, administration of MOR in concentrations of 0.1, 1, 10 or 30 μM concomitantly with 1 or 10 μM CP caused dose-dependent reduction in CP-induced cytotoxicity in vitro. In conclusion, MOR administration might deteriorate CP-induced cardiotoxicity during cancer chemotherapy through oxidant, pro-inflammatory and apoptotic mechanisms, and might reduce CP chemotherapeutic efficacy.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CK-MB:
-
Creatine kinase-MB
- CP:
-
Cisplatin
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- GSH:
-
Reduced glutathione
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase
- MCF-7:
-
Human breast cancer cell line named after the acronym of Michigan Cancer Foundation
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MOR:
-
Morphine
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- SRB:
-
Sulforhodamine B
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Garutti, M., Pelizzari, G., Bartoletti, M., Malfatti, M. C., Gerratana, L., Tell, G., & Puglisi, F. (2019). Platinum salts in patients with breast cancer: a focus on predictive factors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20, ijms20143390.
Oun, R., Moussa, Y. E., & Wheate, N. J. (2018). The side effects of platinum-based chemotherapy drugs: a review for chemists. Dalton Transactions, 47, 6645–6653.
Hanchate, L. P., Sharma, S. R., & Madyalkar, S. (2017). Cisplatin induced acute myocardial infarction and dyslipidemia. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research, 11, OD05–OD07.
Dugbartey, G. J., Peppone, L. J., & de Graaf, I. A. (2016). An integrative view of cisplatin-induced renal and cardiac toxicities: Molecular mechanisms, current treatment challenges and potential protective measures. Toxicology, 371, 58–66.
Afsar, T., Razak, S., Almajwal, A., Shabbir, M., & Khan, M. R. (2019). Evaluating the protective potency of Acacia hydaspica R. Parker on histological and biochemical changes induced by Cisplatin in the cardiac tissue of rats. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 19, 182.
Aboud, H. M., Mahmoud, M. O., Abdeltawab, M. M., Shafiq, A. M., & Sabry, D. (2019). Preparation and appraisal of self-assembled valsartan-loaded amalgamated Pluronic F127/Tween 80 polymeric micelles: Boosted cardioprotection via regulation of Mhrt/Nrf2 and Trx1 pathways in cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity. Journal of Drug Targeting, 28, 282–299.
Ma, W., Yang, L., Liu, H., Chen, P., Ren, H., & Ren, P. (2020). PAXX is a novel target to overcome resistance to doxorubicin and cisplatin in osteosarcoma. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 521, 204–211.
Amable, L. (2016). Cisplatin resistance and opportunities for precision medicine. Pharmacological Research, 106, 27–36.
Staff, N. P., Cavaletti, G., Islam, B., Lustberg, M., Psimaras, D., & Tamburin, S. (2019). Platinum-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: from pathogenesis to treatment. Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System, 24(Suppl 2), S26–S39.
Sommer, C., Klose, P., Welsch, P., Petzke, F., & Häuser, W. (2020). Opioids for chronic non-cancer neuropathic pain. An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy, tolerability and safety in randomized placebo-controlled studies of at least 4 weeks duration. European Journal of Pain, 24, 3–18.
Schuster, M., Bayer, O., Heid, F., & Laufenberg-Feldmann, R. (2018). Opioid rotation in cancer pain treatment. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, 115, 135–142.
Skrabalova, J., Karlovska, I., Hejnova, L., & Novotny, J. (2018). Protective effect of morphine against the oxidant-induced injury in H9c2 cells. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 18, 374–385.
Chen, Z., Spahn, D. R., Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Chu, H., & Liu, Z. (2016). Morphine postconditioning protects against reperfusion injury: the role of protein kinase C-epsilon, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and mitochondrial permeability transition pores. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, 39, 1930–1940.
Hole, L. D., Larsen, T. H., Fossan, K. O., Limé, F., & Schjøtt, J. (2014). Morphine enhances doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in the rat. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 14, 251–259.
Cao, L. H., Li, H. T., Lin, W. Q., Tan, H. Y., Xie, L., Zhong, Z. J., & Zhou, J. H. (2016). Morphine, a potential antagonist of cisplatin cytotoxicity, inhibits cisplatin-induced apoptosis and suppression of tumor growth in nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts. Science and Reports, 6, 18706.
Buege, J. A., & Aust, S. D. (1978). Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods in Enzymology, 52, 302–310.
Sastry, K. V., Moudgal, R. P., Mohan, J., Tyagi, J. S., & Rao, G. S. (2002). Spectrophotometric determination of serum nitrite and nitrate by copper-cadmium alloy. Analytical Biochemistry, 306, 79–82.
El-Sheikh, A. A., Abdelzaher, W. Y., Gad, A. A., & Abdel-Gaber, S. A. (2019). Purine versus non-purine xanthine oxidase inhibitors against cyclophosphamide-induced cardiac and bone marrow toxicity in rats. Human Experiment of Toxicology, 39, 249–261.
Vichai, V., & Kirtikara, K. (2006). Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nature Protocols, 1, 1112–1116.
Lin, M. T., Ko, J. L., Liu, T. C., Chao, P. T., & Ou, C. C. (2018). Protective effect of D-methionine on body weight loss, anorexia, and nephrotoxicity in cisplatin-induced chronic toxicity in rats. Integrative Cancer Therapies, 17, 813–824.
Aminian, A., Javadi, S., Rahimian, R., Dehpour, A. R., Asadi, A. F., Moghaddas, P., & Mehr, S. E. (2016). Enhancement of cisplatin nephrotoxicity by morphine and its attenuation by the opioid antagonist naltrexone. Acta Medica Iranica, 54, 422–429.
Samarghandian, S., Afshari, R., & Farkhondeh, T. (2014). Effect of long-term treatment of morphine on enzymes, oxidative stress indices and antioxidant status in male rat liver. Int J Clin Exper Med, 7, 1449–1453.
Zhao, L. (2019). Protective effects of trimetazidine and coenzyme Q10 on cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity by alleviating oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Anatolian Journal of Cardiology, 22, 232–239.
Mahmoudi, S., Farshid, A. A., Tamaddonfard, E., Imani, M., & Noroozinia, F. (2019). Behavioral, histopathological, and biochemical evaluations on the effects of cinnamaldehyde, naloxone, and their combination in morphine-induced cerebellar toxicity. Drug and Chemical Toxicology, 25, 1–12.
Arabian, M., Aboutaleb, N., Soleimani, M., Ajami, M., Habibey, R., Rezaei, Y., & Pazoki-Toroudi, H. (2018). Preconditioning with morphine protects hippocampal CA1 neurons from ischemia-reperfusion injury via activation of the mTOR pathway. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology, 96, 80–87.
Amini-Khoei, H., Hosseini, M. J., Momeny, M., Rahimi-Balaei, M., Amiri, S., Haj-Mirzaian, A., Khedri, M., Jahanabadi, S., Mohammadi-Asl, A., Mehr, S. E., & Dehpour, A. R. (2016). Morphine attenuated the cytotoxicity induced by arsenic trioxide in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Biological Trace Element Research, 173, 132–139.
Rajani, S. F., Imani, A., Faghihi, M., Izad, M., Kardar, G. A., & Salehi, Z. (2019). Post-infarct morphine treatment mitigates left ventricular remodeling and dysfunction in a rat model of ischemia-reperfusion. European Journal of Pharmacology, 847, 61–71.
Doyle, H. H., & Murphy, A. Z. (2018). Sex-dependent influences of morphine and its metabolites on pain sensitivity in the rat. Physiology & Behavior, 187, 32–41.
Mansouri, M. T., Naghizadeh, B., Ghorbanzadeh, B., Amirgholami, N., Houshmand, G., & Alboghobeish, S. (2020). Venlafaxine inhibits naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal symptoms: role of inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide. Metabolic Brain Disease, 35, 305–313.
Amri, J., Sadegh, M., Moulaei, N., & Palizvan, M. R. (2018). Transgenerational modification of hippocampus TNF-alpha and S100B levels in the offspring of rats chronically exposed to morphine during adolescence. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 44, 95–102.
Lu, R. B., Wang, T. Y., Lee, S. Y., Chen, S. L., Chang, Y. H., Chen, P. S., Lin, S. H., Chu, C. H., Huang, S. Y., Tzeng, N. S., Lee, H., Chen, K. C., Yang, Y. K., Chen, P., Chen, S. H., & Hong, J. S. (2019). Correlation between interleukin-6 levels and methadone maintenance therapy outcomes. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 204, 107516.
Li, M. C., Yu, J. H., Yu, S. S., Chi, Y. Y., & Xiang, Y. B. (2015). MicroRNA-873 inhibits morphine-induced macrophage apoptosis by elevating A20 expression. Pain Medicine, 16, 1993–1999.
Taye, A., & El-Sheikh, A. A. (2013). Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1 pathways. European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 43, 740–745.
Joshi, J. C., Ray, A., & Gulati, K. (2014). Differential modulatory effects of morphine on acute and chronic stress induced neurobehavioral and cellular markers in rats. European Journal of Pharmacology, 729, 17–21.
Meza-Morales, W., Estévez-Carmona, M. M., Alvarez-Ricardo, Y., Obregón-Mendoza, M. A., Cassani, J., Ramírez-Apan, M. T., Escobedo-Martínez, C., Soriano-García, M., Reynolds, W. F., & Enríquez, R. G. (2019). Full structural characterization of homoleptic complexes of diacetylcurcumin with Mg, Zn, Cu, and Mn: cisplatin-level cytotoxicity in vitro with minimal acute toxicity in vivo. Molecules, 24, 1598.
Cao, W. Q., Zhai, X. Q., Ma, J. W., Fu, X. Q., Zhao, B. S., Zhang, P., & Fu, X. Y. (2020). Natural borneol sensitizes human glioma cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by triggering ROS-mediated oxidative damage and regulation of MAPKs and PI3K/AKT pathway. Pharmaceutical Biology, 58, 72–79.
Ghavami, G., & Sardari, S. (2020). Synergistic effect of vitamin c with cisplatin for inhibiting proliferation of gastric cancer cells. Iran Biomedical Journal, 24, 119–127.
Niu, D. G., Peng, F., Zhang, W., Guan, Z., Zhao, H. D., Li, J. L., Wang, K. L., Li, T. T., Zhang, Y., Zheng, F. M., Xu, F., Han, Q. N., Gao, P., Wen, Q. P., & Liu, Q. (2015). Morphine promotes cancer stem cell properties, contributing to chemoresistance in breast cancer. Oncotarget, 6, 3963–3976.
Chen, Y., Qin, Y., Li, L., Chen, J., Zhang, X., & Xie, Y. (2017). Morphine can inhibit the growth of breast cancer MCF-7 cells by arresting the cell cycle and inducing apoptosis. Biological &/and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 40, 1686–1692.
Nishiwada, T., Kawaraguchi, Y., Uemura, K., & Kawaguchi, M. (2019). Morphine inhibits cell viability and growth via suppression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human oral cancer HSC-3 cells. Journal of Anesthesia, 33, 408–415.
Amini, K., Zhaleh, H., & Tahvilian, R. (2019). Effects of low-dose morphine suppress methamphetamine-induced cell death by inhibiting the ROS generation and caspase-3 activity. Bratislavske Lekarske Listy, 120, 336–343.
Morsy, M. A., Younis, N. S., El-Sheikh, A. A. K., Al Turaifi, F. H., El-Daly, M., & Mohafez, O. M. (2020). Protective mechanisms of piperine against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity may be mediated through TGFBRAP1. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences, 24, 10169–10180.
Morsy, M. A., El-Sheikh, A. A. K., Ibrahim, A. R. N., Venugopala, K. N., & Kandeel, M. (2020). In silico and in vitro identification of secoisolariciresinol as a re-sensitizer of P-glycoprotein-dependent doxorubicin-resistance NCI/ADR-RES cancer cells. PeerJ, 8, e9163.
El-Sheikh, A. A., Morsy, M. A., & Okasha, A. M. (2017). Inhibition of NF-kappaB/TNF-alpha pathway may be involved in the protective effect of resveratrol against cyclophosphamide-induced multi-organ toxicity. Immunopharmacology and Immunotoxicology, 39, 180–187.
Funding
This research was funded by Deanship of Scientific Research at Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University (Grant No# 240/S/39).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The procedures of the experiments were ethically approved by the Institutional Review Board of Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Saudi Arabia (IRB number 17-0194).
Additional information
Handling Editor: Y. James Kang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Sheikh, A.A.K., Khired, Z. Morphine Deteriorates Cisplatin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Rats and Induces Dose-Dependent Cisplatin Chemoresistance in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Cardiovasc Toxicol 21, 553–562 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-021-09646-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-021-09646-1