Abstract
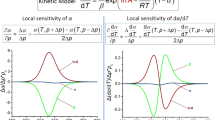
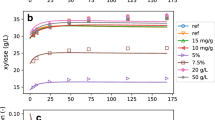
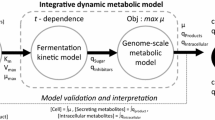
Lignocellulosic biomass is mainly composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin. Fuzzy logic, in turn, is a branch of many-valued logic based on the paradigm of inference under vagueness. This paper presents a methodology, based on computational intelligence, for modeling the kinetics of a complex reactional system. The design of a fuzzy interpolator to model cellulose hydrolysis is reported, within the perspective of applying kinetic models in bioreactor engineering. Experimental data for various types of lignocellulosic materials were used to develop the interpolator. New experimental data from the enzymatic hydrolysis of a synthetic substrate, on the other hand, were used to validate the methodology. The accuracy of the results indicates that this is a promising approach to extend the application of models fitted for specific situations to different cases, thus enhancing their generality.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sun, Y., & Cheng, J. (2002). Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: a review. Bioresource Technology, 83, 1–11.
Eklund, R., Galbe, M., & Zacchi, G. (1990). Optimization of temperature and enzyme concentration in the enzyme saccharification of steam-pretreated willow. Enzyme and Microbial Technology, 12, 225–228.
Granda, C. B. (2007). Enzymatic hydrolysis of lime-pretreated corn stover and investigation of the HCH-1 Model: Inhibition pattern, degree of inhibition, validity of simplified HCH-1 Model. Bioresource Technology, 98, 2969–2977.
Hahn-Hagerdal, B., Galbe, M., Gorwa-Grauslund, M. F., Lidén, G., & Zacchi, G. (2006). Bio-ethanol—the fuel of tomorrow from the residues of today. Trends in Biotechnology, 24, 549–556.
Pandey, A., Soccol, C. R., Nigam, P., Brand, D., Mohan, R., & Roussoss, S. (2000). Biotechnology potential of agro-industrial residues. I: sugarcane bagasse. Bioresource Technology, 74, 69–80.
Hamelinck, C. N., Hooijdonk, G. V., & Faaij, A. P. C. (2005). Ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass: techno-economic performance in short-, middle- and long-term. Biomass and Bioenergy, 28, 384–410.
Rabelo, S. C. (2007). Avaliação do desempenho do pré-tratamento com peroxide de hidrogênio alcalino para a hidrólise enzimática de cana-de-açúcar. Dissertation. State University of Campinas.
Cunha, C. M., Silva, F. T. (2001). Characterization of carbohydrates present in hydrolyzate obtained from sugar cane bagasse pretreated by explosion. In: 6th Brazilian Symposium Chemistry Lignins and other Wood Components, VII, pp. 221-226.
Gámez, S., González-Cabriales, J. J., Ramírez, J. A., Garrote, G., & Vázquez, M. (2006). Study of hydrolysis of sugar cane bagasse using phosphoric acid. Journal of Food Engineering, 74, 78–88.
Laser, M., Schulman, D., Allen, S. G., Lichwa, J., Antal, M. J., Jr., & Lynd, L. R. (2002). A comparison of liquid hot water and steam pretreatments of sugar cane bagasse for bioconversion to ethanol. Bioresource Technology, 81, 33–44.
Vallander, L., & Eriksson, K. E. L. (1985). Enzymatic saccharification of pretreated wheat straw. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 27, 650–659.
Sousa, R., Jr., Carvalho, M. L., Giordano, R. L. C., & Giordano, R. C. (2011). Recent trends in the modeling of cellulose hydrolysis. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 28, 545–564.
Zhang, Y. H. P., & Lynd, L. R. (2004). Toward an aggregated understanding of enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose: noncomplexed cellulose systems. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 88, 797–824.
Cavalcanti-Montaño, I. D., Suarez, C. A. G., Rodríguez-Zúñiga, U. F., Giordano, R. L. C., Giordano, R. C., & Sousa, R., Jr. (2013). Optimal bioreactor operational policies for the enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. Bioenergy Research, 6, 776–785.
Bezerra, R. M. F., & Dias, A. A. (2004). Discrimination among eight modified Michaelis-Menten kinetics models of cellulose hydrolysis with a large range of substrate/enzyme ratios. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 112, 173–184.
Carrillo, F., LIS, M. J., Colom, X., López-Mesas, M., & Valldeperas, J. (2005). Effect of alkali pretreatment on cellulose hydrolysis of wheat straw: Kinetic study. Process Biochemistry, 40, 3360–3364.
Chrastil, J. (1988). Determination of the first order consecutive reaction rate constants from final products. Computers and Chemistry, 12, 289–292.
Chrastil, J. (1988). Enzymic product formation curves with the normal or diffusion limited reaction mechanism and in the presence of substrate receptors. International Journal of Biochemistry, 20, 683–693.
Carvalho, M. L., Sousa, R., Jr., Rodríguez-Zúñiga, U. F., Suarez, C. A. G., Rodrigues, D. S., Giordano, R. C., et al. (2013). Kinetic study of the enzymatic hydrolysis of sugarcane bagasse. Brazilian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 30, 437–447.
Carvalho, M. (2011). Estudo cinético da hidrólise enzimática de celulose de bagaço de cana-de-açúcar. Dissertation, Federal University of Sao Carlos.
Adney, B., Baker, J. Chemical analysis and testing task: https://engineering.purdue.edu/LORRE/research/LAP-006.pdf. Revised 2013.
Ghose, T. K. (1987). Measurement of cellulase activity. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 59, 257–268.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Bezdek, J. (1981). Fuzzy models and algorithms for pattern recognition and image processing. New York: Wiley.
Nelles, O. (2001). Nonlinear system identication. Berlin: Springer.
Chiu, S. L. (1994). Fuzzy model identification based on cluster estimation. Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems, 2, 267–278.
Bezdek, J. C., Ehrlich, R., et al. (1984). FCM: the fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Computers and Geosciences, 10, 191–203.
Pedrycz, W. (1990). Processing in relation structures: fuzzy relational equations. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 40, 87–100.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the support of Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP-BIOEN), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suarez, C.A.G., Cavalcanti-Montaño, I.D., da Costa Marques, R.G. et al. Modeling the Kinetics of Complex Systems: Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Substrates. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173, 1083–1096 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0912-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0912-4