Abstract
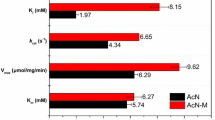
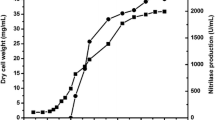
2,6-Difluorobenzamide is an important intermediate with many applications in pesticide industries. Through screening a library of recombinant nitrile hydratases, the nitrile hydratase from Aurantimonas manganoxydans ATCC BAA-1229 was selected for production of 2,6-difluorobenzamide from 2,6-difluorobenzonitrile. Key parameters of the biocatalytic process, including temperature, pH, substrate loading, and substrate feeding mode, were optimized. Finally, 314 g/L of 2,6-difluorobenzamide was produced in a simple batch process within 11 h without formation of any by-product in an economical non-buffer system and similar result was obtained when scaled up to 30 L. This study constitutes the first report of 2,6-difluorobenzamide significant production using a recombinant Escherichia coli-based biocatalyst.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, L., Ou, X. M., Mao, C. H., Shang, J., Huang, R. Q., Bi, F. C., & Wang, Q. M. (2007). Synthesis and bioassay evaluation of 1-(4-substitutedideneaminooxymethyl)-phenyl-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)ureas. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 15, 3678–3683.
Huff, R. K. (1979). Oxadiazindione derivatives useful as insecticides. US Patent 4,150,158.
Parkins, A. W. (1996). Catalytic hydration of nitriles to amides. Platinum Metals Review, 40, 169–174.
Prasad, S., & Bhalla, T. C. (2010). Nitrile hydratases (NHases): at the interface of academia and industry. Biotechnology Advances, 28, 725–741.
Mauger, J., Nagasawa, T., & Yamada, H. (1989). Synthesis of various aromatic amide derivatives using nitrile hydratase of Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1. Tetrahedron, 45, 1347–1354.
Tang, R., Shen, Y., Wang, M., Zhai, Y., & Gao, Q. (2017). Highly chemoselective and efficient production of 2,6-difluorobenzamide using Rhodococcus ruber CGMCC3090 resting cells. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 124, 641–646.
Gilligan, T., Yamada, H., & Nagasawa, T. (1993). Production of S-(+)-2-phenylpropionic acid from (R,S)-2-phenylpropionitrile by the combination of nitrile hydratase and stereoselective amidase in Rhodococcus equi TG328. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 39, 720–725.
Nagasawa, T., Takeuchi, K., Nardi-Dei, V., Mihara, Y., & Yamada, H. (1991). Optimum culture conditions for the production of cobalt-containing nitrile hydratase by Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 34, 783–788.
Zhang, J., Wang, M., Sun, H., Li, X. D., & Zhong, L. P. (2009). Isolation and characterization of Rhodococcus ruber CGMCC3090 that hydrolyzes aliphatic, aromatic and heterocyclic nitriles. African Journal of Biotechnology, 820, 5467–5486.
Rosano, G. L., & Ceccarelli, E. A. (2014). Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: advances and challenges. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5, 172.
Reisinger, C., Osprian, I., Glieder, A., Schoemaker, H. E., Griengl, H., & Schwab, H. (2004). Enzymatic hydrolysis of cyanohydrins with recombinant nitrile hydratase and amidase from Rhodococcus erythropolis. Biotechnology Letters, 26, 1675–1680.
Petrillo, K. L., Wu, S., Hann, E. C., Cooling, F. B., Ben-Bassat, A., Gavagan, J. E., Dicosimo, R., & Payne, M. S. (2005). Over-expression in Escherichia coli of a thermally stable and regio-selective nitrile hydratase from Comamonas testosteroni 5-MGAM-4D. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 67, 664–670.
Kim, S.-H., & Oriel, P. (2000). Cloning and expression of the nitrile hydratase and amidase genes from Bacillus sp. BR449 into Escherichia coli. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 27, 492–501.
Akimasa, M., Shinya, F., Kiyoshi, I., Hirofumi, S., & Takayoshi, W. (2010). Mutational and structural analysis of cobalt-containing nitrile hydratase on substrate and metal binding. The FEBS Journal, 271, 429–438.
Li, J., Wang, P., He, J. Y., Huang, J., & Tang, J. (2013). Efficient biocatalytic synthesis of (R)-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl] ethanol by a newly isolated Trichoderma asperellum ZJPH0810 using dual cosubstrate: ethanol and glycerol. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97, 6685–6692.
Zheng, R. C., Yin, X. J., & Zheng, Y. G. (2016). Highly regioselective and efficient production of 1-cyanocyclohexaneacetamide by Rhodococcus aetherivorans ZJB1208 nitrile hydratase. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 91, 1314–1319.
Nagasawa, T., Mathew, C. D., Mauger, J., & Yamada, H. (1988). Nitrile Hydratase-Catalyzed Production of Nicotinamide from 3-Cyanopyridine in Rhodococcus rhodochrous J1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 54, 1766–1769.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21476199, 21676240).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Pei, X., Xu, G. et al. Efficient Production of 2,6-Difluorobenzamide by Recombinant Escherichia coli Expressing the Aurantimonas manganoxydans Nitrile Hydratase. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 187, 439–448 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2823-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2823-2