Abstract
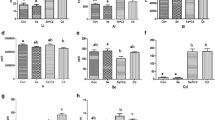
Increasing evidence indicates that selenium (Se) could antagonize metal toxicity, including cadmium (Cd) toxicity. However, the effects of Se on Cd-induced changes in the ion profile in the pancreas of chickens have not been reported. In the present study, 128 Hy-Line brown laying chickens were divided into the control group, Se-treated group, Se/Cd-treated group, and Cd-treated group, and we detected the concentrations of 28 ions in the four groups by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. In the Cd-treated group, the accumulation of Cd in the pancreas was 836.8 times higher that than in the control group (27,353.71 ppb/32.69 ppb). Meanwhile, the Ca, Ti, Fe, Mo, Li, Al, and Pb levels increased and the Cr, Mn, Ni, Cu, Zn, Se, Sr, and Sb levels decreased due to sub-chronic Cd poisoning. The Fe, Mo, Ba, and Pb levels decreased in the Se/Cd-treated group. Our findings suggest that Cd can accumulate in the chicken pancreas and affect the ion profiles, whereas Se can ameliorate the accumulation of Cd and change the ion profiles in the chicken pancreas.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaličanin BM (2009) Determination of very toxic metal—cadmium in natural water samples. Desalination 249(1):58–62
Smolik B, Malinowska K (2008) Effect of soil contamination with cadmium on the element content in spring wheat (Triticum vulgare). Science 217(4562):860–861
Hu JZ, Pei DL, Liang F, Shi GX (2009) Growth responses of Sagittaria sagittifolia L. plants to water contamination with cadmium. Russ J Plant Physiol 56(5):686–694
Ke S, Cheng XY, Zhang N, Hu HG, Yan Q, Hou LL, Sun X, Chen ZN (2015) Cadmium contamination of rice from various polluted areas of China and its potential risks to human health. Environ Monit Assess 187(7):408
Ferramola ML, Díaz MFFP, Honoré SM, Sánchez SS, Antón RI, Anzulovich AC, Giménez MS (2012) Cadmium-induced oxidative stress and histological damage in the myocardium. Effects of a soy-based diet. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 265(3):380–389
Wang L, Li J, Li J, Liu Z (2010) Effects of lead and/or cadmium on the oxidative damage of rat kidney cortex mitochondria. Biol Trace Elem Res 137(1):69–78
Casalino E, Calzaretti G, Sblano C, Landriscina C (2002) Molecular inhibitory mechanisms of antioxidant enzymes in rat liver and kidney by cadmium. Toxicology 179(1):37–50
Schwartz GG, Reis IM (2000) Is cadmium a cause of human pancreatic cancer? Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 9(2):139–145
Wang L, Zhou X, Yang D, Wang Z (2011) Effects of lead and/or cadmium on the distribution patterns of some essential trace elements in immature female rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 30(12):1914–1923
Lin W, Jin C, Chen DW, Liu XZ, Hao L, Liu ZP (2009) Role of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and intracellular homeostasis in primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells exposed to cadmium. Biol Trace Elem Res 127(1):53–68
Ishitobi H, Mori K, Yoshida K, Watanabe C (2007) Effects of perinatal exposure to low-dose cadmium on thyroid hormone-related and sex hormone receptor gene expressions in brain of offspring. Neurotoxicology 28(4):790–797
Yao HD, Wu Q, Zhang ZW, Zhang JL, Li S, Huang JQ, Ren FZ, Xu SW, Wang XL, Lei XG (2013) Gene expression of endoplasmic reticulum resident selenoproteins correlates with apoptosis in various muscles of se-deficient chicks. J Nutr 143(5):613–619
Kumar M, Bijo AJ, Baghel RS, Reddy CRK, Jha B (2012) Selenium and spermine alleviate cadmium induced toxicity in the red seaweed Gracilaria dura by regulating antioxidants and DNA methylation. Plant Physiol Biochem 51(2):129–138
Arthur JR, Mckenzie RC, Beckett GJ (2003) Selenium in the immune system. J Nutr 133(5 Suppl 1):1457S–1459S
Cao C, Fan R, Zhao J, Zhao X, Yang J, Zhang Z, Xu S (2017) Impact of exudative diathesis induced by selenium deficiency on LncRNAs and their roles in the oxidative reduction process in broiler chick veins. Oncotarget. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14971
Yang T, Zhao Z, Liu T, Zhang Z, Wang P, Xu S, Len XG, Shan A (2017) Oxidative stress induced by Se-deficient high-energy diet implicates neutrophil dysfunction via Nrf2 pathway suppression in swine. Oncotarget. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14550
Brenneisen P, Steinbrenner H, Sies H (2005) Selenium, oxidative stress, and health aspects. Mol Asp Med 26(4–5):256–267
Yao HD, Wu Q, Zhang ZW, Shu L, Wang XL, Lei XG, Xu SW (2013) Selenoprotein W serves as an antioxidant in chicken myoblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830(4):3112–3120
Beckett GJ, Arthur JR (2005) Selenium and endocrine systems. J Endocrinol 184(3):455
Zhao X, Yao H, Fan R, Zhang Z, Xu S (2014) Selenium deficiency influences nitric oxide and selenoproteins in pancreas of chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 161(3):341–349
Schrauzer GN (1987) Effects of selenium antagonists on cancer susceptibility: new aspects of chronic heavy metal toxicity. J UOEH 9(Suppl):208
Wang Y, Wu Y, Luo K, Liu Y, Zhou M, Yan S, Shi H, Cai Y (2013) The protective effects of selenium on cadmium-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis via mitochondria pathway in mice kidney. Food Chem Toxicol 58(6):61–67
Li X, Xing M, Chen M, Zhao J, Fan R, Xia Z, Cao C, Jie Y, Zhang Z, Xu S (2017) Effects of selenium-lead interaction on the gene expression of inflammatory factors and selenoproteins in chicken neutrophils. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf:447–453
Xu T, Gao X, Liu G (2016) The antagonistic effect of selenium on lead toxicity is related to the ion profile in chicken liver. Biol Trace Elem Res 169(2):365–373
Yang DYY, Chen YWW, Gunn JMGM, Belzile NB (2008) Selenium and mercury in organisms: interactions and mechanisms. Environ Rev 16(NA):71–92
Yao H, Fan R, Zhao X, Zhao W, Liu W, Yang J, Sattar H, Zhao J, Zhang Z, Xu S (2016) Selenoprotein W redox-regulated Ca2+ channels correlate with selenium deficiency-induced muscles Ca2+ leak. Oncotarget 7(36):57618–57632
Jihen EH, Imed M, Fatima H, Abdelhamid K (2008) Protective effects of selenium (Se) and zinc (Zn) on cadmium (Cd) toxicity in the liver and kidney of the rat: histology and Cd accumulation. Food Chem Toxicol 46(11):3522–3527
Winiarskamieczan A, Krusiński R, Kwiecień M (2013) Tannic acid influence on lead and cadmium accumulation in the hearts and lungs of rats. Adv Clin Exp Med 22(5):615–620
Zhang R, Wang L, Zhao J, Chao W, Bao J, Li J (2016) Effects of selenium and cadmium on ion profiles in the brains of chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 174(1):1–8
Mcclusky LM (2008) Cadmium accumulation and binding characteristics in intact Sertoli/germ cell units, and associated effects on stage-specific functions in vitro: insights from a shark testis model. J Appl Toxicol Jat 28(2):112–121
Schwartz GG (2002) Cadmium is a risk factor for human pancreatic cancer. US
Özkan-Yılmaz F, Özlüer-Hunt A, Gündüz SG, Berköz M, Yalın S (2014) Effects of dietary selenium of organic form against lead toxicity on the antioxidant system in Cyprinus carpio. Fish Physiol Biochem 40(2):355–363
Ciardullo S, Aureli F, Coni E, Guandalini E, Iosi F, Raggi A, Rufo G, Cubadda F (2008) Bioaccumulation potential of dietary arsenic, cadmium, lead, mercury, and selenium in organs and tissues of rainbow trout (Oncorhyncus mykiss) as a function of fish growth. J Agric Food Chem 56(7):2442–2451
Hudson JL (1976) Interactions of selenium, cadmium and copper in sheep. EJC Suppl 27(3):447–452
Zhang R, Wang Y, Wang C, Zhao P, Liu H, Li J, Bao J (2017) Ameliorative effects of dietary selenium against cadmium toxicity is related to changes in trace elements in chicken kidneys. Biol Trace Elem Res 176(2):391–400
Zhang R, Wang L, Zhao J, Wang C, Bao J, Li J (2016) Effects of selenium and cadmium on ion profiles in the brains of chickens. Biol Trace Elem Res 174(1):218–225
He Y, Sun B, Li S, Sun X, Guo Y, Zhao H, Wang Y, Jiang G, Xing M (2016) Simultaneous analysis 26 mineral element contents from highly consumed cultured chicken overexposed to arsenic trioxide by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(21):21741–21750
Sun B, Xing M (2016) Evaluated the twenty-six elements in the pectoral muscle of as-treated chicken by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Biol Trace Elem Res 169(2):1–6
Wang L, Ma Q, Chen X, Sha H, Ma Z (2008) Effects of resveratrol on calcium regulation in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Eur J Pharmacol 580(1–2):271–276
Arkle S, Lee CM, Cullen MJ, Argent BE (1986) Isolation of ducts from the pancreas of copper-deficient rats. Q J Exp Physiol 71(2):249–265
Orlov YP, Lukach VN, Dolgikh VT, Govorova NV, Gluschenko AV (2015) Deferoxamine as pathogenetically valid preparation for complex therapy of patients with acute pancreatitis. Novosti Khirurgii 23(3):286–295
Andrzejewska A, Szynaka B, Stokowska W, Szynaka P (1995) Does lead acetate intoxication damage acinar cell nuclei in the rat pancreas? Ultrastructural observations. Mater Med Pol Polish J Med Pharm 27(2):43–46
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Science Foundation of the Education Department of Heilongjiang Province (Grant No.11551030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All procedures used in this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Northeast Agricultural University.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
All other authors have read the manuscript and agreed to submit it in its current form for consideration for publication in the journal.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, R., Wang, X., Zheng, S. et al. Selenium Supplementation Changes the Ion Profile in the Pancreas of Chickens Treated with Cadmium. Biol Trace Elem Res 181, 133–141 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1034-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1034-y