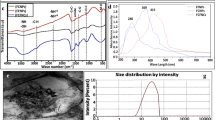
Abstract
Nanoclays may enter human body through various routes such as through the respiratory and gastrointestinal tract, skin, blood, etc. There is dearth of such studies evaluating the interaction of clay nanoparticles with human cells. In particular, the interaction of proteins and nucleic acids with nanoparticles of different aspect ratio remains a domain that is very poorly probed and understood. In the present study, we address the issue of cytotoxicity and antimicrobial attributes of two distinct nanoclay platelets namely, laponite (diameter = 25 nm and thickness = 1 nm) and montmorillonite (MMT, diameter = 300 nm and thickness = 1 nm), having different aspect ratio (25:1 vs 300:1). Cytotoxicity was assessed in both prokatyotes: Escherichia coli, eukaryotes-human embryonic kidney (HEK), and cervical cancer SiHa cell lines, and a comparative size-based analysis of the toxicity were made at different exposure time points by MTT assay. The antimicrobial activity of the nanoclays was evaluated by disc diffusion method (Kirbey-Bauer protocol). Laponite exhibited maximum efficacy as an antimicrobial agent against E. coli. Comparatively smaller size laponite could preferentially enter the cells, leading to relatively wider or larger zone of inhibition. On contradictory; laponite showed 74.67 % survival while MMT showed 89.02 % survival in eukaryotic cells at 0.00001 % (w/v) concentration. In summary, both MMT and laponite indicated cytotoxicity at 0.05 % concentration within 24 h of exposure on HEK and cervical cancer (SiHa) cell lines. The toxicity was possibly dependent on size, aspect ratio, and concentration.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruzicka, B., Zaccarelli, E., Zulian, L., Angelini, R., Sztucki, M., Moussaid, A., et al. (2011). Nature Materials, 10, 56.
Baek, M., Lee, J. A., & Choi, S. J. (2012). Molecular & Cellular Toxicology, 8, 95.
Chithrani, B. D., & Chan, W. C. W. (2007). Nano Letters, 7, 1542.
Wang, Y., Li, D., Li, P., Wang, W., Ren, W., Dong, S., et al. (2007). Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 111, 16833.
Dijkstra, M., Hansen, J. P., & Madden, P. A. (1995). Physical Review Letters, 75, 2236.
Bonn, D., Tanaka, H., Wegdam, G., Kellay, H., & Meunier, J. (1998). Europhysics Letters, 45, 52.
Coussot, P., Nguyen, Q. D., Huynh, H. T., & Bonn, D. (2002). Physical Review Letters, 88, 218301.
Ruzicka, B., Zulian, L., & Ruocco, G. (2004). Physical Review Letters, 93, 258301.
Abou, B., & Gallet, F. (2004). Physical Review Letters, 93, 160603.
Cummins, H. Z. (2007). Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 353, 3891.
Farouji, S. J., Wegdam, G. H., & Bonn, D. (2004). Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter, 16, L471.
Ruzicka, B., Zulian, L., & Ruocco, G. (2006). Langmuir, 22, 1106.
Pujala, R. K., Pawar, N., & Bohidar, H. B. (2011). Langmuir, 27, 5193.
Van Olphen, H. (1997). An Introduction to Clay Colloid Chemistry. New York: Willey and Sons.
Shalkevich, A., Stradner, A., Bhat, S. K., Muller, F., & Schurtenberger, P. (2007). Langmuir, 23, 3570.
Hubbard, J. B., & Douglas, J. F. (1993). Physical Review E, 47, R2983.
Durán, J. D. G., Ramos-Tejada, M. M., Arroyo, F. J., & González-Caballero, F. (2000). Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 229, 107.
Cadene, A., Durand-Vidal, S., Turq, P., & Brendle, J. J. (2005). Colloid and Interface Science, 285, 719.
Mohanty, B., Verma, A. K., Claesson, P., & Bohidar, H. B. (2007). Nanotechnology, 18, 445102.
Saxena, A., Sachin, K., Bohidar, H. B., & Verma, A. K. (2005). Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 45, 42.
Olphen, H. V. (1977). An introduction to clay colloid chemistry. New York: John-Wiley.
Hou, W., Zhao, W., & Li, D. (2004). Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 22, 459.
Laponite Technical Bulletin Laponite Industries Limited, LI04/90/A (1990).
Kong, B., Seog, J. H., Graham, L. M., & Lee, S. B. (2011). Nanomedicine (London, England), 6(5), 929.
Shah, N. B., Dong, J., & Bischof, J. C. (2011). Molecular Pharmaceutics, 8(1), 176.
Berder, A., & Sachs, F. (2009). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106, 6626.
Wiliams, R. L., Hadley, M. J., Jiang, P. J., Rowson, N. A., Mendes, P. M., Rappoport, J. Z., et al. (2013). Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 1, 4370.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rawat, K., Agarwal, S., Tyagi, A. et al. Aspect Ratio Dependent Cytotoxicity and Antimicrobial Properties of Nanoclay. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 174, 936–944 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0983-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0983-2