Abstract
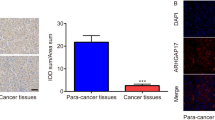
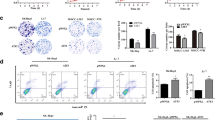
Rho GTPase activating protein 18 (ARHGAP18), a member of the RhoGAP gene family that increases GTP hydrolysis and inhibits RhoGTPase, was recently discovered to play a role in the development of breast cancer. However, its exact biological role in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear. In our present study, we comprehensively assessed ARHGAP18 expression and its correlation with the prognostic value of cancer patients in databases. Cell proliferation and colony formation assays were employed to monitor cell growth. Luciferase reporter assay, Chromatin immunoprecipitation qPCR (ChIP-qPCR), immunofluorescence were performed for mechanism research. The expression of genes and proteins was detected by real-time PCR and western blotting. According to the findings of this research, ARHGAP18 protein levels are increased in HCC tissues compared to adjacent nontumor tissues, and ARHGAP18 overexpression is associated with poor survival. The results of a gain- and loss-of-function experiment with HCC cells in vitro demonstrated that ARHGAP18 stimulated cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Mechanistically, we found that the transcription factor GATA binding protein 1 (GATA1) could bind to the ARHGAP18 promoter and facilitate ARHGAP18 expression. Further studies revealed that the effects of ARHGAP18 silencing on HCCLM3 and Bel-7402 cells were blocked by GATA1 overexpression. In conclusion, GATA1-mediated ARHGAP18 up-regulation plays an important role in HCC tumorigenesis and might be a potential therapeutic target for HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data of this paper is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hartke, J., Johnson, M., & Ghabril, M. (2017). The diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Seminars in Diagnostic Pathology, 34, 153–159.
Wu, H., Wang, M. D., Liang, L., Xing, H., Zhang, C. W., Shen, F., Huang, D. S., & Yang, T. (2021). Nanotechnology for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Surveillance. Diagnosis to Management, 17, e2005236.
Vogel, A., & Martinelli, E. (2021). Updated treatment recommendations for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Annals of Oncology: Official Journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology, 32, 801–805.
Yang, J. D., Hainaut, P., & Gores, G. J. (2019). A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 16, 589–604.
Ogunwobi, O. O., Harricharran, T., Huaman, J., Galuza, A., Odumuwagun, O., Tan, Y., Ma, G. X., & Nguyen, M. T. (2019). Mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma progression. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 25, 2279–2293.
Juaid, N., & Amin, A. (2021). Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Biomolecules: Molecular Targets Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22, 10774.
El-Khoueiry, A. B., Hanna, D. L., Llovet, J., & Kelley, R. K. (2021). Cabozantinib: An evolving therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 98, 102221.
Li, X., Liu, Q., Liu, S., Zhang, J., & Zhang, Y. (2008). New member of the guanosine triphosphatase activating protein family in the human epididymis. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica, 40, 855–863.
Humphries, B., Wang, Z., Li, Y., Jhan, J., Jiang, Y., & Yang, C. (2017). ARHGAP18 Downregulation by miR-200b suppresses metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by enhancing activation of RhoA. Cancer Research, 77, 4051–4064.
Aguilar-Rojas, A., Maya-Núñez, G., Huerta-Reyes, M., Pérez-Solis, M., Silva-García, R., Guillén, N., & Olivo-Marin, J. (2018). Activation of human gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor promotes down regulation of ARHGAP18 and regulates the cell invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology, 460, 94–103.
Prins, M. M. C., Giugliano, F. P., van Roest, M., van de Graaf, S. F. J., Koelink, P. J. and Wildenberg, M. E. (2021). Thiopurines correct the effects of autophagy impairment on intestinal healing - a potential role for ARHGAP18/RhoA. Disease Models & Mechanisms, 14, dmm047233.
Dibus, M., Brábek, J., & Rösel, D. (2020). A Screen for PKN3 Substrates Reveals an Activating Phosphorylation of ARHGAP18. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21, 7769.
Hao, L., Pang, K., Pang, H., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., He, H., Zhou, R., Shi, Z., & Han, C. (2020). Knockdown of P3H4 inhibits proliferation and invasion of bladder cancer. Aging, 12, 2156–2168.
Zhao, Z., Zhao, Z., Wang, J., Zhang, H., Xi, Z., & Xia, Q. (2022). ABCC6 Knockdown Fuels Cell Proliferation by Regulating PPARα in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Frontiers in Oncology, 12, 840287.
Sun, M., Zhang, X., Bi, F., Wang, D., Zhou, X., Li, X. and Yang, Q. (2022) FTO Inhibits Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Progression by Destabilising SNAI1 mRNA through IGF2BP2. Cancers, 14, 5218.
Zhan, Y., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Fang, Y., Xie, Y., Zheng, Y., Li, G., Liang, L., & Ding, Y. (2022). NUPR1 contributes to radiation resistance by maintaining ROS homeostasis via AhR/CYP signal axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Medicine, 20, 365.
Kong, X., Zheng, Z., Song, G., Zhang, Z., Liu, H., Kang, J., Sun, G., Sun, G., Huang, T., Li, X., Rong, D., Wang, K., Tang, W., & Xia, Y. (2022). Over-expression of GUSB leads to primary resistance of Anti-PD1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Frontiers in Immunology, 13, 876048.
Hou, Y., Dong, Z., Zhong, W., Yin, L., Li, X., & Kuerban, G. (2022). FOXM1 promotes drug resistance in cervical cancer cells by regulating ABCC5 gene transcription. BioMed Research International, 2022, 3032590.
Wang, J., Wang, Z., Wang, H., Wanyan, Z., Pan, Y., Zhu, F., Tao, Q., & Zhai, Z. (2019). SENEXStress-induced premature senescence promotes proliferation by activating the and p16/Retinoblastoma (Rb) pathway in diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma. Turkish Journal of Haematology: Official Journal of Turkish Society of Haematology, 36, 247–254.
Aleskandarany, M., Sonbul, S., Surridge, R., Mukherjee, A., Caldas, C., Diez-Rodriguez, M., Ashankyty, I., Albrahim, K., Elmouna, A., Aneja, R., Martin, S., Ellis, I., Green, A., & Rakha, E. (2017). Rho-GTPase activating-protein 18: A biomarker associated with good prognosis in invasive breast cancer. British Journal of Cancer, 117, 1176–1184.
Li, Y., Ji, S., Fu, L., Jiang, T., Wu, D., & Meng, F. (2018). ARHGAP18Over-expression of suppressed cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and tumor growth in gastric cancer by restraining over-activation of MAPK signaling pathways. OncoTargets and Therapy, 11, 279–290.
Huang, S., Zhao, Z., Weng, G., He, X., Wu, C., Fu, C., Sui, Z., Zhong, X., & Liu, T. (2016). The correlation of microRNA-181a and target genes with poor prognosis of glioblastoma patients. International Journal of Oncology, 49, 217–224.
Evans, T., & Felsenfeld, R. G. (1988). An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 85, 5976–5980.
Arkoun, B., Robert, E., Boudia, F., Mazzi, S., Dufour, V., Siret, A., Mammasse, Y., Aid, Z., Vieira, M., Imanci, A., Aglave, M., Cambot, M., Petermann, R., Souquere, S., Rameau, P., Catelain, C., Diot, R., Tachdjian, G., Hermine, O., Droin, N., Debili, N., Plo, I., Malinge, S., Soler, E., Raslova, H., Mercher, T. and Vainchenker, W. (2022). Stepwise GATA1 and SMC3 mutations alter megakaryocyte differentiation in a Down syndrome leukemia model. The Journal of Clinical Investigation,132, e156290.
Li, Z., Sheng, B., Zhang, T., Wang, T., Chen, D., An, G., Wang, X., Meng, H., & Yang, L. (2022). Zkscan3 affects erythroblast development by regulating the transcriptional activity of GATA1 and KLF1 in mice. Journal of Molecular Histology, 53, 423–436.
Chung, H., Lin, B., Lin, Y., Chang, C., Tzou, W., Pei, T., & Hu, C. (2021). Meis1, Hi1α, and GATA1 are integrated into a hierarchical regulatory network to mediate primitive erythropoiesis. FASEB Journal: Official Publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 35, e21915.
Gao, Y., Wang, R., Liu, J., Zhao, K., Qian, X., He, X., & Liu, H. (2022). SENP1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer invasion and metastasis via enhancing CSN5 transcription mediated by GATA1 deSUMOylation. International Journal of Biological Sciences, 18, 2186–2201.
Andrieux, L., Fautrel, A., Bessard, A., Guillouzo, A., Baffet, G., & Langouët, S. (2007). GATA-1 is essential in EGF-mediated induction of nucleotide excision repair activity and ERCC1 expression through ERK2 in human hepatoma cells. Cancer Research, 67, 2114–2123.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all participants for their contributions to the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PC and XL performed the experiments and data analysis. PC and QW conceived and designed the study. YL and XB did the analysis and interpretation of data. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not Applicable.
Consent for Publication
All authors agreed to publish the research on this journal.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Liu, X., Liu, Y. et al. ARHGAP18 is Upregulated by Transcription Factor GATA1 Promotes the Proliferation and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 196, 679–689 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04459-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-023-04459-0