Abstract
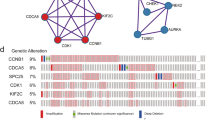
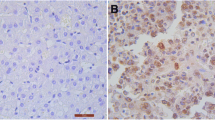
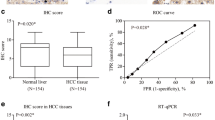
CDCA8 expression is abnormally high in a variety of cancers and involved in the biological process of tumor malignancy. In this study, we discovered that the expression of CDCA8 was up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma cancer (HCC) tissues and high levels of CDCA8 are associated with larger tumor size, higher AFP (α-fetoprotein) levels, and unfavorable prognosis. Cell functional experiments revealed that CDCA8 silencing remarkably inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis in SNU-387 and Hep-3B cells. The results of flow cytometry showed that CDCA8 regulated CDK1 and cyclin B1 expression to arrest at the S phase, inhibited proliferation, and promoted apoptosis. In addition, in vivo studies have confirmed that silencing CDCA8 could regulate CDK1/cyclin B1 signaling axis to inhibit the growth of HCC xenograft tumor. Our study demonstrated CDCA8 acts an oncogene to facilitate cell proliferation of HCC via regulating cell cycle, indicating the promising application value of CDCA8 for HCC diagnosis and clinical treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data and materials in the manuscript will be made available by the corresponding authors.
References
Wang, W., et al. (2022). The potential roles of exosomal non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Frontiers in Oncology, 12, 790916.
Niu, Z., et al. (2020). Role of long noncoding RNA-mediated competing endogenous RNA regulatory network in hepatocellular carcinoma. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 26(29), 4240–4260.
Liu, M. X., et al. (2018). Metabolic reprogramming by PCK1 promotes TCA cataplerosis, oxidative stress and apoptosis in liver cancer cells and suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene, 37(12), 1637–1653.
Qi, G., et al. (2021). CDCA8, targeted by MYBL2, promotes malignant progression and olaparib insensitivity in ovarian cancer. American Journal of Cancer Research, 11(2), 389–415.
Cui, X., et al. (2021). Cell division cycle associated 8: A novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 25(24), 11097–11112.
Wang, X., et al. (2021). Double-targeting CDCA8 and E2F1 inhibits the growth and migration of malignant glioma. Cell Death & Disease, 12(2), 146.
Wan, S., et al. (2022). Overexpression of CDCA8 predicts poor prognosis and promotes tumor cell growth in prostate cancer. Frontiers in Oncology, 12, 784183.
Bu, Y., et al. (2019). CDCA8 is a key mediator of estrogen-stimulated cell proliferation in breast cancer cells. Gene, 703, 1–6.
Hayama, S., et al. (2007). Phosphorylation and activation of cell division cycle associated 8 by aurora kinase B plays a significant role in human lung carcinogenesis. Cancer Research, 67(9), 4113–4122.
Gruber, M., Handle, F., & Culig, Z. (2020). The stem cell inhibitor salinomycin decreases colony formation potential and tumor-initiating population in docetaxel-sensitive and docetaxel-resistant prostate cancer cells. The Prostate, 80(3), 267–273.
Yang, J., & Yang, Y. (2022). Long noncoding RNA endogenous bornavirus-like nucleoprotein acts as an oncogene by regulating microRNA-655-3p expression in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Bioengineered, 13(3), 6409–6419.
Ma, C., Zhang, Q., & Greten, T. F. (2021). MDSCs in liver cancer: A critical tumor-promoting player and a potential therapeutic target. Cellular Immunology, 361, 104295.
Hu, C., et al. (2021). miR-133b inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting CDCA8. Pathology, Research and Practice, 223, 153459.
Phan, N. N., et al. (2018). Distinct expression of CDCA3, CDCA5, and CDCA8 leads to shorter relapse free survival in breast cancer patient. Oncotarget, 9(6), 6977–6992.
Gao, X., et al. (2020). Knockdown of CDCA8 inhibits the proliferation and enhances the apoptosis of bladder cancer cells. PeerJ, 8, e9078.
Dai, C., et al. (2015). Transcriptional activation of human CDCA8 gene regulated by transcription factor NF-Y in embryonic stem cells and cancer cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 290(37), 22423–22434.
Li, L., et al. (2016). Hepatic loss of borealin impairs postnatal liver development, regeneration, and hepatocarcinogenesis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 291(40), 21137–21147.
Wang, X., et al. (2022). MiR-133a-3p inhibits the malignant progression of oesophageal cancer by targeting CDCA8. Journal of Biochemistry, 170(6), 689–698.
Santamaría, D., et al. (2007). Cdk1 is sufficient to drive the mammalian cell cycle. Nature, 448(7155), 811–815.
Deng, Y., et al. (2019). Sp1 contributes to radioresistance of cervical cancer through targeting G2/M cell cycle checkpoint CDK1. Cancer Management and Research, 11, 5835–5844.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all participates for their contributions for the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y. C.: Writing, conceptualization, methodology, software
N. J.: Data curation, writing, original draft preparation, and editing the manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute & Hospital and written consent approval was obtained from all participants.
Consent to Participate
Yes
Consent for Publication
Yes
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Supplementary Fig. 3
Supplementary file3 (png 222 KB)

Supplementary Fig. 6
Supplementary file6 (png 193 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Y., Jiang, N. CDCA8 Facilitates Tumor Proliferation and Predicts a Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 196, 1481–1492 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04603-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04603-w