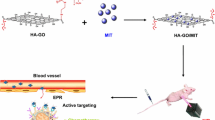
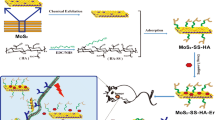
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a serious illness with a high rate of mortality. A high dose of theranostic drugs with efficient diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities should be required. Chemo-photothermal therapy is presently recognized as a secure method of cancer treatment that specifically targets tumour tissue or cells. Additionally, the success of cancer therapy is increased by the use of targeted nanoparticles. The current study aims to investigate the interaction between phototherapy and the anti-hepatocellular carcinoma treatment combination HA-GEM-MoS2/ZnO nanocomposites (NCs) loaded with gemcitabine and molybdenum disulphide. NCs were synthesized and characterized using FT-IR, XRD, TEM, and DLS analyses. The present investigation shows that the synthesized HA-MoS2/ZnO nanocomposites were elongated spherical in shape and their sizes ranged from 62.3 to 75.7 nm according to the estimation using XRD results, which is consistent with TEM findings. Further, HA-MoS2/ZnO nanocomposites could effectively encapsulate the GEM, showing dual pH and thermal triggered drug release behaviour. The result of cell uptake tests clearly demonstrated improved cellular uptake of synthesized nanocomposites following HA and GEM-loaded NCs in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. In addition, combination therapies caused the highest incidence of cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma, according to cytotoxicity experiments and showed a good compatibility. In vitro studies prove that HA-GEM-MoS2/ZnO nanocomposites enhanced tumour treatment that combines chemotherapy and photothermal therapy to remove the tumour and prevent relapses. Still, no studies have been done to see if gemcitabine-encapsulated HA-MoS2/ZnO NCs inhibit human hepatocellular carcinoma cell. Hence, the current study can give a new paradigm for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer and the outcome may be helpful to improve the quality of cancer patient’s life.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R. L., Torre, L. A., & Jemal, A. (2018). Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 68(6), 394–424.
Vetrivel, C., Sivarasan, G., Durairaj, K., Ragavendran, C., Kamaraj, C., Karthika, S., & Lo, H. M. (2023). MoS2-ZnO nanocomposite mediated immunosensor for non-invasive electrochemical detection of IL8 oral tumor biomarker. Diagnostics, 13, 1464.
Miller, K. D., Siegel, R. L., Lin, C. C., Mariotto, A. B., Kramer, J. L., Rowland, J. H., Stein, K. D., Alteri, R., & Jemal, A. (2016). Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 66(4), 271–289.
Bhirde, A. A., Chikkaveeraiah, B. V., Avinash, S., Gang, N., Jin, A. J., Ankur, K., Zhe, W., Sachin, P., Vyomesh, P., & Gorbach, A. M. (2014). Targeted therapeutic nanotubes influence the viscoelasticity of cancer cells to overcome drug resistance. ACS Nano, 8, 4177–4189.
Sherlock, S. P., Tabakman, S. M., Xie, L., & Dai, H. (2011). Photothermally enhanced drug delivery by ultrasmall multifunctional FeCo/graphitic-shell nanocrystals. ACS Nano, 5, 1505–1512.
Liu, H., Chen, D., Li, L., Liu, T., Tan, L., Wu, X., & Tang, F. (2011). Multifunctional gold nanoshells on silica nanorattles: A platform for the combination of photothermal therapy and chemotherapy with low systemic toxicity. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 50, 891–895.
Yanbo, Y., Jianrong, W., David, H. B., Shiwei, N., YuLi, X. Z., Xiaotian, X., & Li-Min, Z. (2020). A multifunctional nanoplatform based on MoS2-nanosheets for targeted drug delivery and chemo-photothermal therapy. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 185, 110585.
Gaofeng, S., Minjiang, C., Jingjing, S., Xiaoling, X., Chenying, L., Yuyin, D., Min, X., Zhongwei, Z., Minxia, Z., Kai, F., Xiaoxi, F., Shiji, F., Bufu, T. D., Yongzhong, D., & Jiansong, J. (2021). Sialic acid-engineered mesoporous polydopamine nanoparticles loaded with SPIO and Fe3+ as a novel theranostic agent for T1/T2 dual-mode MRI-guided combined chemo-photothermal treatment of hepatic cancer. Bioactive Materials, 6, 1423–1435.
Lv, R., Yang, D., Yang, P., Xu, J., He, F., Gai, S., Li, C., Dai, Y., Yang, G., & Lin, J. (2016). Integration of upconversion nanoparticles and ultrathin black phosphorus for efficient photodynamic theranostics under 808 nm near-infrared light irradiation. Chemistry of Materials, 28(13), 4724–4734.
Nandi, S., Bhunia, S. K., Zeiri, L., Pour, M., Nachman, I., Raichman, D., Lellouche, J. M., & Jelinek, R. (2017). Bifunctional carbon-dot-WS2 nanorods for photothermal therapy and cell imaging. Chemistry, 23(4), 963–969.
Li, D., Meng, Z., Fan, Xu., Yingzhi, C., Binfan, C., Ya, C., Huihai, Z., Hongyue, J., & Yongzhuo, H. (2018). Biomimetic albumin-modified gold nanorods for photothermo-chemotherapy and macrophage polarization modulation. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 8(1), 74–84.
Shun, S., Hongyan, T., Xiaotong, Z., Jinfeng, R., Zhiqing, P., Dangge, W., Huile, G., Yong, Q., & Xinguo, J. (2013). Targeting mesoporous silica-encapsulated gold nanorods for chemo- photothermal therapy with near-infrared radiation. Biomaterials, 34(12), 3150–3158.
Reza, A., Seyed, H. R., Mohammad, R. Y., Roya, S., & Effat, A. (2020). Novel chemo-photothermal therapy in breast cancer using methotrexate-loaded folic acid conjugated Au@SiO 2 nanoparticles. Nanoscale Research Letters, 15, 62.
Vimala, K., Shanthi, K., Sundarraj, S., & Kannan, K. (2017). Synergistic effect of chemo-photothermal for breast cancer therapy using folic acid (FA) modified zinc oxide nanosheet. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science., 488, 92–108.
Voiry, R., Fullon, J., Yang, C. D. C. C., Silva, E., Kappera, R., Bozkurt, I., Kaplan, D., Lagos, M. J., Batson, P. E., & Gupta, G. (2016). The role of electronic coupling between substrate and 2D MoS2 nanosheets in electrocatalytic production of hydrogen. Nature Materials, 15(9), 1003.
Li, X., Shan, J., Zhang, W., Su, S., Yuwen, L., & Wang, L. (2017). Recent advances in synthesis and biomedical applications of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 13(5), 1602660.
Zhang, Y., Xiu, W., Sun, Y., Zhu, D., Zhang, Q., Yuwen, L., Weng, L., Teng, Z., & Wang, L. (2017). RGD-QD-MoS 2 nanosheets for targeted fluorescent imaging and photothermal therapy of cancer. Nanoscale, 9(41), 15835–15845.
Dicker, K. T., Gurski, L. A., Pradhan-Bhatt, S., Witt, R. L., Farach-Carson, M. C., & Jia, X. (2014). Hyaluronan: A simple polysaccharide with diverse biological functions. Acta Biomaterialia, 10(4), 1558–1570.
Zhong, Y., Goltsche, K., Cheng, L., Xie, F., Meng, F., Deng, C., Zhong, Z., & Haag, R. (2016). Hyaluronic acid-shelled acid-activatable paclitaxel prodrug micelles effectively target and treat CD44-overexpressing human breast tumor xenografts in vivo. Biomaterials, 84, 250–261.
Chen, X., Liu, Z., Parker, S. G., Zhang, X., Gooding, J. J., Ru, Y., Liu, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2016). Light-induced hydrogel based on tumour-targeting mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a theranostic platform for sustained cancer treatment. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 8(25), 15857–15863.
Goncalves, D. P. N., Rodriguez, R. D., Kurth, T., Bray, L. J., Binner, M., Jungnickel, C., Gur, F., Poser, S. W., Schmidt, T. L., Zahn, D. R. T., Androutsellis-Theotokis, A., Schlierf, M., & Werner, C. (2017). Enhanced targeting of invasive glioblastoma cells by peptide-functionalized gold nanorods in hydrogel-based 3D cultures. Acta Biomaterialia, 58, 12–25.
Dong, X., Yin, W., Zhang, X., Zhu, S., He, X., Yu, J., Xie, J., Guo, Z., Yan, L., Liu, X., Wang, Q., Gu, Z., & Zhao, Y. (2018). Intelligent MoS2 nanotheranostic for targeted and Enzyme-/pH-/NIR-responsive drug delivery to overcome cancer chemotherapy resistance guided by PET imaging. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10(4), 4271–4284.
Krishnan, U., Kaur, M., Kaur, G., Singh, K., Dogra, A. R., Kumar, M., & Kumar, A. (2018). MoS2 /ZnO nanocomposites for efficient photocatalytic degradation of industrial pollutants. Materials Research Bulletin., 111, 212–221.
Ren, Z., Han, X., Wang, L., & Wang, Y. (2022). Hyaluronic acid-functionalized ZnO nanoparticles co-deliver AS and GOD for synergistic cancer starvation and oxidative damage. Scientific Reports., 12, 4574.
Vimala, K., Sundarraj, S., Paulpandi, M., Vengatesan, S., & Kannan, K. (2014). Green synthesized doxorubicin loaded zinc oxide nanoparticles regulates the Bax and Bcl-2 expression in breast and colon carcinoma. Process Biochemistry, 49(1), 160–172.
Xie, M., Na, Y., Jiaxi, C., Mei, Y., Tongtong, D., Yeping, L., & Chunlai, F. (2020). Layered MoS2 nanosheets modified by biomimetic phospholipids: Enhanced stability and its synergistic treatment of cancer with chemo-photothermal therapy. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces., 187, 110631.
Chen, Y., Tan, C., Zhang, H., & Wang, L. (2015). Two-dimensional graphene analogues for biomedical applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 44(9), 2681–2701.
Liu, J., Zheng, J., Nie, H., Zhang, D., Cao, D., Xing, C., Li, B., & Jia, L. (2019). Molybdenum disulfide-based hyaluronic acid-guided multifunctional theranostic nanoplatform for magnetic resonance imaging and synergetic chemo-photothermal therapy. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science., 548, 131–144.
Cai, H., Ruobing, W., Xingren, G., Meiyu, S., Fei, Y., Bai, J., & Yahui, L. (2021). Combining gemcitabine-loaded macrophage-like nanoparticles and erlotinib for pancreatic cancer therapy. Mol. Pharmaceutics., 18, 2495–2506.
Wang, S., Chen, Y., Li, X., Gao, W., Zhang, L., Liu, L., Zheng, Y., Chen, H., & Shi, J. (2015). Injectable 2D MoS2-integrated drug delivering implant for highly efficient NIR-triggered synergistic tumor hyperthermia. Advanced Materials, 27(44), 7117–7122.
Zhenkun, R., Xibin, H., Lixin, W., & Yi, W. (2022). Hyaluronic acid-functionalized ZnO nanoparticles co-deliver AS and GOD for synergistic cancer starvation and oxidative damage. Scientific Reports, 12, 4574.
Funding
Shanghai Jinshan District Science and Technology Innovation Fund Project (No.2019-3-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GW planned, designed, and wrote the original draft of this manuscript. Artwork–figures, conceptualization, and supervision were done by DY.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
NA.
Consent to Participate
NA.
Consent for Publication
All authors agreed to publish this paper in this journal.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Yu, D. Novel Chemo-Photothermal Therapy in Hepatic Cancer Using Gemcitabine-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Conjugated MoS2/ZnO Nanocomposites. Appl Biochem Biotechnol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04796-0
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04796-0