Abstract
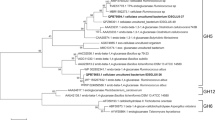
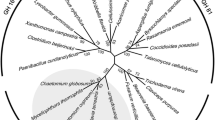
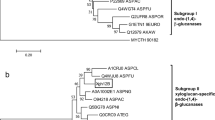
β-1,3-glucanases are the main digestive enzymes of plant and fungal cell wall. Transcriptomic analysis of the fungus-growing termite Macrotermes barneyi revealed a high expression of a predicted β-1,3(4)-glucanase (Mbbgl) transcript in termite gut. Here, we described the cDNA cloning, heterologous expression, and enzyme characterization of Mbbgl. Sequence analysis and RT-PCR results showed that Mbbgl is a termite-origin GH16 β-1,3(4)-glucanase. The recombinant enzyme showed the highest activity towards laminarin and was active optimally at 50 °C, pH 5.5. The enzyme displayed endo/exo β-1,3(4)-glucanase activities. Moreover, Mbbgl had weak transglycosylation activity. The results indicate that Mbbgl is an endogenous digestive β-1,3(4)-glucanase, which contributes to the decomposition of plant biomass and fungal hyphae. Additionally, the multiple activities, pH, and ion stabilities make Mbbgl a potential candidate for application in the food industry.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Labourel, A., Jam, M., Jeudy, A., Hehemann, J. H., Czjzek, M., & Michel, G. (2014). The beta-glucanase ZgLamA from Zobellia galactanivorans evolved a bent active site adapted for efficient degradation of algal laminarin. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289(4), 2027–2042.
Stone, B. A. (2009). Chemistry of β-glucans. In Chemistry, Biochemistry and Biology of (1,3)-β-Glucans and related polysaccharides (Bacic, A.,Fincher, G. B., and Stone, B. A., eds) Academic Press, Orlando,Fleming, C. pp5–46.
Zhang, B., Liu, Y., Yang, H., Yan, Q., Yang, S., Jiang, Z. Q., & Li, S. (2017). Biochemical properties and application of a novel beta-1,3-1,4-glucanase from Paenibacillus barengoltzii. Food Chemistry, 234, 68–75.
Hung, Y. L., Chen, H. J., Liu, J. C., & Chen, Y. C. (2012). Catalytic efficiency diversification of duplicate beta-1,3-1,4-glucanases from Neocallimastix patriciarum J11. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 78(12), 4294–4300.
Delp, G., & Palva, E. T. (1999). A novel flower-specific Arabidopsis gene related to both pathogen-induced and developmentally regulated plant beta-1,3-glucanase genes. Plant Molecular Biology, 39(3), 565–575.
Linton, S. M., Cameron, M. S., Gray, M. C., Donald, J. A., Saborowski, R., von Bergen, M., Tomm, J. M., & Allardyce, B. J. (2015). A glycosyl hydrolase family 16 gene is responsible for the endogenous production of beta-1,3-glucanases within decapod crustaceans. Gene., 569(2), 203–217.
Zakharenko, A. M., Kusaykin, M. I., Kovalchuk, S. N., Anastyuk, S. D., Ly, B. M., Sova, V. V., Rasskazov, V. A., & Zvyagintseva, T. N. (2011). Enzymatic and molecular characterization of an endo-1,3-beta-d-glucanase from the crystalline styles of the mussel Perna viridis. Carbohydrate Research, 346(2), 243–252.
Meng, D. D., Wang, B., Ma, X. Q., Ji, S. Q., Lu, M., & Li, F. L. (2016). Characterization of a thermostable endo-1,3(4)-beta-glucanase from Caldicellulosiruptor sp. strain F32 and its application for yeast lysis. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 100(11), 4923–4934.
Yang, S. Q., Xiong, H., Yang, H. Y., Yan, Q. J., & Jiang, Z. Q. (2015). High-level production of beta-1,3-1,4-glucanase by Rhizomucor miehei under solid-state fermentation and its potential application in the brewing industry. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 118(1), 84–91.
Chaari, F., & Chaabouni, S. E. (2019). Fungal beta-1,3-1,4-glucanases: production, proprieties and biotechnological applications. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 99(6), 2657–2664.
Wojtkowiak, A., Witek, K., Hennig, J., & Jaskolski, M. (2013). Structures of an active-site mutant of a plant 1,3-beta-glucanase in complex with oligosaccharide products of hydrolysis. Acta Crystallographica. Section D, Biological Crystallography, 69(Pt 1), 52–62.
Wan, L., Zha, W., Cheng, X., Liu, C., Lv, L., Liu, C., Wang, Z., Du, B., Chen, R., Zhu, L., & He, G. (2011). A rice beta-1,3-glucanase gene Osg1 is required for callose degradation in pollen development. Planta., 233(2), 309–323.
Schaeffer, H. J., Leykam, J., & Walton, J. D. (1994). Cloning and targeted gene disruption of EXG1, encoding exo-beta 1, 3-glucanase, in the phytopathogenic fungus Cochliobolus carbonum. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 60(2), 594–598.
Souza, R. S., Diaz-Albiter, H. M., Dillon, V. M., Dillon, R. J., & Genta, F. A. (2016). Digestion of yeasts and beta-1,3-glucanases in mosquito larvae: physiological and biochemical considerations. Plos One, 11(3), e0151403.
Pauchet, Y., Freitak, D., Heidel-Fischer, H. M., Heckel, D. G., & Vogel, H. (2009). Immunity or digestion: glucanase activity in a glucan-binding protein family from Lepidoptera. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284(4), 2214–2224.
Hamilton, C., Lay, F., & Bulmer, M. S. (2011). Subterranean termite prophylactic secretions and external antifungal defenses. Journal of Insect Physiology, 57(9), 1259–1266.
Linton, S. M. (2020). Review: The structure and function of cellulase (endo-beta-1,4-glucanase) and hemicellulase (beta-1,3-glucanase and endo-beta-1,4-mannase) enzymes in invertebrates that consume materials ranging from microbes, algae to leaf litter. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part B, Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 240, 110354.
Waldron, R., McGowan, J., Gordon, N., Mitchell, E. B., Fitzpatrick, D. A., & Doyle, S. (2019). Characterisation of three novel beta-1,3 glucanases from the medically important house dust mite Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (airmid). Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 115, 103242.
Souza, R. S., Gama, M., Schama, R., Lima, J. B. P., Diaz-Albiter, H. M., & Genta, F. A. (2019). Biochemical and functional characterization of glycoside hydrolase family 16 genes in Aedes aegypti larvae: identification of the major digestive beta-1,3-glucanase. Frontiers in Physiology, 10, 122.
Lee, H., Kwon, H. M., Park, J. W., Kurokawa, K., & Lee, B. L. (2009). N-terminal GNBP homology domain of Gram-negative binding protein 3 functions as a beta-1,3-glucan binding motif in Tenebrio molitor. BMB Reports, 42(8), 506–510.
Fabrick, J. A., Baker, J. E., & Kanost, M. R. (2003). cDNA cloning, purification, properties, and function of a beta-1,3-glucan recognition protein from a pyralid moth, Plodia interpunctella. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 33(6), 579–594.
Bragatto, I., Genta, F. A., Ribeiro, A. F., Terra, W. R., & Ferreira, C. (2010). Characterization of a beta-1,3-glucanase active in the alkaline midgut of Spodoptera frugiperda larvae and its relation to beta-glucan-binding proteins. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 40(12), 861–872.
Genta, F. A., Bragatto, I., Terra, W. R., & Ferreira, C. (2009). Purification, characterization and sequencing of the major beta-1,3-glucanase from the midgut of Tenebrio molitor larvae. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 39(12), 861–874.
Kikuchi, T., Shibuya, H., & Jones, J. T. (2005). Molecular and biochemical characterization of an endo-beta-1,3-glucanase from the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus acquired by horizontal gene transfer from bacteria. The Biochemical Journal, 389(Pt 1), 117–125.
Romero Victorica, M., Soria, M. A., Batista-Garcia, R. A., Ceja-Navarro, J. A., Vikram, S., Ortiz, M., Ontanon, O., Ghio, S., Martinez-Avila, L., Quintero Garcia, O. J., Etcheverry, C., Campos, E., Cowan, D., Arneodo, J., & Talia, P. M. (2020). Neotropical termite microbiomes as sources of novel plant cell wall degrading enzymes. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 3864.
Ni, J., & Tokuda, G. (2013). Lignocellulose-degrading enzymes from termites and their symbiotic microbiota. Biotechnology Advances, 31(6), 838–850.
Brune, A. (2014). Symbiotic digestion of lignocellulose in termite guts. Nature Reviews. Microbiology, 12(3), 168–180.
Javadzadeh, S. G., & Asoodeh, A. (2020). A novel textile dye degrading extracellular laccase from symbiotic bacterium of Bacillus sp. CF96 isolated from gut termite (Anacanthotermes). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 145, 355–363.
Otani, S., Challinor, V. L., Kreuzenbeck, N. B., Kildgaard, S., Krath Christensen, S., Larsen, L. L. M., Aanen, D. K., Rasmussen, S. A., Beemelmanns, C., & Poulsen, M. (2019). Disease-free monoculture farming by fungus-growing termites. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 8819.
Aanen, D. K., Eggleton, P., Rouland-Lefevre, C., Guldberg-Froslev, T., Rosendahl, S., & Boomsma, J. J. (2002). The evolution of fungus-growing termites and their mutualistic fungal symbionts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 99(23), 14887–14892.
Rosengaus, R. B., Schultheis, K. F., Yalonetskaya, A., Bulmer, M. S., DuComb, W. S., Benson, R. W., Thottam, J. P., & Godoy-Carter, V. (2014). Symbiont-derived beta-1,3-glucanases in a social insect: mutualism beyond nutrition. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5607.
Li, H., Yelle, D. J., Li, C., Yang, M., Ke, J., Zhang, R., Liu, Y., Zhu, N., Liang, S., Mo, X., Ralph, J., Currie, C. R., & Mo, J. (2017). Lignocellulose pretreatment in a fungus-cultivating termite. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 114(18), 4709–4714.
Wu, Y., Chi, S., Yun, C., Shen, Y., Tokuda, G., & Ni, J. (2012). Molecular cloning and characterization of an endogenous digestive beta-glucosidase from the midgut of the fungus-growing termite Macrotermes barneyi. Insect Molecular Biology, 21(6), 604–614.
Juncosa, M., Pons, J., Dot, T., Querol, E., & Planas, A. (1994). Identification of active site carboxylic residues in Bacillus licheniformis 1,3-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucanohydrolase by site-directed mutagenesis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269(20), 14530–14535.
Genta, F. A., Terra, W. R., & Ferreira, C. (2003). Action pattern, specificity, lytic activities, and physiological role of five digestive beta-glucanases isolated from Periplaneta americana. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 33(11), 1085–1097.
Fuchs, K. P., Zverlov, V. V., Velikodvorskaya, G. A., Lottspeich, F., & Schwarz, W. H. (2003). Lic16A of Clostridium thermocellum, a non-cellulosomal, highly complex endo-beta-1,3-glucanase bound to the outer cell surface. Microbiology., 149(Pt 4), 1021–1031.
Wang, J., Kang, L., Liu, Z., & Yuan, S. (2017). Gene cloning, heterologous expression and characterization of a Coprinopsis cinerea endo-beta-1,3(4)-glucanase. Fungal Biology, 121(1), 61–68.
Genta, F. A., Dumont, A. F., Marana, S. R., Terra, W. R., & Ferreira, C. (2007). The interplay of processivity, substrate inhibition and a secondary substrate binding site of an insect exo-beta-1,3-glucanase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1774(9), 1079–1091.
Kumagai, Y., & Ojima, T. (2010). Isolation and characterization of two types of beta-1,3-glucanases from the common sea hare Aplysia kurodai. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part B, Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 155(2), 138–144.
Kumagai, Y., & Ojima, T. (2009). Enzymatic properties and the primary structure of a beta-1,3-glucanase from the digestive fluid of the Pacific abalone Haliotis discus hannai. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Part B, Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, 154(1), 113–120.
De Sousa, G., Dos Santos, V. C., de Figueiredo Gontijo, N., Constantino, R., de Oliveira Paiva, E. S. G., Bahia, A. C., Gomes, F. M., & de Alcantara Machado, E. (2017). Morphophysiological study of digestive system litter-feeding termite Cornitermes cumulans (Kollar, 1832). Cell and Tissue Research, 368(3), 579–590.
Ni, J., Wu, Y., Yun, C., Yu, M., & Shen, Y. (2014). cDNA cloning and heterologous expression of an endo-beta-1,4-glucanase from the fungus-growing termite Macrotermes barneyi. Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology, 86(3), 151–164.
Javaheri-Kermani, M., & Asoodeh, A. (2019). A novel beta-1,4 glucanase produced by symbiotic Bacillus sp. CF96 isolated from termite (Anacanthotermes). International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 131, 752–759.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31970119 and 31272370).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The experiment was designed and performed by Chunjing Cao and Jingjing Li. The data was analyzed by Jingjing Li, Chunjing Cao, and Yutong Jiang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Chunjing Cao, Jingjing Li, and Jinfeng Ni. The manuscript was reviewed and edited by Qihong Huang, Yulong Shen, and Jinfeng Ni. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors had read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Cao, C., Jiang, Y. et al. A Novel Digestive GH16 β-1,3(4)-Glucanase from the Fungus-Growing Termite Macrotermes barneyi. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 192, 1284–1297 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03368-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-020-03368-w