Abstract
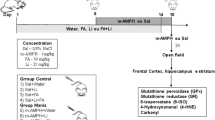
Heroin use, withdrawal syndrome, and heroin-related deaths are still the most serious public health problems. Antioxidants and bio-elements are essential for metabolism in living organisms. To our knowledge, there are no data about the effect of antioxidant therapy on the levels of bio-elements and antioxidant enzymes in the naloxone (NX)-induced heroin withdrawal syndrome. Therefore, in the present study for the first time, we have investigated the role of antioxidant therapy, melatonin, and vitamin E plus Se, on the trace and major elements and antioxidant enzymes in the heroin addiction or heroin withdrawal in rats. Glutathione peroxidase levels were increased and catalase levels were decreased in the all study groups when compared to the sham group. The level of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the fixed dose of heroin (FDH) given group was lower; however, in the variable doses of heroin (VDH) given group SOD level was higher. Furthermore, in withdrawal syndrome, Fe, Mg, Mn, and Ti levels were diminished and Al, Ca, and Cu levels were increased in the FDH+NX group. Moreover, Mg, Mn, and Se levels were also diminished and Al level was increased in the VDH+NX group. In conclusion, our results obviously indicated that heroin effected both bio-element status and antioxidant enzyme activities and, exogenous melatonin or vE+Se therapy might relieve on the element and antioxidant enzyme the destructive activity caused by heroin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaffe JA, Kimmel PL (2006) Chronic nephropathies of cocaine and heroin abuse: a critical review. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:655–667
Ferri M, Davoli M, Perucci CA. Heroin maintenance for chronic heroin dependents. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 2. Art. No.: CD003410. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003410.pub2
Pinelli A, Cighetti G, Trivulzio S (2008) Plasma malondialdehyde levels and opiate withdrawal signs observed in rats treated with morphine plus naloxone: effects of α-lipoic acid administration. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 22(4):439–445
Suresh S, Anand KJS (1998) Opioid tolerance in neonates: mechanisms, diagnosis, assessment and management. Semin Perinatol 22:425–433
Anand KJS, Arnold JH (1994) Opioid tolerance and dependence in infants and children. Crit Care Med 22:334–342
Evangelou A, Kalfakakou V, Georgakas P, Koutras V, Vezyraki P, Iliopoulou L, Vadalouka A (2000) Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) effects on withdrawal syndrome of heroin abusers. In Vivo 14(2):363–366
Xu B, Wang Z, Li G, Li B, Lin H, Zheng R, Zheng Q (2006) Heroin-administered mice involved in oxidative stress and exogenous antioxidant-alleviated withdrawal syndrome. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 99:153–161
Pan J, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Ouyang Z, Zheng Q, Zheng R (2005) Oxidative stress in heroin administered mice and natural antioxidants protection. Life Sci 77:183–193
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Mayo JC et al (2003) Melatonin as an antioxidant: biochemical mechanisms and patho physiological implications in humans. Acta Biochim Pol 50:1129–1146
Zisapel N (2001) Circadian rhythm sleep disorders: pathophysiology and potential approaches to management. CNS Drugs 15:311–328
Armstrong SM (1989) Melatonin and circadian control in mammals. Experientia 45:932–938
Carrillo-Vico A, Guerrero JM, Lardone PJ, Reiter RJ (2005) A review of the multiple actions of melatonin on the immune system. Endocr 27:189–200
Scheer FA, Van Montfrans GA, Van Someren EJ, Mairuhu G, Buijs RM (2004) Daily night-time melatonin reduces blood pressure in male patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 43:192–197
Blask DE, Dauchy RT, Sauer LA (2005) Putting cancer to sleep at night: the neuroendocrine ⁄circadian melatonin signal. Endocr 27:179–188
Cardinali DP, Ladizesky MG, Boggio V, Cutrera RA, Mautalen CA (2003) Melatonin effects on bone: experimental facts and clinical perspectives. J Pineal Res 34:81–87
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Osuna C, Gitto E (2000) Actions of melatonin in the reduction of oxidative stress: a review. J Biomed Res 7:444–458
Ogutcu A, Uzunhisarcikli M, Kalender S, Durak D, Bayrakdar F, Kalender Y (2006) The effects of organophosphate insecticide diazinon on malondialdehyde levels and myocardial cells in rat heart tissue and protective role of vitamin E. Pestic Biochem Physiol 86:93–98
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem Biol Interact 160:1–40
Blot WJ, Li JY, Taylor PR et al (1993) Nutrition intervention trials in Linxian, China: supplementation with specific vitamin/mineral combinations, cancer incidence, and disease-specific mortality in the general population. J Natl Cancer Inst 85(18):1483–1492
Lippman SM, Goodman PJ, Klein EA et al (2005) Designing the selenium and vitamin E cancer prevention trial (SELECT). J Natl Cancer Inst 97(2):94–102
Klein EA (2009) Selenium and vitamin E: interesting biology and dashed hope. J Natl Cancer Inst 101(5):283–285
Değer Y, Şahin A, Dede S, Kiliçalp D, Cemek M (2004) Effects of nigella sativa and vitamin E+Se in CCl4-treated rats. Indian Vet J 81:647–649
Cemek M, Büyükben A, Büyükokuroğlu ME, Aymelek F, Tür L (2009) Protective roles of vitamin E (a-tocopherol), selenium and vitamin E plus selenium in organophosphate toxicity in vivo: a comparative study. Pestic Biochem Physiol. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2009.09.009
Valko MH, Morris MTD (2005) Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem 12:1161–1208
Lysle DT, How T (2000) Heroin modulates the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Immunopharmacology 46:181–192
Martin TJ, Smith JE, Dworkin SI (1998) Training dose and session time as contextual determinants of heroin self-administration in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 60:415–421
Martin TJ, Walker LE, Sizemore GM, Smith JE (1996) Within-session determination of dose–response curves for heroin self-administration in rats: comparison with between-session determination and effects of naltrexone. Drug Alcohol Depend 41:93–100
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Flohe L, Otting F (1984) Superoxide dismutase assays. Methods Enzymol 105:93–104
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Shi J, Li S, Zhang X, Wang X, Foll BL, Zhang XY, Kosten TR, Lu L (2009) Time-dependent neuroendocrine alterations and drug craving during the first month of abstinence in heroin addicts. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. doi:10.1080/00952990902933878
Govitrapong P, Suttitum T, Kotchabhakdi N, Uneklabh T (1998) Alterations of immune functions in heroin addicts and heroin withdrawal subjects. J Pharma Exp Thera 286:883–889
Zhou J, Si P, Ruan Z, Ma S, Yan X, Sun L, Peng F, Yuan H, Cai D, Ding D, Xu S (2001) Primary studies on heroin abuse and injury induced by oxidation and lipoperoxidation. Chinese Med J 114:297–302
Díaz-Flores Estévez JF, Díaz-Flores Estévez F, Hernández Calzadilla C, Rodríguez Rodríguez EM, Díaz Romero C, Serra-Majem L (2004) Application of linear discriminant analysis to the biochemical and haematological differentiation of opiate addicts from healthy subjects: a case-control study. Eur J Clin Nutr 58(3):449–455
Oliveira MT, Rego AC, Morgadinho MT, Macedo TRA, Oliveira CR (2002) Toxic effects of opioid and stimulant drugs on undifferentiated PC12 cells. Ann NY Acad Sci 965:487–496
Singhal PC, Pamarthi M, Shah R, Chandra D, Gibbons N (1994) Morphine stimulates superoxide formation by glomerular mesangial cells. Inflammation 18:293–299
Mates JM (2000) Effects of antioxidant enzymes in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology. Toxicology 153:83–104
Geffard M, Gaffori O, Chauveau J (1981) Dramatic increase in pineal melatonin levels in the rat after subcutaneous injection of des-tyrosine1-gamma-endorphin. Neurosci Lett 27:329–334
Esposti D, Esposti G, Lissoni P et al (1988) Action of morphine on melatonin release in the rat. J Pineal Res 5:35–39
Tomas-Zapico C, Coto-Montes A (2005) A proposed mechanism to explain the stimulatory effect of melatonin on antioxidative enzymes. J Pineal Res 39:99–104
Tan DX, Reiter RJ, Manchester LC, Yan MT, El-Sawi M, Sainz RM, Mayo JC, Kohen R, Allegra M, Hardeland R (2002) Chemical and physical properties and potential mechanisms: melatonin as a broad spectrum antioxidant and free radical scavenger. Curr Top Med Chem 2:181–197
Traber MG, Packer L (1995) Vitamin E: beyond antioxidant function. Am J Clin Nutr 62:1501S–1509S
Cantürk NZ, Cantürk Z, Utkan NZ, Yenisey C, Ozbilim G, Yıldırım C, Yalman Y (1998) Cytoprotective effects of alpha tocopherol against liver injury induced by extrahepatic biliary obstruction. East Afr Med J 75:77–80
House Hearing, April 26–28, 1971, Crime Select Committee, US Government Publications, 92nd Congress, Part 1, Oct. 1971, Entry No. 14,939, pp 273–322
Nagamatsu K, Hasegawa A (1993) Effect of sodium selenite on morphine-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Drug Chem Toxicol 16(3):241–253
Zhang YT, Zheng QS, Pan J, Zheng RL (2004) Oxidative damage of biomolecules in mouse liver induced by morphine and protected by antioxidants. Basic Clin Pharm Toxicol 95:53–58
Montilla P, Cruz A, Padillo FJ, Tunez I, Gascon F, Munoz MC, Gomez M, Pera C (2001) Melatonin versus vitamin E as protective treatment against oxidative stress after extra-hepatic bile duct ligation in rats. J Pineal Res 31:138–144
Windisch W (2002) Interaction of chemical species with biological regulation of the metabolism of essential trace elements. Anal Bioanal Chem 372:421–425
Rodriguez EM, Sanz Alaejos M, Diaz Romero C (1994) Urinary selenium concentrations in heroin abusers. Clin Chim Acta 231(1):39–46
Diaz-Flores JF, Sanudo RI, Rodriguez EM (2004) Serum concentrations of macro and trace elements in heroin addicts of the Canary Islands. J Trace Elem Med Biol 17:235–242
Elnimr T, Hashem A, Assar R (1996) Heroin dependence effects on some major and trace elements. Biol Trace Element Res 54:153–158
Cemek M, Büyükokuroğlu ME, Yilmaz E, Büyükben A, Aymelek F (2009) Effects of Matricaria chamomilla on element status in ethanol-intoxicated rats. Revue Med Vet 160(10):443–448
Cemek M, Büyükokuroğlu ME, Yürümez Y, Yavuz Y, Aslan A, Büyükben A, Aymelak F (2010) Tissue trace and major element levels in organophosphate insecticide fenthion (Lebaycid®) toxicity in rats: prophylactic and therapeutic effect of exogenous melatonin. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:206–212
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by TUBITAK (grant no: 105T198). The authors thanks the Turkish Grain Board General Directorate, Opium & Alkaloids Affairs Department (Ankara, Turkey) for valuable assistance in providing of heroin, and Ertan Seven and Taner Bora (from General Directorate of Securit, The Department of Criminal Police Laboratories, Ankara, Turkey) for valuable assistance in content analysis of heroin.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cemek, M., Büyükokuroğlu, M.E., Hazman, Ö. et al. Antioxidant Enzyme and Element Status in Heroin Addiction or Heroin Withdrawal in Rats: Effect of Melatonin and Vitamin E Plus Se. Biol Trace Elem Res 139, 41–54 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8634-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8634-0