Abstract
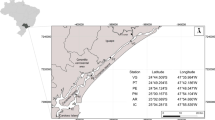
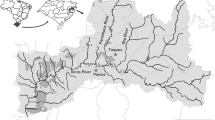
Histopathologies are widely recognized as biomarkers of environmental pollution. In this sense, we evaluated the putative relationship of gill histopathologies and distinct ecological impacts in two regions of Todos os Santos Bay (BTS), Brazil, the largest bay in Northeastern Brazil, South Atlantic. We compared the presence and concentration of metals (Al, As, Ba, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, V, and Zn) in water, sediments, and gills and gill histopathologies of a demersal fish (Diapterus rhombeus) and a benthic fish (Ogcocephalus vespertilio). As expected, fish and sediment samples from historically contaminated areas (Aratu) showed more remarkable traces of metals than apparently low-impact areas (Jaguaripe). Likewise, the DTC (degree of tissue change) index and the volume densities were higher in fish caught in Aratu. In addition, the Diapterus rhombeus species showed more potential than Ogcocephalus vespertilio for risk assessment as it showed more responses to the environment reflected on more histopathologies. These data support the effectiveness of incorporating functional gill morphology to monitor impacts on estuarine biota that can be used as a reference to improve the management of ecosystems and prevent harm to human health.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Lu Y, Yuan J, Lu X, Su C et al (2018) Major threats of pollution and climate change to global coastal ecosystems and enhanced management for sustainability. Environ Pollut 239:670–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.016
Whitfield AK, Elliott M (2002) Fishes as indicators of environmental and ecological changes within estuaries: a review of progress and some suggestions for the future. J Fish Biol 61:229–250. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2002.tb01773.x
Wild-Allen K, Skerratt J, Whitehead J, Rizwi F, Parslow J (2013) Mechanisms driving estuarine water quality: a 3-D biogeochemical model for informed management. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 135:33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2013.04.009
Arizzi Novelli A, Losso C, Libralato G, Tagliapietra D, Pantanib C, Volpi GA (2006) Is the 1:4 elutriation ratio reliable? Ecotoxicological comparison of four different sediment: water proportions. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 65:306–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2005.08.010
Barišić J, Dragun Z, Ramani S, Filipović VM, Krasnići N, Čož-Rakovac R, Kostov V, Rebok K, Jordanova M (2015) Evaluation of histopathological alterations in the gills of Vardar chub (Squalius vardarensis Karaman) as an indicator of river pollution. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 118:158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.04.027
Araújo CFS, Lopes MV, Mirian RV, Menezes-Filho JA (2016) Cadmium and lead in seafood from the Aratu Bay, Brazil and the human health risk assessment. Environ Monit Assess 188:259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5262-y
Vieira LR, Gravato C, Soares AMVM, Morgado F, Guilhermino F (2009) Acute effects of copper and mercury on the estuarine fish Pomatoschistus microps: Linking biomarkers to behavior. Chemosphere 76:1416–1427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.06.005
Guntenspergen GR, Baldwin AH, Hogan DM, Neckles HA, Nielsen MG (2009) Valuing urban wetlands: modification, preservation and restoration. In: McDonnell MJ, Hahs AK, 24. Breuste JH (ed) Ecology of cities and towns: a comparative approach. Cambridge University, pp 516–520
Hatje V, Andrade RLB, de Oliveira CC, Polejack A, Gxaba T (2021) Pollutants in the South Atlantic Ocean: sources, knowledge gaps and perspectives for the decade of Ocean Science. Front Mar Sci 8:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2021.644569
Mathews T, Fisher NS (2008) Evaluating the trophic transfer of cadmium, polonium, and methylmercury in an estuarine food chain. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1093–1101. https://doi.org/10.1897/07-318.1
Vasanthi LA, Revathi P, Mini J, Munuswamy N (2013) Integrated use of histological and ultrastructural biomarkers in Mugil cephalus for assessing heavy metal pollution in Ennore estuary, Chennai. Chemosphere 91:1156–1164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.01.021
Rajeshkumar S, Li X (2018) Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish species from the Meiliang Bay, Taihu Lake, China. Toxicol Rep 5:288–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2018.01.007
Has-Schon E, Bogut I, Strelec I (2006) Heavy metal profile in five fish species included in human diet, domiciled in the end flow of River Neretva (Croatia). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:545–551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-0047-2
Plessl C, Otachi EO, Körner W, Avenant-Oldewage A, Jirsa F (2017) Fish as bioindicators for trace element pollution from two contrasting lakes in the Eastern Rift Valley, Kenya: spatial and temporal aspects. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:19767–19776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9518-z
Mallat J (1985) Fish gill structural changes induced by toxicants and other irritants: a statistical review. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 42:630–648. https://doi.org/10.1139/f85-083
Hatje V, Barros F (2012) Overview of the 20th century impact of trace metal contamination in the estuaries of Todos os Santos Bay: past, present and future 418 scenarios. Mar Pollut Bull 64:2603–2614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2012.07.009
Barros F, Hatje V, Figueiredo MB, Magalhães WF, Dórea HS, Emídio ES (2008) The structure of the benthic macrofaunal assemblages and sediments characteristics of the Paraguaçu estuarine system, NE, Brazil. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 78:753–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2008.02.016
Reis-Filho JA, Giarrizzo T (2016) Microgobius meeki as a potential bio-indicator of habitat disturbance in shallow estuarine areas: a useful tool for the assessment of estuarine quality. J Fish Biol 23:126–134. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfb.13007
Chaves PTCC, Otto G (1999) Aspectos biológicos de Diapterus rhombeus (Cuvier) (Teleostei, Gerreidae) na baía de Guaratuba, Paraná, Brasil. Rev Bras Zool 15:289–295
Gibran FZ, Castro RMC (1999) Activity, feeding behaviour and diet of Ogcocephalus vespertilio in southern west Atlantic. J Fish Biol 55:588–595. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1999.tb00701.x
Ferreira AN, Beretta M, Mafalda PO Jr (2012) Assessing the impact of dredging on phytoplankton association of Aratu harbor, in Todos os Santos Bay, Bahia state. Arquivos de Ciências do Mar, Fortaleza 45:30–46
Rocha TS, Sales EA, Beretta M, Oliveira IB (2016) Effects of dredging at Aratu port in All Saints Bay, Brazil: monitoring the metal content in water and sediments. Environ Monit Assess 188:394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5396-y
Krull M, Abessa DMS, Hatje V, Barros F (2014) Integrated assessment of metal contamination in sediments from two tropical estuaries. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 106:195–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.038
Conama. Conselho Nacional do Meio Ambiente/Ministério do Meio Ambiente (2012) Resolução n° 454, de 1° de novembro de 2012 http://www2.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi=693
Poleksić V, Mitrović-Tutundžić V (1994) Fish gills as a monitor of sublethal and chronic effects of pollution. In: Müller R, Lloyd R (eds) Sublethal and chronic effects of pollutants on freshwater fish. Fishing News Books, Oxford, pp 339–352
Abdel-Moneim AM, Mohamed A, Al-Kahtani A, Elmenshawy OM (2012) Histopathological biomarkers in gills and liver of Oreochromis niloticus from polluted wetland environments, Saudi Arabia. Chemosphere 88:1028–1035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.04.001
Monteiro SM, Rocha E, Fontaínhas-Fernandes A, Sousa M (2008) Quantitative histopathology of Oreochromis niloticus gills after copper exposure. J Fish Biol 73:1376–1392. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.2008.02009.x
Howard CV, Reed MG (2005) Unbiased stereology: three-dimensional measurement in microscopy. Bios Scientific Publishers, Oxford
Anderson MJ, Gorley RN, Clarke KR (2001) A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol 26:32–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9993.2001.01070.pp.x
Anderson MJ, Gorley RN, Clarke KR (2008) PERMANOVA+for PRIMER: guide to software and statistical methods. PRIMER-E, Plymouth
Chapman PM, Wang F (2001) Assessing sediment contamination in estuaries. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:3–22. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620200102
Macêdo AKS, dos Santos KPE, Brighenti LS, Windmöller CC, Barbosa FAR, Ribeiro RIMA, dos Santos HB, Thomé RG (2020) Histological and molecular changes in gill and liver of fish (Astyanax lacustris Lütken, 1875) exposed to water from the Doce basin after the rupture of a mining tailings dam in Mariana MG, Brazil. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139505
Mebane CA, Chowdhury MJM, De Schamphelaere KAC, Lofts S, Paquin PR, Santore RC, Wood CM (2020) Metal bioavailability models: current status, lessons learned, considerations for regulatory use, and the path forward. Environ Toxicol Chem 39:60–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.4560
Ardeshir RA, Zolgharnein H, Movahedinia A, Salamat N, Zabihi E (2017) Comparison of waterborne and intraperitoneal exposure to fipronil in the Caspian white fish (Rutilus frisii) on acute toxicity and histopathology. Toxicol Rep 4:348–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2017.06.010
Martins M, Santos JM, Costa MH, Costa PM (2016) Applying quantitative and semi-quantitative histopathology to address the interaction between sediment-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in fish gills. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 131:164–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.04.019
Gauthier PT, Norwood WP, Prepas EE, Pyle GG (2014) Metal–PAH mixtures in the aquatic environment: a review of co-toxic mechanisms leading to more-than-additive outcomes. Aquat Toxicol 154:253–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.05.026
Oliveira Ribeiro CA, Vollaire Y, Sanchez-Chardi A, Roche H (2005) Bioaccumulation and the effects of organochlorine pesticides, PAH and heavy metals in the Eel (Anguilla anguilla) at the Camargue Nature Reserve, France. Aquatic Toxicol 74:53–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2005.04.008
Cruz AL, Prado TM, Maciel LAS, Couto RD (2015) Environmental effects on the gills and blood of Oreochromis niloticus exposed to rivers of Bahia, Brazil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 111:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.09.022
Bao J, Xing Y, Feng C, Kou S, Jiang H, Li X (2020) Acute and sub-chronic effects of copper on survival, respiratory metabolism, and metal accumulation in Cambaroides dauricus. Sci Rep 10:16700. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73940-1
Araujo HRM, Fernandes MN, Cruz AL (2019) Gill morphology and Na+/K+-Atpase activity of Gobionellus oceanicus (Teleostei: Gobiidae) in an estuarine system. Biol Trace Elem Res 187:526–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-018-1393-z
Evans DH, Piermarini PM, Choe KP (2005) The multifunctional fish gill: dominant site of gas exchange, osmoregulation, acid-base regulation, and excretion of nitrogenous waste. Physiol Rev 85:97–177. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00050.2003
Jia YJ, Wang L, Qu Z, Wang C, Yang Z (2017) Effects on heavy metal accumulation in freshwater fishes: species, tissues, and sizes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:9379–9386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8606-4
Teien H-C, Standring WJF, Salbu B (2006) Mobilization of river transported colloidal aluminium upon mixing with seawater and subsequent deposition in fish gills. Sci Total Environ 364:149–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.01.005
CRA. Centro de Recursos Ambientais (2004) Diagnóstico da concentração de metais pesados e hidrocarbonetos de petróleo nos sedimentos e biota da Baía de Todos os Santos. Consórcio BTS Hydros CH2MHILL. Governo do Estado da Bahia
Hatje V, Bícego MC, Carvalho GC, Andrade JB (2009) Todos os Santos Bay: oceanographic aspects/chemical contamination. EDUFBA, Salvador
Beg MU, Al-Jandal N, Al-Subiai S, Karam Q, Husain S, Butt SA, Ali A, Al-Hasan E, Al-Dufaileej S, Al-Husaini M (2015) Metallothionein, oxidative stress and trace metals in gills and liver of demersal and pelagic fish species from Kuwaits’ marine area. Mar Pollut Bull 75:344–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2015.07.058
Cruz AL, Prado RLP, Klein W (2019) The potential respiratory surfaces of a fish living in a historically polluted river. Anim Biol. https://doi.org/10.1163/15707563-20191109
Al-Yousuf MH, El-Shahawi MS, Al-Ghais SM (2000) Trace metals in liver, skin and muscle of Lethrinus lentjan fish species in relation to body length and sex. Sci Total Environ 256:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0048-9697(99)00363-0
Canli M, Atli G (2003) The relationships between heavy metal (Cd, Cr, Cu, Fe, Pb, Zn) levels and the size of six Mediterranean fish species. Environ Pollut 121:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00194-X
Ural M, Yildirim N, Danabas D, Kaplan O, Yildirim NC, Ozcelik M, Kurekci EF (2012) Some heavy metals accumulation in tissues in Capoeta umbla (Heckel, 1843) from Uzuncayir Dam Lake (Tunceli, Turkey). Environ Contam Tox 88:172–176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-011-0474-x
Brunelli E, Mauceri A, Maisano M, Bernab I, Giannetto A, DeDomenico E, Corapi B, Tripepi S, Fasulo S (2011) Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical investigation on the gills of the teleost, Thalassoma pavo L., exposed to cadmium. Acta histochem 113:201–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2009.10.002
Pane EF, Haque A, Wood CM (2004) Mechanistic analysis of acute, Ni-induced respiratory toxicity in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): an exclusively branchial phenomenon. Aquat Toxicol 69:11–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.04.009
Thophon S, Kruatachue M, Upatham ES, Pokethityook P, Sahaphong S, Jaritkhuan S (2003) Histopathological alterations of whiteseabass, Lates calarifera, in acute and subchronic cadmium exposure. Environ Pollut 121:307–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00270-1
Massar B, Dey S, Dutta K (2013) Electron microscopy of fish gill ultra-structure with reference to water pollution by municipal wastes. J Adv Microsc Res 7:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1166/jamr.2012.1109
Macirella R, Brunelli R (2017) Morphofunctional alterations in zebrafish (Danio rerio) gills after exposure to mercury chloride. Int J Mol Sci 18:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040824
Samanta P, Im H, Na J, Jung J (2018) Ecological risk assessment of a contaminated stream using multi-level integrated biomarker response in Carassius auratus. Environ Pollut 233:429–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.10.061
Acknowledgements
H.H.Q.O. and L.A.S.M. thank the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, Brazil (CNPq) and Foundation for Research Support of the state of Bahia, Brazil (FAPESB) for the master’s fellowships. R.M.S. and E.F.E.S. thank CNPq for the scientific initiation scholarships. J.A.C.C.N. and J.A.R.F. thank Coordination of Improvement of Higher-Level Personnel, Brazil (CAPES), Finance Code 001, for PhD fellowships. The authors also thank Ralph Gruppi Thomé (UFSJ, Divinópolis, MG, Brazil) and Marisa Narciso Fernandes (UFSCar, São Carlos, SP, Brazil) for their comments and suggestions, Domingos Cardoso for computer assistance, and the Laboratório de Microscopia Eletrônica, FIOCRUZ, Salvador, Bahia, for the assistance on microscopy electronic transmission.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Institute of Science and Technology in Comparative Physiology (INCT-Comparative Physiology, Brazil) to ALC, and Fapesb (Foundation for Research Support of the State of Bahia, Brazil) (RED0037/2014) on behalf of ALC and PRAMA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.H.Q.O.: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, and writing—original draft
J.A.R.F.: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, resources, supervision and writing—original draft.
J.A.C.C.N.: formal analysis, investigation, resources and writing—original draft
R.M.S.: investigation, formal analysis and writing—review & editing
E.F.E.S.: investigation and formal analysis
L.A.: investigation, formal analysis and writing—review & editing
P.R.A.M.A.: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration and resources
A.L.C.: conceptualization, formal analysis, investigation, funding acquisition, methodology, project administration, resources, supervision and writing—review & editing
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The local ethics committee approved these procedures on animal use (Comitê de Ética no Uso de Animais, Instituto de Biologia, Universidade Federal da Bahia, 23/2015).
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publish
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliveira, H.H.Q., Reis-Filho, J.A., Nunes, J.A.C.C. et al. Gill Histopathological Biomarkers in Fish Exposed to Trace Metals in the Todos os Santos Bay, Brazil. Biol Trace Elem Res 200, 3388–3399 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02930-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-021-02930-9