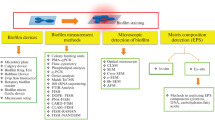
Abstract
Biofilm is the conglomeration of microbial cells which is associated with a surface. In the recent times, the study of biofilm has gained popularity and vivid research is being done to know about the effects of biofilm and that it consists of many organisms which are symbiotic in nature, some of which are human pathogens. Here, in this study, we have discussed about biofilms, its formation, relevance of its presence in the biosphere, and the possible remediations to cope up with its negative effects. Since removal of biofilm is difficult, emphasis has been made to suggest ways to prevent biofilm formation and also to devise ways to utilize biofilm in an economically and environment-friendly method.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sentenac, H., Loyau, A., Leflaive, J., & Schmeller, D. S. (2022). The significance of biofilms to human, animal, plant and ecosystem health. Functional Ecology, 36(2), 294–313.
O’Toole, G., Kaplan, H. B., & Kolter, R. (2000). Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annual Review of Microbiology, 54, 49–79.
Hall-Stoodley, L., Costerton, J. W., & Stoodley, P. (2004). Bacterial biofilms: From the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2(2), 95–108.
López, D., Vlamakis, H., & Kolter, R. (2010). Biofilms. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 2(7), a000398.
Lorite, G. S., Rodrigues, C. M., De Souza, A. A., Kranz, C., Mizaikoff, B., & Cotta, M. A. (2011). The role of conditioning film formation and surface chemical changes on Xylella fastidiosa adhesion and biofilm evolution. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 359, 289–295.
Jr Dunne, W. M. (2002). Bacterial adhesion: Seen any good biofilms lately? Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 15, 155–166.
Carniello, V., Peterson, B. W., van der Mei, H. C., & Busscher, H. J. (2018). Physico-chemistry from initial bacterial adhesion to surface-programmed biofilm growth. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 261, 1–14.
Zheng, S., Bawazir, M., Dhall, A., Kim, H. E., He, L., Heo, J., & Hwang, G. (2021). Implication of surface properties, bacterial motility, and hydrodynamic conditions on bacterial surface sensing and their initial adhesion. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9, 82.
Teixeira, P., & Oliveira, R. (1999). Influence of surface characteristics on the adhesion of Alcaligenes denitrificans to polymeric substrates. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 13, 1287–1294.
Wong, G. C., Antani, J. D., Lele, P. P., Chen, J., Nan, B., Kühn, M. J., ... & Dunkel, J. (2021). Roadmap on emerging concepts in the physical biology of bacterial biofilms: From surface sensing to community formation. Physical Biology, 18(5), 051501.
Ghilini, F., Pissinis, D. E., Miñán, A., Schilardi, P. L., & Diaz, C. (2019). How functionalized surfaces can inhibit bacterial adhesion and viability. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 5(10), 4920–4936.
Berne, C., Ducret, A., Hardy, G. G., & Brun, Y. V. (2015). Adhesins involved in attachment to abiotic surfaces by gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology Spectrum, 3(4). https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec. MB-0018–2015.
Petrova, O. E., & Sauer, K. (2012). Sticky situations: Key components that control bacterial surface attachment. Journal of Bacteriology, 194(10), 2413–2425.
Abraham, W. R. (2016). Going beyond the control of quorum-sensing to combat biofilm infections. Antibiotics, 5, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics5010003
Li, Y.-H., & Tian, X. (2012). Quorum Sensing and Bacterial Social Interactions in Biofilms. Sensors, 12(3), 2519–2538.
Papenfort, K., & Bassler, B. L. (2016). Quorum sensing signal–response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 14(9), 576–588.
Fahs, A., Quiles, F., Jamal, D., Humbert, F., & Francius, G. (2014). In situ analysis of bacterial extracellular polymeric substances from a Pseudomonas fluorescens biofilm by combined vibrational and single molecule force spectroscopies. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 118, 6702–6713.
Flemming, H. C. (2016). EPS-then and now. Microorganisms, 4, 41.
Toyofuku, M., Inaba, T., Kiyokawa, T., Obana, N., Yawata, Y., & Nomura, N. (2016). Environmental factors that shape biofilm formation. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 80(1), 7–12.
Frederick, M. R., Kuttler, C., Hense, B. A., & Eberl, H. J. (2011). A mathematical model of quorum sensing regulated EPS production in biofilm communities. Theoretical Biology & Medical Modelling, 8, 8.
Garnett, J. A., & Matthews, S. (2012). Interactions in bacterial biofilm development: A structural perspective. Current Protein and Peptide Science, 13, 739–755.
Díaz-Salazar, C., Calero, P., Espinosa-Portero, R., Jiménez-Fernández, A., Wirebrand, L., Velasco-Domínguez, M. G., ... & Govantes, F. (2017). The stringent response promotes biofilm dispersal in Pseudomonas putida. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 1–13.
Kaplan, J. Á. (2010). Biofilm dispersal: Mechanisms, clinical implications, and potential therapeutic uses. Journal of Dental Research, 89(3), 205–218.
Kostakioti, M., Hadjifrangiskou, M., & Hultgren, S. J. (2013). Bacterial biofilms: Development, dispersal, and therapeutic strategies in the dawn of the postantibiotic era. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine, 3(4), a010306.
Lee, K., & Yoon, S. S. (2017). Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm, a programmed bacterial life for fitness. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 27(6), 1053–1064.
Fleming, D., & Rumbaugh, K. P. (2017). Approaches to dispersing medical biofilms. Microorganisms, 5(2), 15.
Flemming, H. C., & Wuertz, S. (2019). Bacteria and archaea on Earth and their abundance in biofilms. Nature Reviews. Microbiology, 17(4), 247–260.
Zhang, N., Wang, D., Liu, Y., Li, S., Shen, Q., & Zhang, R. (2014). Effects of different plant root exudates and their organic acid components on chemotaxis, biofilm formation and colonization by beneficial rhizosphere-associated bacterial strains. Plant and Soil, 374(1/2), 689–700.
Pintelon, T. R., Picioreanu, C., van Loosdrecht, M. C., & Johns, M. L. (2012). The effect of biofilm permeability on bio-clogging of porous media. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 109, 1031–1042.
Lin, D., Ma, W., Jin, Z., Wang, Y., Huang, Q., & Cai, P. (2016). Interactions of EPS with soil minerals: A combination study by ITC and CLSM. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 138, 10–16.
Zhang, Y., Tang, Q., Shi, P., & Katsumi, T. (2021). Influence of bio-clogging on permeability characteristics of soil. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 49(3), 707–721.
Lou, Y., Chang, W., Cui, T., Wang, J., Qian, H., Ma, L., ... & Zhang, D. (2021). Microbiologically influenced corrosion inhibition mechanisms in corrosion protection: A review.Bioelectrochemistry, 141, 107883.
Petrova, O. E., Schurr, J. R., Schurr, M. J., & Sauer, K. (2012). Microcolony formation by the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa requires pyruvate and pyruvate fermentation. Molecular Microbiology, 86, 819–835.
Hollibaugh, J. T., Wong, P. S., & Murrell, M. C. (2000). Similarity of particle-associated and free-living bacterial communities in northern San Francisco Bay, California. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 21(2), 103–114.
Ghiglione, J. F., Mevel, G., Pujo-Pay, M., Mousseau, L., Lebaron, P., & Goutx, M. (2007). Diel and seasonal variations in abundance, activity, and community structure of particle-attached and free-living bacteria in NW Mediterranean Sea. Microbial Ecology, 54(2), 217–231.
Burmølle, M., Ren, D., Bjarnsholt, T., & Sørensen, S. J. (2014). Interactions in multispecies biofilms: Do they actually matter? Trends in Microbiology, 22(2), 84–91.
Mai-Prochnow, A., Zhou, R., Zhang, T., Ostrikov, K. K., Mugunthan, S., Rice, S. A., & Cullen, P. J. (2021). Interactions of plasma-activated water with biofilms: Inactivation, dispersal effects and mechanisms of action. npj Biofilms and Microbiomes, 7(1), 1–12.
Sheik, C. S., Jain, S., & Dick, G. J. (2014). Metabolic flexibility of enigmatic SAR 324 revealed through metagenomics and metatranscriptomics. Environmental Microbiology, 16(1), 304–317.
Simon, H. M., Smith, M. W., & Herfort, L. (2014). Metagenomic insights into particles and their associated microbiota in a coastal margin ecosystem. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 466.
Orcutt, B. N., Sylvan, J. B., Knab, N. J., & Edwards, K. J. (2011). Microbial ecology of the dark ocean above, at, and below the seafloor. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 75, 361–422.
Dang, H., Zhou, H., Yang, J., Ge, H., Jiao, N., Luan, X., ... & Klotz, M. G. (2013). Thaumarchaeotal signature gene distribution in sediments of the northern South China Sea: An indicator of the metabolic intersection of the marine carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycles?. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79(7), 2137–2147.
Salta, M., Wharton, J. A., Blache, Y., Stokes, K. R., & Briand, J. F. (2013). Marine biofilms on artificial surfaces: Structure and dynamics. Environmental Microbiology, 15(11), 2879–2893.
Dybowska-Józefiak, M., & Wesołowska, M. (2021). Internal abiotic components that influence the development of biocorrosion on ETICS plasters. Materials (Basel, Switzerland), 15(1), 127.
Cottingham, K. L., Chiavelli, D. A., & Taylor, R. K. (2003). Environmental microbe and human pathogen: The ecology and microbiology of Vibrio cholerae. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment, 1(2), 80–86.
Varin, K. J., Lin, N. H., & Cohen, Y. (2013). Biofouling and cleaning effectiveness of surface nanostructured reverse osmosis membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 446, 472–481.
Shi, X., Xie, N., & Gong, J. (2011). Recent progress in the research on microbially influenced corrosion: A bird’s eye view through the engineering lens. Recent Patents on Corrosion Science, 1(2), 118–131.
Cross, T. (2006). Accelerated low water corrosion—A universal phenomenon. Corros Manage, 69, 18–19.
Benedetti, I., de Lorenzo, V., & Nikel, P. I. (2016). Genetic programming of catalytic Pseudomonas putida biofilms for boosting biodegradation of haloalkanes. Metabolic Engineering, 33, 109–118.
Jahid, I. K., & Ha, S. D. (2012). A review of microbial biofilms of produce: Future challenge to food safety. Food Science and Biotechnology, 21(2), 299–316.
Srey, S., Jahid, I. K., & Ha, S. D. (2013). Biofilm formation in food industries: A food safety concern. Food Control, 31(2), 572–585.
Takahashi, H., Miya, S., Igarashi, K., Suda, T., Kuramoto, S., & Kimura, B. (2009). Biofilm formation ability of Listeria monocytogenes isolates from raw ready-to-eat seafood. Journal of Food Protection, 72(7), 1476–1480.
Nitschke, M., Araújo, L. V., Costa, S. G., Pires, R. C., Zeraik, A. E., Fernandes, A. C., Freire, D. M., & Contiero, J. (2009). Surfactin reduces the adhesion of food-borne pathogenic bacteria to solid surfaces. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 49(2), 241–247.
Galgano, F., Condelli, N., Caruso, M. C., Colangelo, M. A., & Favati, F. (2015). Probiotics and prebiotics in fruits and vegetables: Technological and sensory aspects. Beneficial Microbes in Fermented and Functional Foods; Rai, VR, Bai, JA, Eds, 189–206.
Kirtonia, K., Salauddin, M., Bharadwaj, K. K., Pati, S., Dey, A., Shariati, M. A., Tilak, V. K., Kuznetsova, E., & Sarkar, T. (2021). Bacteriocin: A new strategic antibiofilm agent in food industries. Biocatalysts and Agricultural Biotechnology, 36, 102141.
Gómez, N. C., Ramiro, J. M., Quecan, B. X., & de Melo Franco, B. D. (2016). Use of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria (LAB) biofilms for the control of Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella Typhimurium, and Escherichia coli O157: H7 biofilms formation. Frontiers in Microbiology, 7, 863.
Yang, S. C., Lin, C. H., Sung, C. T., & Fang, J. Y. (2014). Antibacterial activities of bacteriocins: Application in foods and pharmaceuticals. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 241.
Rakin, A., Boolgakowa, E., & Heesemann, J. (1996). Structural and functional organization of the Yersinia pestis bacteriocin pesticin gene cluster. Microbiology (Reading, England), 142(Pt 12), 3415–3424.
Riley, M. A. (1993). Molecular mechanisms of colicin evolution. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 10(6), 1380–1395.
Grim, C. J., Kozlova, E. V., Sha, J., Fitts, E. C., van Lier, C. J., Kirtley, M. L., Joseph, S. J., Read, T. D., Burd, E. M., Tall, B. D., Joseph, S. W., Horneman, A. J., Chopra, A. K., & Shak, J. R. (2013). Characterization of Aeromonas hydrophila wound pathotypes by comparative genomic and functional analyses of virulence genes. mBio, 4, 2e00064-13.
Odeyemi, O. A., & Ahmad, A. (2017). Antibiotic resistance profiling and phenotyping of Aeromonas species isolated from aquatic sources. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 24(1), 65–70.
Sumner, J., & Ross, T. (2002). A semi-quantitative seafood safety risk assessment. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 77, 55–59.
Nelson, E. J., Harris, J. B., Morris, J. G., Jr., Calderwood, S. B., & Camilli, A. (2009). Cholera transmission: The host, pathogen and bacteriophage dynamic. Nature Reviews. Microbiology, 7(10), 693–702.
Katarzyna Czaczyk, Kamila Myszka Department of Biotechnology and Food Microbiology, University of Life Sciences, Poznań, Poland.
Fuster-Valls, N., Hernández-Herrero, M., Marín-de-Mateo, M., & Rodríguez-Jerez, J. J. (2008). Effect of different environmental conditions on the bacteria survival on stainless steel surfaces. Food Control, 19(3), 308–314.
Branda, S. S., Vik, Å., Friedman, L., & Kolter, R. (2005). Biofilms: The matrix revisited. Trends in Microbiology, 13(1), 20–26.
Shi, X., & Zhu, X. (2009). Biofilm formation and food safety in food industries. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 20(9), 407–413.
Burmølle, M., Kjøller, A., & Sørensen, S. J. (2011). Biofilms in soil. Encycl Agrophys, 8, 70–74.
Roy, B., Maitra, D., & Mitra, A. K. (2021). Methods of sample preparation and assay of bacterial biofilms with special reference to their significance in agriculture and extreme environments. In Analytical Methodologies for Biofilm Research (pp. 39–65). Springer
Lugtenberg, B., & Kamilova, F. (2009). Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Annual Review of Microbiology, 63, 541–556.
Rudrappa, T., Biedrzycki, M. L., & Bais, H. P. (2008). Causes and consequences of plant-associated biofilms. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 64(2), 153–166.
Kyrkou, I., Pusa, T., Ellegaard-Jensen, L., Sagot, M. F., & Hansen, L. H. (2018). Pierce’s disease of grapevines: A review of control strategies and an outline of an epidemiological model. Frontiers in Microbiology, 9, 2141.
Danhorn, T., & Fuqua, C. (2007). Biofilm formation by plant-associated bacteria. Annual Review of Microbiology, 61, 401–422.
Mori, Y., Inoue, K., Ikeda, K., Nakayashiki, H., Higashimoto, C., Ohnishi, K., Kiba, A., & Hikichi, Y. (2016). The vascular plant-pathogenic bacterium Ralstonia solanacearum produces biofilms required for its virulence on the surfaces of tomato cells adjacent to intercellular spaces. Molecular Plant Pathology, 17(6), 890–902.
Clutterbuck, A. L., Woods, E. J., Knottenbelt, D. C., Clegg, P. D., Cochrane, C. A., & Percival, S. L. (2007). Biofilms and their relevance to veterinary medicine. Veterinary Microbiology, 121(1–2), 1–17.
Hancock, V., Dahl, M., & Klemm, P. (2010). Probiotic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 outcompetes intestinal pathogens during biofilm formation. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 59(Pt 4), 392–399.
Choi, J., Shin, D., & Ryu, S. (2007). Implication of quorum sensing in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium virulence: The luxS gene is necessary for expression of genes in pathogenicity island 1. Infection and Immunity, 75(10), 4885–4890.
Hardie, K. R., & Heurlier, K. (2008). Establishing bacterial communities by ‘word of mouth’: LuxS and autoinducer 2 in biofilm development. Nature Reviews. Microbiology, 6(8), 635–643.
Rubin, J., Walker, R. D., Blickenstaff, K., Bodeis-Jones, S., & Zhao, S. (2008). Antimicrobial resistance and genetic characterization of fluoroquinolone resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from canine infections. Veterinary Microbiology, 131(1–2), 164–172.
Gundogdu, O., Mills, D. C., Elmi, A., Martin, M. J., Wren, B. W., & Dorrell, N. (2011). The Campylobacter jejuni transcriptional regulator Cj1556 plays a role in the oxidative and aerobic stress response and is important for bacterial survival in vivo. Journal of Bacteriology, 193(16), 4238–4249.
Boyen, F., Eeckhaut, V., Van Immerseel, F., Pasmans, F., Ducatelle, R., & Haesebrouck, F. (2009). Quorum sensing in veterinary pathogens: Mechanisms, clinical importance and future perspectives. Veterinary Microbiology, 135(3–4), 187–195.
Römling, U., & Balsalobre, C. (2012). Biofilm infections, their resilience to therapy and innovative treatment strategies. Journal of Internal Medicine, 272(6), 541–561.
Chen, L., & Wen, Y. M. (2011). The role of bacterial biofilm in persistent infections and control strategies. International Journal of Oral Science, 3(2), 66–73.
Awan, A. B., Yan, A., Sarwar, Y., Schierack, P., & Ali, A. (2021). Detection of synergistic antimicrobial resistance mechanisms in clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from post-operative wound infections. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 105(24), 9321–9332.
Ayala, F. R., Bauman, C., Cogliati, S., Leñini, C., Bartolini, M., & Grau, R. (2017). Microbial flora, probiotics, Bacillus subtilis and the search for a long and healthy human longevity. Microbial Cell (Graz, Austria), 4(4), 133–136.
Hammami, R., Fernandez, B., Lacroix, C., & Fliss, I. (2013). Anti-infective properties of bacteriocins: An update. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 70(16), 2947–2967.
Pandey, K., Naik, S., & Vakil, B. (2015). Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics-A review. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 52(12), 7577–7587.
Alhede, M., Er, Ö., Eickhardt, S., Kragh, K., Alhede, M., Christensen, L. D., ... & Bjarnsholt, T. (2014). Bacterial biofilm formation and treatment in soft tissue fillers. Pathogens and Disease, 70(3), 339–346.
Yamamoto, S., Tsuda, H., Miyai, K., Takano, M., Tamai, S., & Matsubara, O. (2011). Gene amplification and protein overexpression of MET are common events in ovarian clear-cell adenocarcinoma: Their roles in tumor progression and prognostication of the patient. Modern Pathology, 24(8), 1146–1155.
Allhorn, M., Arve, S., Brüggemann, H., & Lood, R. (2016). A novel enzyme with antioxidant capacity produced by the ubiquitous skin colonizer Propionibacterium acnes. Scientific Reports, 6(1), 1–12.
Ghosh, S., Sarkar, T., & Chakraborty, R. (2021). Formation and development of biofilm – An alarming concern in food safety preservatives. Biocatalysts and Agricultural Biotechnology., 38, 102210.
Hall-Stoodley, L., Stoodley, P., Kathju, S., Høiby, N., Moser, C., Costerton, J. W., Moter, A., & Bjarnsholt, T. (2012). Towards diagnostic guidelines for biofilm-associated infections. FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology, 65(2), 127–145.
Fastenberg, J. H., Hsueh, W. D., Mustafa, A., Akbar, N. A., & Abuzeid, W. M. (2016). Biofilms in chronic rhinosinusitis: Pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. World Journal of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, 2(4), 219–229.
Fischer, A. J., Singh, S. B., LaMarche, M. M., Maakestad, L. J., Kienenberger, Z. E., Peña, T. A., ... & Limoli, D. H. (2021). Sustained coinfections with Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 203(3), 328–338.
Fastenberg, J. H., Hsueh, W. D., Mustafa, A., Akbar, N. A., & Abuzeid, W. M. (2016). Biofilms in chronic rhinosinusitis: Pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. World Journal of Otorhinolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery, 2(4), 219–229.
Black, C. E., & Costerton, J. W. (2010). Current concepts regarding the effect of wound microbial ecology and biofilms on wound healing. The Surgical Clinics of North America, 90(6), 1147–1160.
Rediske, A. M., Roeder, B. L., Nelson, J. L., Robison, R. L., Schaalje, G. B., Robison, R. A., & Pitt, W. G. (2000). Pulsed ultrasound enhances the killing of Escherichia coli biofilms by aminoglycoside antibiotics in vivo. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 44(3), 771–772.
Kohnen, W., & Jansen, B. (2000). Changing material surface chemistry for preventing bacterial adhesion. In Handbook of bacterial adhesion (pp. 581–589). Humana Press.
Nezami, N., Xing, M., Groenwald, M., Silin, D., Kokabi, N., & Latich, I. (2019). Risk factors of infection and role of antibiotic prophylaxis in totally implantable venous access port placement: Propensity score matching. Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology, 42(9), 1302–1310.
Nevius, B. A., Chen, Y. P., Ferry, J. L., & Decho, A. W. (2012). Surface-functionalization effects on uptake of fluorescent polystyrene nanoparticles by model biofilms. Ecotoxicology, 21, 2205–2213.
Kroll, A., Behra, R., Kaegi, R., & Sigg, L. (2014). Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of freshwater biofilms stabilize and modify CeO2 and Ag nanoparticles. PLoS ONE, 9, e110709.
Ikuma, K., Decho, A. W., & Lau, B. L. (2015). When nanoparticles meet biofilms-interactions guiding the environmental fate and accumulation of nanoparticles. Frontiers in Microbiology, 6, 591.
Babauta, J. T., Nguyen, H. D., Harrington, T. D., Renslow, R., & Beyenal, H. (2012). pH, redox potential and local biofilm potential microenvironments within Geobacter sulfurreducens biofilms and their roles in electron transfer. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 109(10), 2651–2662.
Kalathil, S., Lee, J., & Cho, M. H. (2011). Electrochemically active biofilm-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles in water. Green Chemistry, 13(6), 1482–1485.
Khan, M. M., Kalathil, S., Han, T. H., Lee, J., & Cho, M. H. (2013). Positively charged gold nanoparticles synthesized by electrochemically active biofilm—A biogenic approach. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 13(9), 6079–6085.
Khan, M. M., Ansari, S. A., Lee, J. H., Ansari, M. O., Lee, J., & Cho, M. H. (2014). Electrochemically active biofilm assisted synthesis of Ag@ CeO2 nanocomposites for antimicrobial activity, photocatalysis and photoelectrodes. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 431, 255–263.
Bruins, M. R., Kapil, S., & Oehme, F. W. (2000). Microbial resistance to metals in the environment. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 45(3), 198–207.
Ji, G., & Silver, S. (1995). Bacterial resistance mechanisms for heavy metals of environmental concern. Journal of Industrial Microbiology, 14(2), 61–75.
Mergeay, M., Monchy, S., Vallaeys, T., Auquier, V., Benotmane, A., Bertin, P., ... & Wattiez, R. (2003). Ralstonia metallidurans, a bacterium specifically adapted to toxic metals: Towards a catalogue of metal-responsive genes. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 27(2–3), 385–410.
Hong, C., Hao, H., & Haiyun, W. (2009). Process optimization for PHA production by activated sludge using response surface methodology. Biomass and Bioenergy., 33, 721–727.
Ebrahimpour, A., Rahman, R. N. Z. R. A., Ch’ng, D. H. E., Basri, M., & Salleh, A. B. (2008). A modeling study by response surface methodology and artificial neural network on culture parameters optimization for thermostable lipase production from a newly isolated thermophilic Geobacillus sp. strain ARM. BMC Biotechnol, 8(1), 96.
Roy, R., Tiwari, M., Donelli, G., & Tiwari, V. (2018). Strategies for combating bacterial biofilms: A focus on anti-biofilm agents and their mechanisms of action. Virulence, 9(1), 522–554.
Cairns, L. S., Hobley, L., & Stanley-Wall, N. R. (2014). Biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis: New insights into regulatory strategies and assembly mechanisms. Molecular Microbiology, 93(4), 587–598.
Fong, J., & Yildiz, F. H. (2015). Biofilm matrix proteins. Microbiology Spectrum, 3(2). https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.MB-0004-2014
Hathroubi, S., Servetas, S. L., Windham, I., Merrell, D. S., & Ottemann, K. M. (2018). Helicobacter pylori biofilm formation and its potential role in pathogenesis. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews: MMBR, 82(2), e00001-18.
Beloin, C., Roux, A., & Ghigo, J. M. (2008). Escherichia coli biofilms. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, 322, 249–289.
Wang, H., Wang, H., Xing, T., Wu, N., Xu, X., & Zhou, G. (2016). Removal of Salmonella biofilm formed under meat processing environment by surfactant in combination with bio-enzyme. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 66, 298–304.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge University of Engineering and Management, Kolkata, and all the members of the Department of Biotechnology for their kind cooperation in completion of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SM: conceptualization, supervision; SB: review of existing literature; SP: writing original draft; SN: writing original draft; SP: supervision, writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable. The manuscript does not contain data collected from animals and humans.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable. The manuscript does not contain any individual person’s data.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, S., Bhattacharjee, S., Paul, S. et al. Biofilm—a Syntrophic Consortia of Microbial Cells: Boon or Bane?. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 195, 5583–5604 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04075-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-022-04075-4