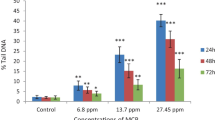
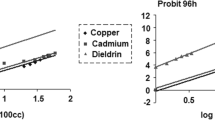
Abstract
Despite not being redox-active metals, Cd and Zn can disrupt cellular redox homeostasis by acting pro-oxidatively. The aim of this study was to examine the effects of exposure to Zn (14 and 72 mg/L) and Cd (7.7 and 77 mg/L) for 24 and 48 h on oxidative and antioxidative parameters and the activity of glutathione-S-transferase in Artemia franciscana tissue. In addition, the neurotoxicity of the metals was examined by determining the activity of acetylcholinesterase (AChE). In A. franciscana tissue, Cd (0.0026 ± 0.0001 mg/L) was detected only after 48 h of exposure to 77 mg/L Cd. After 24 h, the 14- and 72-mg/L Zn treatments resulted in significant increases in the Zn concentration (0.54 ± 0.026 mg/L (p < 0.01) and 0.68 ± 0.035 (p < 0.0001), respectively) in A. franciscana tissue compared with the control level, and significant increases were also detected after 48 h (0.59 ± 0.02 (p < 0.0001) and 0.79 ± 0.015 (p < 0.0001), respectively). The malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration in the metal-treated samples was increased after 24 h of exposure, whereas after 48 h, an increase in the MDA concentration was detected only with 7.7. mg/L Cd. A significant increase in the H2O2 concentration after 24 h was measured only after treatment with 72 mg/L Zn. The treatment with 7.7 mg/L Cd for 24 h induced a significant increase in the AChE activity, whereas 48 h of treatment with 77 mg/L Cd and 14 mg/L Zn significantly inhibited AChE. The results indicate that lipid peroxidation resulting from metal toxicity may constitute the basis of neurotoxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable reques.
References
Lane TW, Morel FM (2000) A biological function for cadmium in marine diatoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(9):4627–4631. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.090091397
Rani A, Kumar A, Lal A, Pant M (2014) Cellular mechanisms of cadmium-induced toxicity: a review. Int J Environ Health Res 24(4):378–399. https://doi.org/10.1080/09603123.2013.835032
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine. In: Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (eds) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 1–25
Marreiro DDN, Cruz KJC, Morais JBS, Beserra JB, Severo JS, De Oliveira ARS (2017) Zinc and oxidative stress: current mechanisms. Antioxidants 6(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox6020024
Mousavi SR, Galavi M, Rezaei M (2013) Zinc (Zn) importance for crop production - a review. Int J Agron Plant Prod 4(1):64–68
Olechnowicz J, Tinkov A, Skalny A, Suliburska J (2018) Zinc status is associated with inflammation, oxidative stress, lipid, and glucose metabolism. J Physiol Sci 68(1):19–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-017-0571-7
Banaszak M, Górna I, Przysławski J (2021) Zinc and the innovative zinc-α2-glycoprotein adipokine play an ımportant role in lipid metabolism: a critical review. Nutrients 13(6):2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13062023
Fosmire GJ (1990) Zinc toxicity. Am J Clin Nutr 51(2):225–227. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/51.2.225
Hussain S, Khan M, Sheikh TMM, Mumtaz MZ, Chohan TA, Shamim S, Liu Y (2022) Zinc essentiality, toxicity, and ıts bacterial bioremediation: a comprehensive insight. Front Microbiol 13:900740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.900740
Li XF, Wang PF, Feng CL, Liu DQ, Chen JK, Wu FC (2019) Acute toxicity and hazardous concentrations of zinc to native freshwater organisms under different pH values in China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 103(1):120–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2441-2
Zyadah MA, Abdel-Baky TE (2000) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of copper, zinc, and cadmium in some aquatic organisms. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 64(5):740–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001280000066
Lee SR (2018) Critical role of zinc as either an antioxidant or a prooxidant in cellular systems. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:9156285. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9156285
Wang Y, Fang J, Leonard SS, Rao KMK (2004) Cadmium inhibits the electron transfer chain and induces reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med 36(11):1434–1443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.03.010
Wu H, Xuan R, Li Y, Zhang X, Wang Q, Wang L (2013) Effects of cadmium exposure on digestive enzymes, antioxidant enzymes, and lipid peroxidation in the freshwater crab Sinopotamon henanense. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 20(6):4085–4092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1362-6
Trevisan R, Flesch S, Mattos JJ, Milani MR, Bainy ACD, Dafre AL (2014) Zinc causes acute impairment of glutathione metabolism followed by coordinated antioxidant defenses amplification in gills of brown mussels Perna perna. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 159:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2013.09.007
Sarasamma S, Audira G, Juniardi S, Sampurna BP, Liang S-T, Hao E, Lai Y-H, Hsiao C-D (2018) Zinc chloride exposure inhibits brain acetylcholine levels, produces neurotoxic signatures, and diminishes memory and motor activities in adult zebrafish. Int J Mol Sci 19(10):3195. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103195
Zhang H, Reynolds M (2019) Cadmium exposure in living organisms: a short review. Sci Total Environ 678:761–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.395
Thanan R, Oikawa S, Hiraku Y, Ohnishi S, Ma N, Pinlaor S, Yongvanit P, Kawanishi S, Murata M (2015) Oxidative stress and its significant roles in neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Int J Mol Sci 16(1):193–217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16010193
Juan CA, Pérez de la Lastra JM, Plou FJ, Pérez-Lebeña E (2021) The chemistry of reactive oxygen species (ROS) revisited: outlining their role in biological macromolecules (dna, lipids and proteins) and ınduced pathologies. Int J Mol Sci 22(9):4642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094642
Deidda I, Russo R, Bonaventura R, Costa C, Zito F, Lampiasi N (2021) Neurotoxicity in marine invertebrates: an update. Biology 10(2):161. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10020161
Gupta R, Shukla RK, Chandravanshi LP, Srivastava P, Dhuriya YK, Shanker J, Singh MP, Pant AB, Khanna VK (2017) Protective role of quercetin in cadmium-induced cholinergic dysfunctions in rat brain by modulating mitochondrial integrity and MAP kinase signaling. Mol Neurobiol 54(6):4560–4583. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9950-y
Moyano P, de Frias M, Lobo M, Anadon MJ, Sola E, Pelayo A, Díaz MJ, Frejo MT, Del Pino J (2018) Cadmium induced ROS alters M1 and M3 receptors, leading to SN56 cholinergic neuronal loss, through AChE variants disruption. Toxicology 394:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2017.12.006
Grammou A, Papadimitriou C, Samaras P, Vasara E, Papadopoulos AI (2011) Effect of municipal waste water effluent upon the expression of glutathione S-transferase isoenzymes of brine shrimp Artemia. Chemosphere 84(1):105–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.047
Ensibi C, Yahia MND (2017) Toxicity assessment of cadmium chloride on planktonic copepods Centropages ponticus using biochemical markers. Toxicol Rep 4:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2017.01.005
Livingstone DR (2001) Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar Pollut Bull 42(8):656–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-326X(01)00060-1
Khaliq MA, James B, Chen YH, Saqib HSA, Li HH, Jayasuriya P, Guo W (2019) Uptake, translocation, and accumulation of Cd and its interaction with mineral nutrients (Fe, Zn, Ni, Ca, Mg) in upland rice. Chemosphere 215:916–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.077
Zhang Y, Lu X, Wang N, Xin M, Geng S, Jia J, Meng Q (2016) Heavy metals in aquatic organisms of different trophic levels and their potential human health risk in Bohai Bay. China Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(17):17801–17810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6948-y
Rai PK, Lee SS, Zhang M, Tsang YF, Kim KH (2019) Heavy metals in food crops: health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. Environ Int 125:365–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.01.067
Le Saux A, David E, Betoulle S, Bultelle F, Rocher B, Barjhoux I, Cosio C (2020) New insights in to cellular ımpacts of metals in aquatic animals. Environments 7(6):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments7060046
Cavion F, Fusco L, Sosa S, Manfrin C, Alonso B, Zurutuza A, Della Loggia R, Tubaro A, Prato M, Pelin M (2020) Ecotoxicological impact of graphene oxide: toxic effects on the model organism Artemia franciscana. Environ Sci Nano 7:3605–3615. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0en00747a
Nunes BS, Carvalho FD, Guilhermino LM, Van Stappen G (2006) Use of the genus Artemia in ecotoxicity testing. Environ Pollut 144(2):453–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.037
Ntungwe NE, Domínguez-Martín EM, Roberto A, Tavares J, Isca VMS, Pereira P, Cebola M-J, Rijo P (2020) Artemia species: an important tool to screen general toxicity samples. Curr Pharm Des 26(24):2892–2908
Baharom ZS, Ishak MY (2015) Determination of heavy metal accumulation in fish species in Galas River, Kelantan and Beranang Mining Pool, Selangor. Procedia Environ Sci 30:320–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proenv.2015.10.057
Baki MA, Hossain MM, Akter J, Quraishi SB, Shojib MFH, Ullah AA, Khan MF (2018) Concentration of heavy metals in seafood (fishes, shrimp, lobster and crabs) and human health assessment in Saint Martin Island, Bangladesh. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 159:153–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.04.035
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
Lowry O, Rosebrough N, Farr A, Randall R (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 673–684
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44(1):276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8
Slater TF (1984) Overview of methods used for detecting lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 105:283–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05036-9
Alexieva V, Sergiev I, Mapelli S, Karanov E (2001) The effect of drought and ultraviolet radiation on growth and stress markers in pea and wheat. Plant Cell Environ 24(12):1337–1344. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3040.2001.00778.x
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249(22):7130–7139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)42083-8
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V, Featherstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7(2):88–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9
Devi SS, Sethu M, Lalithambigai P, Priya PG (2017) Study on the effect of Artemia franciscana on the uptake of Zn(II) and Cu(II). J Water Chem Technol 39(1):40–46. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X17010076
Thall A, Acey R (1985) Cadmium binding proteins in developing Artemia. Fed Proc 44(5):1461
Rafiee P, Matthews CO, Bagshaw JC, MacRae TH (1986) Reversible arrest of Artemia development by cadmium. Can J Zool 64(8):1633–1641. https://doi.org/10.1139/z86-246
Mohiseni M, Farhangi M, Agh N, Mirvaghefi A, Talebi K (2017) Toxicity and bioconcentration of cadmium and copper in Artemia urmiana nauplii. Iran J Toxicol 11(1):33–41
Mohamed AH, Sheir SK, Osman GY, Abd-El Azeem HH (2014) Toxic effects of heavy metals pollution on biochemical activities of the adult brine shrimp, Artemia salina. Can J Pure Appl Sci 8(3):3019–3028
Trinchella F, Riggio M, Filosa S, Volpe MG, Parisi E, Scudiero R (2006) Cadmium distribution and metallothionein expression in lizard tissues following acute and chronic cadmium intoxication. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 144(3):272–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2006.09.004
Acey RA, Yoshida BN, Edep ME (1989) Metalloproteins in developing Artemia. In: Warner AH, MacRae TH, Bagshaw JC (eds) Cell and molecular biology of Artemia development. Plenum Press, New York, pp 203–219
Barata C, Markich SJ, Baird DJ, Taylor G, Soares AMVM (2002) Genetic variability in sublethal tolerance to mixtures of cadmium and zinc in clones of Daphnia magna Straus. Aquat Toxicol 60(1–2):85–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-445X(01)00275-2
Tamás MJ, Sharma SK, Ibstedt S, Jacobson T, Christen P (2014) Heavy metals and metalloids as a cause for protein misfolding and aggregation. Biomolecules 4(1):252–267. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom4010252
Sarabia R, Del Ramo J, Varo I, Diaz-Mayans J, Torreblanca A (2002) Comparing the acute response to cadmium toxicity of nauplii from different populations of Artemia. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(2):437–444. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620210229
Sandrini JZ, Regoli F, Fattorini D, Notti A, Inácio AF, Linde-Arias AR, Laurino J, Bainy ACD, Marins LFF, Monserrat JM (2006) Short-term responses to cadmium exposure in the estuarine polychaete Laeonereis acuta (Polychaeta, Nereididae): subcellular distribution and oxidative stress generation. Environ Toxicol Chem 25(5):1337–1344. https://doi.org/10.1897/05-275R.1
Pacheco GKÑ, Maldonado NSS, Alta RYP, Vitorino HA (2021) Short exposure of Artemia salina to group-12 metals: comparing hatchability, mortality, lipid peroxidation, and swimming speed. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 213:112052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112052
Ates M, Daniels J, Arslan Z, Farah IO, Rivera HF (2013) Comparative evaluation of impact of Zn and ZnO nanoparticles on brine shrimp (Artemia salina) larvae: effects of particle size and solubility on toxicity. Environ Sci Process Impacts 15(1):225–233. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2EM30540B
Wang J, Zhu X, Huang X, Gu L, Chen Y, Yang Z (2016) Combined effects of cadmium and salinity on juvenile Takifugu obscurus: cadmium moderates salinity tolerance; salinity decreases the toxicity of cadmium. Sci Rep 6:30968. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30968
Ortega P, Vitorino HA, Moreira RG, Pinheiro MAA, Almeida AA, Custódio MR, Zanotto FP (2017) Physiological differences in the crab Ucides cordatus from two populations inhabiting mangroves with different levels of cadmium contamination. Environ Toxicol Chem 36(2):361–371. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3537
Jiang Q-C, Dilixiati A, Zhang C, Liu X-Z, Huang W-T, Lv L-L, Wang Q, Yang J-X (2013) Metabolic and antioxidant responses in juveniles of Cherax quadricarinatus under acute cadmium stress. J Crustac Biol 33(4):552–556. https://doi.org/10.1163/1937240X-00002149
Wang M-H, Wang G-Z (2009) Biochemical response of the copepod Tigriopus japonicus Mori experimentally exposed to cadmium. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 57:707–717. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-009-9319-6
Pirsaheb M, Azadi NA, Miglietta ML, Sayadi MH, Blahova J, Fathi M, Mansouri B (2019) Toxicological effects of transition metal-doped titanium dioxide nanoparticles on goldfish (Carassius auratus) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Chemosphere 215:904–915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.111
Jemec A, Drobne D, Tišler T, Trebše P, Roš M, Sepčić K (2007) The applicability of acetylcholinesterase and glutathione S-transferase in Daphnia magna toxicity test. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 144(4):303–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2006.10.002
Nunes B, Carvalho F, Guilhermino L (2006) Effects of widely used pharmaceuticals and a detergent on oxidative stress biomarkers of the crustacean Artemia parthenogenetica. Chemosphere 62(4):581–594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.06.013
Najimi S, Bouhaimi A, Daubèze M, Zekhnini A, Pellerin J, Narbonne JF, Moukrim A (1997) Use of acetylcholinesterase in Perna perna and Mytilus galloprovincialis as a biomarker of pollution in Agadir Marine Bay (South of Morocco). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 58(6):901–908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001289900419
Gagné F, Cejka P, André C, Hausler R, Blaise C (2007) Neurotoxicological effects of a primary and ozonated treated wastewater on freshwater mussels exposed to an experimental flow-through system. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 146(4):460–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2007.04.006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Biljana Kukavica: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, ınvestigation, data curation, writing — original draft. Biljana Davidović-Plavšić: conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, ınvestigation, data curation, review and correction. Ana Savić: data curation, review and correction. Dejan Dmitrović: conceptualization, methodology, review and correction. Goran Šukalo: conceptualization, methodology, review and correction. Sandra Đurić-Savić: formal analysis, data curation. Goran Vučić: formal analysis, data curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Medical Faculty University of Banja Luka (No. 18/1.190–18/22).
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information

Supplementary Figure 1:
Online Resource 1 Representative native SOD gel of control and treated samples of A. franciscana after 24 and 48 h. The arrow indicates the detected SOD isoform and its Rf value (PNG 482 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kukavica, B., Davidović-Plavšić, B., Savić, A. et al. Oxidative Stress and Neurotoxicity of Cadmium and Zinc on Artemia franciscana. Biol Trace Elem Res 201, 2636–2649 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03352-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-022-03352-x